(Press-News.org) Bare minimum reimbursement rates could be a factor in why some clinics may be struggling to offer HPV vaccination in the U.S.
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researcher Kalyani Sonawane, Ph.D., and a team of researchers from South Carolina and Texas decided to quantify private insurance reimbursement rates for the HPV vaccine after several qualitative studies noted that health care providers were dissatisfied with HPV vaccine reimbursement by private insurance companies.
The results of their investigation were published July 24 in the Annals of Family Medicine.
They found that non-pediatric specialties were reimbursed at lower rates compared with pediatricians.
Although all specialties received at least the minimum payment recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, that rate covers only the cost of the vaccine itself, Sonawane said.
Family medicine doctors received an average of 34 cents above the recommended rate, which would have to cover all of the indirect costs of vaccination, like storage, administration, insurance and record-keeping. In contrast, pediatricians received an average of $5.08 above the recommended rate.
“Family physicians – who are so critical and important, especially in rural areas where not all patients have access to pediatricians – are not receiving adequate reimbursement for the HPV vaccine, which is sort of a disincentive for them to offer this critical cancer-preventive vaccine,” Sonawane said.
“We did find that the number of doses administered by each specialty was slightly sensitive to the reimbursement level or the margin that they were receiving through the reimbursements, and family physicians were most sensitive to the change in reimbursement,” she added.
The HPV, or human papillomavirus, vaccine is recommended for adolescents at age 11 or 12, although it can be given starting at age 9 and up to age 45.
It protects men and women against HPV strains that can cause six types of cancer. The Healthy People 2030 goal is to have 80% of adolescents up to date on HPV vaccines by then. Right now, about 62% are up to date.
After lagging behind other states, South Carolina is now on par with national averages. Hollings has made a special effort to increase HPV vaccination rates, launching a statewide campaign in 2019 to improve them.
In 2021, Hollings launched the Community Health Van, which travels across the state offering HPV and other childhood vaccines as well as cancer education.
Sonawane suspects that the lower reimbursement rates for family physicians could contribute to geographic disparities in vaccination rates. Adolescents in rural areas are less likely to be up to date on vaccines than those in urban or suburban areas. Part of the issue is parental hesitancy about vaccines, she said. Lack of availability, though, if doctors in rural areas don’t stock the vaccine, could be another barrier.
“The key message here is that, yes, we are meeting the minimum threshold that the CDC has put out there, but that may not be enough to sustain vaccination programs, particularly in family medicine clinics,” she said.
About MUSC Hollings Cancer Center
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center is South Carolina’s only National Cancer Institute-designated cancer center with the largest academic-based cancer research program in the state. The cancer center comprises more than 130 faculty cancer scientists and 20 academic departments. It has an annual research funding portfolio of more than $44 million and sponsors more than 200 clinical trials across the state. Dedicated to preventing and reducing the cancer burden statewide, the Hollings Office of Community Outreach and Engagement works with community organizations to bring cancer education and prevention information to affected populations. Hollings offers state-of-the-art cancer screening, diagnostic capabilities, therapies and surgical techniques within its multidisciplinary clinics. Hollings specialists include surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, radiologists, pathologists, psychologists and other clinical providers equipped to provide the full range of cancer care. For more information, visit hollingscancercenter.musc.edu.
END
HPV vaccine cost reimbursement could hinder vaccine access, study suggests
2023-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: An inverse model for food webs and ecosystem stability
2023-07-25
In a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, authors Gabriel Gellner and Kevin McCann from the University of Guelph and SFI External Professor Alan Hastings (UC Davis) invert a classical approach to modeling food webs. Instead of trying to replicate stable, complex ecosystems using simplistic representations of species interactions, the authors’ novel inverse method assumes the ecosystems exist and works backward to characterize food webs that support that assumption. Their work represents a significant step toward addressing a fundamental ecological question of how biodiversity ...
New algorithm maps safest routes for city drivers
2023-07-25
Most navigation apps can show you the fastest possible route to your destination and some can even suggest an eco-friendly route calculated to produce the least amount of carbon emissions.
But what if they could also map the safest route with the lowest possible risk of a crash?
A new algorithm developed by UBC researchers could make this a reality. Led by Dr. Tarek Sayed, professor in the UBC department of civil engineering, and PhD student Tarek Ghoul, the group developed a new approach ...
