(Press-News.org) Researchers from the Netherlands conducted an observational study to determine the association between personal continuity and potentially inappropriate prescriptions (PIPs) by family physicians in older patients. PIPs can be categorized as potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) and potential prescribing omissions (PPOs). The study utilized anonymized routine care data from 269,478 patients, receiving care in 48 Dutch family practices, from 2013 to 2018. They included all patients 65 and older with five or more contacts with their practice in six years, giving them a sample of 25,854 individuals. Personal continuity was measured using three established indices: Usual Provider Continuity (UPC); the Bice-Boxerman Continuity of Care Index (BBI); and the Herfindahl Index (HI). The prevalence of PIPs were determined using screening tools. To assess the association, they conducted analyses with and without adjustment for number of chronic conditions, age and sex.
Higher scores in BBI, HI and UPC were associated with a significant reduction in potentially inappropriate prescriptions. Within the UPC, BBI and HI measures, the mean personal continuity was 0.70 (0.19), 0.55 (0.24) and 0.59 (0.22), respectively. Among more than 25,000 patients the researchers examined, 72.2% and 74.3% had one or more potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) or PPOs, respectively; and 30.9% and 34.2% had three or more PIMs or PPOs, respectively. The authors conclude that higher personal continuity is associated with more appropriate prescribing and argue that increasing personal continuity may improve quality of prescriptions and reduce harmful consequences.
What We Know: Prescription management is an important aspect of primary care for older patients as inappropriate prescribing can result in avoidable adverse events such as hospitalizations, falls and acute kidney injury.
What This Study Adds: Researchers found a significant association between increased rates of primary care continuity, as measured by three indices, and a decrease in potentially inappropriate prescriptions (PIPs) among primary care patients. For potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs), this effect was only observed in the patient group with five to 18 chronic conditions compared to the groups with fewer chronic conditions.
Personal Continuity and Appropriate Prescribing in Primary Care
Otto R. Maarsingh, MD, PhD, et al
Amsterdam UMC location Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Department of General Practice, and Amsterdam Public Health Research Institute,
Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
Permanent link
END
Greater primary care continuity among older people is associated with fewer inappropriate prescriptions and prescribing omissions
Personal continuity and appropriate prescribing in primary care
2023-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Primary care clinics that improved patient access, identified at-risk patients and expanded services experienced reductions in acute hospitalizations
2023-07-25
Researchers from Mathematica studied high-performing Comprehensive Primary Care Plus (CPC+) sites to identify key strategies that contributed to significant reductions in acute hospitalization rates. Researchers identified CPC+ practice sites with the highest likelihood of achieving substantial reductions in Medicare acute hospitalization rates between 2016 and 2018, and referred to them as "Acute Hospitalization Rate (AHR) high-performers." Afterwards, they conducted telephone interviews and within- and cross-case comparative analyses of 14 of these primary care practice sites, ...
Primary care doctors face barriers in treating alcoholism
2023-07-25
Researchers explored how primary care physicians who have some familiarity with medications for alcohol use disorder (MAUD) make prescribing decisions and identify reasons for the underuse of MAUD in primary care. They interviewed 19 primary care physicians who had recently prescribed MAUD to patients in an outpatient setting. These physicians were selected from a large online database of medical professionals. Participating physicians reported several challenges in prescribing MAUD: (1) they had somewhat negative personal beliefs about the effectiveness of medications and the likelihood of patient ...
Family medicine physicians receive lowest HPV vaccine cost reimbursements compared to pediatricians, internal medicine doctors, nurse practitioners and other specialists
2023-07-25
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination coverage has improved in the United States, but privately insured adolescents have lower initiation and completion rates compared to those under public insurance programs. One of the contributing factors to this disparity is the higher cost of the HPV vaccine compared to other routinely recommended adolescent vaccines. While private payers typically reimburse the cost of the HPV vaccine at or above the CDC list price (i.e., $210.99 in 2017-2018), it remains below ...
