(Press-News.org) French researchers conducted a large, simulated study to examine the relationship between the presence of primary care physicians (PCPs) and the ability of patients to register with a PCP. The study aimed to analyze local PCP supply based on various indicators, including PCP presence, patient registration availability for office visits, and patient registration availability for home visits. Out of 5,188 census blocks, 55.4% had at least one PCP, with 38.6% of those blocks allowing registration for office visits and 19.46% allowing registration for home visits. The research revealed that geographic inequalities in patient registration were more significant than those related to PCP density, challenging the assumption that patients could easily find and register with a PCP. They found that doctors were less likely to accept new patients who required time-consuming procedures including home visits and complicated services. Additionally, they were also less likely to accept new patients if they worked in areas that required them to take on the highest work loads (lowest PCP density in the most disadvantaged areas). The authors argue that policy decisions mandating patient registration with a PCP to access health care may unintentionally exclude individuals who are unable to register with a PCP, preventing them from benefiting completely from the health care system.
What We Know: Finding a PCP with whom to register in France is a prerequisite for benefiting fully from the health care system, access to which can be undermined by substantial PCP refusal to register new patients. PCPs can also refuse appointments to unregistered patients.
What This Study Adds: The findings from the study suggest that the number of primary care doctors in a specific area does not correlate with a patient’s ability to register for care from any of those doctors. Patients who requested more complex services or were located in more disadvantaged areas were more likely to be denied registration for a PCP. The researchers contend that the inability of patients to register with a PCP may result in the exclusion of certain patient groups from accessing health care services that require PCP registration. These observations highlight the need for a more nuanced approach in developing policies to ensure equitable health care access for all individuals.
Presence of Primary Care Physicians and Patients’ Ability to Register: A Simulated-Patient Survey in the Paris Region
Raphaëlle Delpech, MD, et al
Department of General Practice, University of Paris-Saclay and CESP (Centre for Research in Epidemiology and Population Health), Inserm U1018, University of Paris-Saclay, UVSQ, Gender, Sexual and Reproductive Health Team, Paris, France
Permanent link
END
Survey suggests geographic inequalities in patient registration versus primary care physician density can exclude patients from comprehensive care access
Presence of primary care physicians and patients’ ability to register: a simulated-patient survey in the Paris region
2023-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Greater primary care continuity among older people is associated with fewer inappropriate prescriptions and prescribing omissions
2023-07-25
Researchers from the Netherlands conducted an observational study to determine the association between personal continuity and potentially inappropriate prescriptions (PIPs) by family physicians in older patients. PIPs can be categorized as potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) and potential prescribing omissions (PPOs). The study utilized anonymized routine care data from 269,478 patients, receiving care in 48 Dutch family practices, from 2013 to 2018. They included all patients 65 and older with five or more contacts with their practice in six years, giving them a sample of 25,854 individuals. ...
Primary care clinics that improved patient access, identified at-risk patients and expanded services experienced reductions in acute hospitalizations
2023-07-25
Researchers from Mathematica studied high-performing Comprehensive Primary Care Plus (CPC+) sites to identify key strategies that contributed to significant reductions in acute hospitalization rates. Researchers identified CPC+ practice sites with the highest likelihood of achieving substantial reductions in Medicare acute hospitalization rates between 2016 and 2018, and referred to them as "Acute Hospitalization Rate (AHR) high-performers." Afterwards, they conducted telephone interviews and within- and cross-case comparative analyses of 14 of these primary care practice sites, ...
Primary care doctors face barriers in treating alcoholism
2023-07-25
Researchers explored how primary care physicians who have some familiarity with medications for alcohol use disorder (MAUD) make prescribing decisions and identify reasons for the underuse of MAUD in primary care. They interviewed 19 primary care physicians who had recently prescribed MAUD to patients in an outpatient setting. These physicians were selected from a large online database of medical professionals. Participating physicians reported several challenges in prescribing MAUD: (1) they had somewhat negative personal beliefs about the effectiveness of medications and the likelihood of patient ...