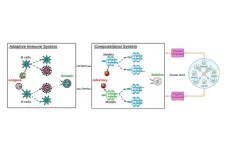
Illinois Tech assistant professor receives award for using insights from human immune system to strengthen AI
2023-07-25
CHICAGO—July 25, 2023—For his groundbreaking research in fortifying artificial intelligence systems with insights gained from the human immune system, Ren Wang of Illinois Institute of Technology has received the prestigious Ralph E. Powe Junior Faculty Enhancement Award from Oak Ridge Associated Universities (ORAU). Wang’s research may be used in the future to strengthen AI systems, making them more robust and resilient.
As AI has increasingly permeated our daily lives through technologies, such as ChatGPT’s natural language ...
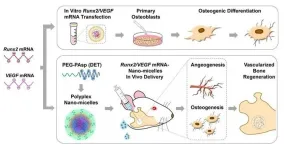
A novel bone regeneration technique with clinical potential
2023-07-25
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify a promising way to improve bone repair with important clinical applications
Tokyo, Japan – Although bones have the ability to regenerate and repair themselves, they are generally unable to do so when the injury is larger than a small break or chip. In a study just published in Inflammation and Regeneration, Japanese researchers have developed a technique for improving bone regeneration over large areas in rats—and their findings may translate well to clinical settings.
As most of us know from experience, bones can repair themselves after a minor break ...
Researchers detail methodological approach to creating joint displays of data collection in mixed methods research
2023-07-25
Researchers present a methodology for developing joint displays of integrated mixed data collection. These joint displays provide a framework for supporting integration of a mixed methodology in research. Drawing upon a convergent mixed methods cohort study – the Early Discharge of Febrile Neutropenic Children with Cancer Study – the authors constructed a joint display of integrated mixed data collection from a patient/caregiver mixed methods survey instrument and manual medical chart abstraction. The paper outlines the methodological approach, including iterative ...
Brazilian researchers identify gynecological concerns of caregivers of young girls and women with Down syndrome
2023-07-25
Brazilian researchers conducted a cross-sectional study to explore the concerns of caregivers of Brazilian girls with Down syndrome (DS) regarding gynecological aspects of DS including menstruation, contraception and sexual practices. The study included 100 caregivers of females aged 9 years or older with DS who had reached menarche. Participating caregivers completed a questionnaire about their concerns around puberty, menstruation, sexuality and contraceptive methods.
Caregivers commonly expressed concerns around menstrual bleeding. Most caregivers ...
Meta-analysis of research on acne reveals that oral isotretinoin, followed by topical antibiotic, benzoyl peroxide and retinoid, are most effective treatments
2023-07-25
In their comprehensive meta-analysis (comprising 221 randomized controlled trials involving 65,601 patients), researchers investigated the effectiveness of various pharmacological therapies for acne vulgaris across diverse age groups and genders. The articles described 37 interventions, with a median patient age of 20 years old and median duration of treatment of 12 weeks. The median total, inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesion counts were 71.5, 27 and 44, respectively.
The study revealed that oral isotretinoin was the most effective treatment (mean difference 48.41; p-score 1.00), followed in efficacy by a triple therapy containing ...
Survey suggests geographic inequalities in patient registration versus primary care physician density can exclude patients from comprehensive care access
2023-07-25
French researchers conducted a large, simulated study to examine the relationship between the presence of primary care physicians (PCPs) and the ability of patients to register with a PCP. The study aimed to analyze local PCP supply based on various indicators, including PCP presence, patient registration availability for office visits, and patient registration availability for home visits. Out of 5,188 census blocks, 55.4% had at least one PCP, with 38.6% of those blocks allowing registration for office visits and 19.46% allowing registration for home ...
Greater primary care continuity among older people is associated with fewer inappropriate prescriptions and prescribing omissions
2023-07-25
Researchers from the Netherlands conducted an observational study to determine the association between personal continuity and potentially inappropriate prescriptions (PIPs) by family physicians in older patients. PIPs can be categorized as potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) and potential prescribing omissions (PPOs). The study utilized anonymized routine care data from 269,478 patients, receiving care in 48 Dutch family practices, from 2013 to 2018. They included all patients 65 and older with five or more contacts with their practice in six years, giving them a sample of 25,854 individuals. ...
Primary care clinics that improved patient access, identified at-risk patients and expanded services experienced reductions in acute hospitalizations
2023-07-25
Researchers from Mathematica studied high-performing Comprehensive Primary Care Plus (CPC+) sites to identify key strategies that contributed to significant reductions in acute hospitalization rates. Researchers identified CPC+ practice sites with the highest likelihood of achieving substantial reductions in Medicare acute hospitalization rates between 2016 and 2018, and referred to them as "Acute Hospitalization Rate (AHR) high-performers." Afterwards, they conducted telephone interviews and within- and cross-case comparative analyses of 14 of these primary care practice sites, ...