(Press-News.org) Most navigation apps can show you the fastest possible route to your destination and some can even suggest an eco-friendly route calculated to produce the least amount of carbon emissions.
But what if they could also map the safest route with the lowest possible risk of a crash?
A new algorithm developed by UBC researchers could make this a reality. Led by Dr. Tarek Sayed, professor in the UBC department of civil engineering, and PhD student Tarek Ghoul, the group developed a new approach which identifies the safest possible route in an urban network using real-time crash risk data, and can be incorporated into navigation apps such as Google Maps.
To conduct their research, the team used data from 10 drones hovering over downtown Athens, Greece, over multiple days and recording factors including vehicle position, speed and acceleration. They used this information to identify near-misses between vehicles and then predicted the risk of crashes in real-time.
“This research is the first to use real-time crash risk data to provide navigation directions and give you the safest possible driving route through a city,” said Dr. Sayed. “The algorithm is capable of adjusting directions in real-time, suggesting detours to avoid hazardous locations. This helps enhance road safety for all users. For instance, companies will be able to route their fleet efficiently, prioritizing safety and reducing crash risk.”
Fastest route not always the safest
The study also found that the fastest routes are not always the safest. For example, the team analyzed a small section of Athens’ urban road network and found only 23 per cent of the fastest routes were also considered to be the safest routes. On average, the safest route used 54 per cent of the roads used in the fastest route. This indicates that road users should consider a mix of safety and efficiency when choosing directions, said Ghoul.
“In the network we looked at, there was a clear trade-off between safety and mobility: The safest route tended to be 22 per cent safer than the fastest route, while the fastest route was only 11 per cent faster than the safest route. This suggests that there are considerable gains in safety on the safest routes with just a small increase in travel time. As well, intermediate routes, which consider both safety and mobility, would yield larger safety benefits that would by far outweigh the increased travel time.”
Connected cities
The researchers are currently extending their research into other cities, including Boston, where autonomous vehicles are being tested that produce not only information about themselves and their navigation, but also about traffic routes and crash risk.
“If an urban road network has access to new technologies such as autonomous vehicle data, cameras and other sensing technologies, new possibilities open up for real-time safety measurement and effective routing,” said Dr. Sayed. “These technologies are now generating unprecedented amounts of data, giving rise to new smart mobility applications in the future.”
The algorithm could also be used for bike routing, with cyclists and pedestrians being some of the most vulnerable users of road networks. “Including pedestrian and cyclist data in future algorithms or navigation tools will allow us to improve their safety significantly,” said Dr. Sayed.
It’s important to use real-time crash risk data in any crash prediction or safety optimization algorithm, he added, in order to reflect current conditions, provide more accurate crash risk estimates, and reduce the number of road collisions. Using this data and advanced modelling techniques allows a safer route algorithm that helps road users prioritize safety without compromising efficiency.
Interview language(s) English (Sayed, Ghoul)
END
New algorithm maps safest routes for city drivers
2023-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Illinois Tech assistant professor receives award for using insights from human immune system to strengthen AI
2023-07-25
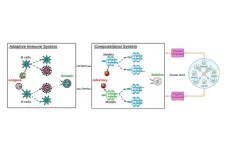
CHICAGO—July 25, 2023—For his groundbreaking research in fortifying artificial intelligence systems with insights gained from the human immune system, Ren Wang of Illinois Institute of Technology has received the prestigious Ralph E. Powe Junior Faculty Enhancement Award from Oak Ridge Associated Universities (ORAU). Wang’s research may be used in the future to strengthen AI systems, making them more robust and resilient.
As AI has increasingly permeated our daily lives through technologies, such as ChatGPT’s natural language ...
A novel bone regeneration technique with clinical potential
2023-07-25
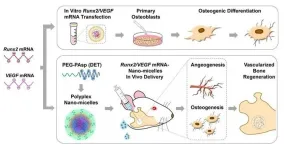
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify a promising way to improve bone repair with important clinical applications
Tokyo, Japan – Although bones have the ability to regenerate and repair themselves, they are generally unable to do so when the injury is larger than a small break or chip. In a study just published in Inflammation and Regeneration, Japanese researchers have developed a technique for improving bone regeneration over large areas in rats—and their findings may translate well to clinical settings.
As most of us know from experience, bones can repair themselves after a minor break ...