SwRI’s Wyrick named GSA Fellow
2023-07-25
SAN ANTONIO — July 25, 2023 —The Geological Society of America (GSA) has elected Southwest Research Institute’s Dr. Danielle Wyrick as a Fellow, recognizing her exemplary scientific achievements, support of young geoscientists and excellent service to GSA. She has played a significant role in GSA’s Planetary Geology Division leadership and committees.
“During my tenure on the board of GSA’s Planetary Geology Division, we adopted the motto ‘when one planet just isn’t enough,’ ...
Physics informed supervised learning framework could make computational imaging faster
2023-07-25
BOSTON - Computational imaging techniques are growing more popular, but the large number of measurements they require often lead to slow speeds or damage to biological samples. A newly developed physics-informed variational autoencoder (P-VAE) framework could help speed up computational imaging by using supervised learning to jointly reconstruct many light sources, each with sparse measurements.
Vidya Ganapati, Assistant Professor of Engineering, Swarthmore College, will present this research at the Optica Imaging Congress. The hybrid meeting will take place 14 – 17 August 2023 in ...
Bacterial testing in kids with sinusitis could slash antibiotic use
2023-07-25
In children with suspected sinusitis, a nasal swab to test for three types of bacteria can tell whether antibiotics are likely to be effective or not, according to a new JAMA study by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC.
“Five million kids in the U.S. get prescribed antibiotics for sinusitis each year,” said lead author Nader Shaikh, M.D., pediatrician at UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh and professor of pediatrics and clinical and translational science at Pitt. “Our study suggests that only half of these kids see an improvement in symptoms with antibiotic use, so ...
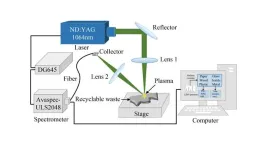
Improving recyclable waste classification with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
2023-07-25
WASHINGTON, July 25, 2023 – Managing and classifying waste accurately for reuse is a growing challenge in environmental protection. Addressing this issue, researchers at Hefei University of Technology in China have embarked on a quest to innovate in the realm of waste management, seeking effective methods that can simplify and improve the identification and classification of recyclable waste.
Delving into the intricacies of waste management, the researchers explored the application of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technology for the identification ...
State restrictions and geographic access to gender-affirming care for transgender youth
2023-07-25
About The Study: State restrictions were associated with significantly increased estimated drive times for youths seeking gender-affirming care. With more than 1 in 4 gender clinics located in states with restrictions, it is unknown whether existing clinics may have capacity to meet the increased need of out-of-state patients.
Authors: Kevin C. Chung, M.D., M.S., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.11299)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
New robot boosts solar energy research
2023-07-25
Researchers have created a robot capable of conducting experiments more efficiently and sustainably to develop a range of new semiconductor materials with desirable attributes. The researchers have already demonstrated that the new technology, called RoboMapper, can rapidly identify new perovskite materials with improved stability and solar cell efficiency.
“RoboMapper allows us to conduct materials testing more quickly, while also reducing both cost and energy overhead – making the entire process more sustainable,” ...
Only 60% of at-risk women report getting counseled on heart health at their postpartum visit
2023-07-25
Heart disease risk factors (being overweight, having diabetes or high blood pressure) increased among birthing adults between 2016 and 2020
Postpartum visits are crucial for checking mom’s heart health after delivery
Each year, 90% of women in the U.S. attend at least one postpartum visit
‘We must take advantage of this prime opportunity when we have a captive audience’
CHICAGO --- Despite having risk factors for heart disease, only 60% of women reported receiving counseling on optimizing their heart health, which includes healthy eating, exercise and losing weight gained during pregnancy at their six-week ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Greater primary care continuity among older people is associated with fewer inappropriate prescriptions and prescribing omissionsPersonal continuity and appropriate prescribing in primary care