(Press-News.org) AURORA, Colo. (July 25, 2023) – Scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have discovered what they believe to be the central mechanism behind cognitive decline associated with normal aging.
“The mechanism involves the mis-regulation of a brain protein known as CaMKII which is crucial for memory and learning,” said the study’s co-senior author Ulli Bayer, PhD, professor of pharmacology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. “This study directly suggests specific pharmacological treatment strategies.”
The study was published today in the journal `Science Signaling.’
Researchers using mouse models found that altering the CaMKII brain protein caused similar cognitive effects as those that happen through normal aging.
Bayer said that aging in mice and humans both decrease a process known as S-nitrosylation, the modification of a specific brain proteins including CaMKII.
“The current study now shows a decrease in this modification of CaMKII is sufficient to cause impairments in synaptic plasticity and in memory that are similar in aging,” Bayer said.
Normal aging reduces the amount of nitric oxide in the body. That in turn reduces nitrosylation which reduces memory and learning ability, the study said.
Bayer said the new research opens the way toward developing drugs and other therapeutic interventions that could normalize the nitrosylation of the protein. He said that holds out the possibility of treating or staving off normal cognitive decline for an unknown period of time.
He pointed out that this would only work in normal age-related cognitive decline, not the decline seen in Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
“We know this protein can be targeted,” Bayer said. “And we think it could be done pharmacologically. That is the next logical step.”
About the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is a world-class medical destination at the forefront of transformative science, medicine, education and patient care. The campus encompasses the University of Colorado health professional schools, more than 60 centers and institutes, and two nationally ranked independent hospitals - UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital and Children's Hospital Colorado - that treat more than two million adult and pediatric patients each year. Innovative, interconnected and highly collaborative, the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus delivers life-changing treatments, patient care and professional training and conducts world-renowned research fueled by over $690 million in research grants. For more information, visit www.cuanschutz.edu.
###
Find the latest University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus news here.
END
Study shows that the shape of objects could be perceived via vision and touch; the inferolateral occipitotemporal cortex selectively encodes object shape even in people who become blind from a very early age, suggesting that the brain is organized as operators that execute a given function regardless of input senses.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3001930
Article Title: Similar object shape representation encoded in the inferolateral occipitotemporal ...
Conversations on social media about female genital mutilation (FGM) have not changed dramatically over the five years to 2020, according to an analysis of English Twitter data, though there was a shift from raising awareness to calling for an end to the practice. Earlier on, users discussing the topic were mainly from the USA and UK, but later the majority came from Nigeria and Kenya. The research, published in PLOS Global Public Health, may be useful in informing communication and designing culturally effective campaigns ...
Researchers from the American Board of Family Medicine and the University of Minnesota Medical School investigated whether participation in medical school repayment programs impacted the care family physicians provided to patients post graduation. By analyzing data from over 10,000 American Board of Family Medicine National Graduate Survey respondents, the authors examined differences in program participation, participant demographics, scope of practice, and the likelihood of serving medically underserved or rural populations.
The study revealed a significant increase in participation in the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program between 2016 and 2020, while participation ...
MIAMI, FLORIDA (JULY 25, 2023) – Cancer centers are uniquely positioned to protect communities and their most vulnerable residents – cancer patients – from climate-driven disasters by bolstering emergency preparedness, noted researchers with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, the American Cancer Society (ACS) and collaborating organizations.
Writing in a commentary in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute (NCI), the researchers noted that all 71* of the country’s NCI-designated ...
Canadian Patients Report High Levels of Satisfaction From an Integrated Model of Virtual and In-Person Care
In an effort to increase access to care in underserved communities, researchers from the University of Ottawa evaluated the implementation of an integrated virtual care (IVC) model. Their study evaluated the overall experience and satisfaction of patients receiving care through a combination of virtual and in-person visits. A secondary aim was to compare the experiences of patients who had been previously seen in person by a family physician before transitioning to the IVC clinics with those who met their family physician virtually for the first ...
Researchers from Virginia Commonwealth University and Case Western Reserve University conducted weekly and monthly surveys of primary care clinicians to examine the use of telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. The e-surveys were conducted between March 2020 and March 2022 and used convenience sampling. A total of 36 surveys were completed, with an average of 937 respondents per survey, representing clinicians from all 50 states and from multiple specialties.
Initially, respondents reported difficulties in implementing telemedicine, citing challenges with infrastructure and reimbursement mechanisms. However, as time progressed, attitudes toward telemedicine became ...
In an effort to increase access to care in underserved communities, researchers from the University of Ottawa evaluated the implementation of an integrated virtual care (IVC) model. Their study evaluated the overall experience and satisfaction of patients receiving care through a combination of virtual and in-person visits. A secondary aim was to compare the experiences of patients who had been previously seen in person by a family physician before transitioning to the IVC clinics with those who met their family physician virtually for the ...
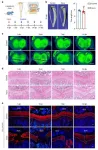
Growth plates (GP), situated at the ends of long bones in children, supply chondrocytes necessary for bone growth. Damage to the growth plate due to fractures often results in arrested bone growth, making it a significant cause of skeletal disorders in children. However, a small percentage of these injuries astonishingly manage to heal themselves, a phenomenon that had remained a mystery until now.
In a new study published in International Journal of Oral Science, Yao Sun from Tongji University and other researchers identified that primary cilia, cellular ...
Bare minimum reimbursement rates could be a factor in why some clinics may be struggling to offer HPV vaccination in the U.S.
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researcher Kalyani Sonawane, Ph.D., and a team of researchers from South Carolina and Texas decided to quantify private insurance reimbursement rates for the HPV vaccine after several qualitative studies noted that health care providers were dissatisfied with HPV vaccine reimbursement by private insurance companies.
The results of their investigation were published July 24 in the Annals of Family Medicine.
They found that ...
In a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, authors Gabriel Gellner and Kevin McCann from the University of Guelph and SFI External Professor Alan Hastings (UC Davis) invert a classical approach to modeling food webs. Instead of trying to replicate stable, complex ecosystems using simplistic representations of species interactions, the authors’ novel inverse method assumes the ecosystems exist and works backward to characterize food webs that support that assumption. Their work represents a significant step toward addressing a fundamental ecological question of how biodiversity ...