Researchers detail methodological approach to creating joint displays of data collection in mixed methods research
2023-07-25
Researchers present a methodology for developing joint displays of integrated mixed data collection. These joint displays provide a framework for supporting integration of a mixed methodology in research. Drawing upon a convergent mixed methods cohort study – the Early Discharge of Febrile Neutropenic Children with Cancer Study – the authors constructed a joint display of integrated mixed data collection from a patient/caregiver mixed methods survey instrument and manual medical chart abstraction. The paper outlines the methodological approach, including iterative ...
Brazilian researchers identify gynecological concerns of caregivers of young girls and women with Down syndrome
2023-07-25
Brazilian researchers conducted a cross-sectional study to explore the concerns of caregivers of Brazilian girls with Down syndrome (DS) regarding gynecological aspects of DS including menstruation, contraception and sexual practices. The study included 100 caregivers of females aged 9 years or older with DS who had reached menarche. Participating caregivers completed a questionnaire about their concerns around puberty, menstruation, sexuality and contraceptive methods.
Caregivers commonly expressed concerns around menstrual bleeding. Most caregivers ...
Meta-analysis of research on acne reveals that oral isotretinoin, followed by topical antibiotic, benzoyl peroxide and retinoid, are most effective treatments
2023-07-25
In their comprehensive meta-analysis (comprising 221 randomized controlled trials involving 65,601 patients), researchers investigated the effectiveness of various pharmacological therapies for acne vulgaris across diverse age groups and genders. The articles described 37 interventions, with a median patient age of 20 years old and median duration of treatment of 12 weeks. The median total, inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesion counts were 71.5, 27 and 44, respectively.
The study revealed that oral isotretinoin was the most effective treatment (mean difference 48.41; p-score 1.00), followed in efficacy by a triple therapy containing ...
Survey suggests geographic inequalities in patient registration versus primary care physician density can exclude patients from comprehensive care access
2023-07-25
French researchers conducted a large, simulated study to examine the relationship between the presence of primary care physicians (PCPs) and the ability of patients to register with a PCP. The study aimed to analyze local PCP supply based on various indicators, including PCP presence, patient registration availability for office visits, and patient registration availability for home visits. Out of 5,188 census blocks, 55.4% had at least one PCP, with 38.6% of those blocks allowing registration for office visits and 19.46% allowing registration for home ...
Greater primary care continuity among older people is associated with fewer inappropriate prescriptions and prescribing omissions
2023-07-25
Researchers from the Netherlands conducted an observational study to determine the association between personal continuity and potentially inappropriate prescriptions (PIPs) by family physicians in older patients. PIPs can be categorized as potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) and potential prescribing omissions (PPOs). The study utilized anonymized routine care data from 269,478 patients, receiving care in 48 Dutch family practices, from 2013 to 2018. They included all patients 65 and older with five or more contacts with their practice in six years, giving them a sample of 25,854 individuals. ...
Primary care clinics that improved patient access, identified at-risk patients and expanded services experienced reductions in acute hospitalizations
2023-07-25
Researchers from Mathematica studied high-performing Comprehensive Primary Care Plus (CPC+) sites to identify key strategies that contributed to significant reductions in acute hospitalization rates. Researchers identified CPC+ practice sites with the highest likelihood of achieving substantial reductions in Medicare acute hospitalization rates between 2016 and 2018, and referred to them as "Acute Hospitalization Rate (AHR) high-performers." Afterwards, they conducted telephone interviews and within- and cross-case comparative analyses of 14 of these primary care practice sites, ...
Primary care doctors face barriers in treating alcoholism
2023-07-25
Researchers explored how primary care physicians who have some familiarity with medications for alcohol use disorder (MAUD) make prescribing decisions and identify reasons for the underuse of MAUD in primary care. They interviewed 19 primary care physicians who had recently prescribed MAUD to patients in an outpatient setting. These physicians were selected from a large online database of medical professionals. Participating physicians reported several challenges in prescribing MAUD: (1) they had somewhat negative personal beliefs about the effectiveness of medications and the likelihood of patient ...
Family medicine physicians receive lowest HPV vaccine cost reimbursements compared to pediatricians, internal medicine doctors, nurse practitioners and other specialists
2023-07-25
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination coverage has improved in the United States, but privately insured adolescents have lower initiation and completion rates compared to those under public insurance programs. One of the contributing factors to this disparity is the higher cost of the HPV vaccine compared to other routinely recommended adolescent vaccines. While private payers typically reimburse the cost of the HPV vaccine at or above the CDC list price (i.e., $210.99 in 2017-2018), it remains below ...