Family medicine physicians receive lowest HPV vaccine cost reimbursements compared to pediatricians, internal medicine doctors, nurse practitioners and other specialists
2023-07-25
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination coverage has improved in the United States, but privately insured adolescents have lower initiation and completion rates compared to those under public insurance programs. One of the contributing factors to this disparity is the higher cost of the HPV vaccine compared to other routinely recommended adolescent vaccines. While private payers typically reimburse the cost of the HPV vaccine at or above the CDC list price (i.e., $210.99 in 2017-2018), it remains below ...
SwRI’s Wyrick named GSA Fellow
2023-07-25
SAN ANTONIO — July 25, 2023 —The Geological Society of America (GSA) has elected Southwest Research Institute’s Dr. Danielle Wyrick as a Fellow, recognizing her exemplary scientific achievements, support of young geoscientists and excellent service to GSA. She has played a significant role in GSA’s Planetary Geology Division leadership and committees.
“During my tenure on the board of GSA’s Planetary Geology Division, we adopted the motto ‘when one planet just isn’t enough,’ ...
Physics informed supervised learning framework could make computational imaging faster
2023-07-25
BOSTON - Computational imaging techniques are growing more popular, but the large number of measurements they require often lead to slow speeds or damage to biological samples. A newly developed physics-informed variational autoencoder (P-VAE) framework could help speed up computational imaging by using supervised learning to jointly reconstruct many light sources, each with sparse measurements.
Vidya Ganapati, Assistant Professor of Engineering, Swarthmore College, will present this research at the Optica Imaging Congress. The hybrid meeting will take place 14 – 17 August 2023 in ...
Bacterial testing in kids with sinusitis could slash antibiotic use
2023-07-25
In children with suspected sinusitis, a nasal swab to test for three types of bacteria can tell whether antibiotics are likely to be effective or not, according to a new JAMA study by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC.
“Five million kids in the U.S. get prescribed antibiotics for sinusitis each year,” said lead author Nader Shaikh, M.D., pediatrician at UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh and professor of pediatrics and clinical and translational science at Pitt. “Our study suggests that only half of these kids see an improvement in symptoms with antibiotic use, so ...
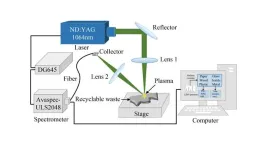
Improving recyclable waste classification with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
2023-07-25
WASHINGTON, July 25, 2023 – Managing and classifying waste accurately for reuse is a growing challenge in environmental protection. Addressing this issue, researchers at Hefei University of Technology in China have embarked on a quest to innovate in the realm of waste management, seeking effective methods that can simplify and improve the identification and classification of recyclable waste.
Delving into the intricacies of waste management, the researchers explored the application of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technology for the identification ...
State restrictions and geographic access to gender-affirming care for transgender youth
2023-07-25
About The Study: State restrictions were associated with significantly increased estimated drive times for youths seeking gender-affirming care. With more than 1 in 4 gender clinics located in states with restrictions, it is unknown whether existing clinics may have capacity to meet the increased need of out-of-state patients.
Authors: Kevin C. Chung, M.D., M.S., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.11299)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
New robot boosts solar energy research
2023-07-25
Researchers have created a robot capable of conducting experiments more efficiently and sustainably to develop a range of new semiconductor materials with desirable attributes. The researchers have already demonstrated that the new technology, called RoboMapper, can rapidly identify new perovskite materials with improved stability and solar cell efficiency.
“RoboMapper allows us to conduct materials testing more quickly, while also reducing both cost and energy overhead – making the entire process more sustainable,” ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Survey suggests geographic inequalities in patient registration versus primary care physician density can exclude patients from comprehensive care accessPresence of primary care physicians and patients’ ability to register: a simulated-patient survey in the Paris region