BOSTON - Computational imaging techniques are growing more popular, but the large number of measurements they require often lead to slow speeds or damage to biological samples. A newly developed physics-informed variational autoencoder (P-VAE) framework could help speed up computational imaging by using supervised learning to jointly reconstruct many light sources, each with sparse measurements.
Vidya Ganapati, Assistant Professor of Engineering, Swarthmore College, will present this research at the Optica Imaging Congress. The hybrid meeting will take place 14 – 17 August 2023 in Boston, Massachusetts.
"This research could be powerful in applications of scientific discovery, taking a computational approach to push imaging devices to see more detail, faster," added Vidhya Ganapati.
Although data-driven approaches can reduce the number of measurements required for computational imaging, they usually require some type of reference data or information that isn’t always possible to acquire. The new physics-informed deep learning technique developed by Ganapati and colleagues doesn’t require any ground-truth or reference sources.
P-VAE relies on sparse measurements, which are computationally easier to handle because they contain data in which most of the values are zero. For P-VAE, sparse measurements are acquired for each source and then used jointly to reconstruct all the sources. By pooling information from measurements across the dataset and incorporating known information about the forward physics of imaging, prior and posterior distributions can be inferred.
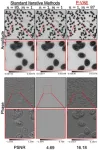
The researchers applied P-VAE to light-emitting diode (LED) array microscopy, which replaces the illumination source of a standard wide-field microscope with a programmable two-dimensional LED array. For each object or field of view imaged, LED illumination patterns are used to create an image stack. Each illumination pattern typically corresponds to one image in the stack, but the researchers showed that applying P-VAE decreases the number of images needed per object, thus reducing the overall acquisition time.
They also applied the technique to computed tomography, which images the internal structure of a sample or object by measuring the attenuation of x-rays through an object at different rotations relative to the beam. Although imaging more rotation angles will improve reconstruction, it also increases the x-ray dose and may cause damage. By applying P-VAE, the researchers jointly reconstructed objects using only sparse measurements.
The open-source code and experimental data for LED microscopy is available at https://github.com/vganapati/LED_PVAE and https://doi.org/10.6084/m9, and the computed tomography code is available at https://github.com/vganapati/CT_PVAE.
About the Optica Imaging Congress
The 2023 Optica Imaging Congress will provide a comprehensive view of the latest developments in imaging and applied optical sciences, covering the forefront advances in imaging and applied optics as well as the application of these technologies to important industrial, military and medical challenges. Monitor the Imaging Congress for the latest information on conference registration. Media registration is free with credential. Digital assets are available as requested.
About Optica
Optica (formerly OSA), Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide, is the society dedicated to promoting the generation, application, archiving and dissemination of knowledge in the field. Founded in 1916, it is the leading organization for scientists, engineers, business professionals, students and others interested in the science of light. Optica’s renowned publications, meetings, online resources and in-person activities fuel discoveries, shape real-life applications and accelerate scientific, technical and educational achievement. Discover more at: Optica.org
Media Contact
mediarelations@optica.org
END
Physics informed supervised learning framework could make computational imaging faster
Researchers apply physics informed approach to LED microscopy and computed tomography
2023-07-25
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bacterial testing in kids with sinusitis could slash antibiotic use
2023-07-25
In children with suspected sinusitis, a nasal swab to test for three types of bacteria can tell whether antibiotics are likely to be effective or not, according to a new JAMA study by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC.
“Five million kids in the U.S. get prescribed antibiotics for sinusitis each year,” said lead author Nader Shaikh, M.D., pediatrician at UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh and professor of pediatrics and clinical and translational science at Pitt. “Our study suggests that only half of these kids see an improvement in symptoms with antibiotic use, so ...
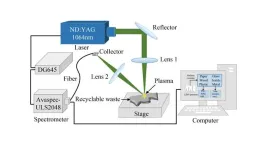
Improving recyclable waste classification with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
2023-07-25
WASHINGTON, July 25, 2023 – Managing and classifying waste accurately for reuse is a growing challenge in environmental protection. Addressing this issue, researchers at Hefei University of Technology in China have embarked on a quest to innovate in the realm of waste management, seeking effective methods that can simplify and improve the identification and classification of recyclable waste.
Delving into the intricacies of waste management, the researchers explored the application of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technology for the identification ...
State restrictions and geographic access to gender-affirming care for transgender youth
2023-07-25
About The Study: State restrictions were associated with significantly increased estimated drive times for youths seeking gender-affirming care. With more than 1 in 4 gender clinics located in states with restrictions, it is unknown whether existing clinics may have capacity to meet the increased need of out-of-state patients.
Authors: Kevin C. Chung, M.D., M.S., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.11299)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
New robot boosts solar energy research
2023-07-25
Researchers have created a robot capable of conducting experiments more efficiently and sustainably to develop a range of new semiconductor materials with desirable attributes. The researchers have already demonstrated that the new technology, called RoboMapper, can rapidly identify new perovskite materials with improved stability and solar cell efficiency.
“RoboMapper allows us to conduct materials testing more quickly, while also reducing both cost and energy overhead – making the entire process more sustainable,” ...
Only 60% of at-risk women report getting counseled on heart health at their postpartum visit
2023-07-25
Heart disease risk factors (being overweight, having diabetes or high blood pressure) increased among birthing adults between 2016 and 2020
Postpartum visits are crucial for checking mom’s heart health after delivery
Each year, 90% of women in the U.S. attend at least one postpartum visit
‘We must take advantage of this prime opportunity when we have a captive audience’
CHICAGO --- Despite having risk factors for heart disease, only 60% of women reported receiving counseling on optimizing their heart health, which includes healthy eating, exercise and losing weight gained during pregnancy at their six-week ...
Vegetarian dietary patterns and cardiometabolic risk in people with or at high risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-07-25
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that consuming a vegetarian diet may modestly but significantly improve cardiometabolic outcomes beyond standard pharmacological therapy in individuals at high risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), highlighting the potential protective and synergistic effects of vegetarian diets for the primary prevention of CVD.
Authors: Tian Wang, A.P.D., R.D., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.25658)
Editor’s ...
DNA testing before tissue diagnosis and time to treatment in lung cancer
2023-07-25
About The Study: The use of plasma circulating tumor DNA testing before tissue diagnosis among patients with suspected advanced lung cancer may expedite biomarker testing and accelerate time to treatment.
Authors: Natasha B. Leighl, M.D., of the University Health Network in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.25332)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
Origins of glioma brain cancer found to be in the epigenome
2023-07-25
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Study Title: Modeling Epigenetic Lesions that Cause Gliomas
Publication: Cell, Tuesday, July 25, 2023 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.06.022)
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Authors: Gilbert J. Rahme, PhD; Nauman M. Javed, MD, PhD; Kaitlyn L. Puorro; Volker Hovestadt, PhD; Sarah E. Johnstone, MD, PhD; Bradley E. Bernstein, MD, PhD
Summary:
While cancers often originate from mutations and other alterations of cells' DNA, researchers in the Bernstein Laboratory at Dana-Farber and the Broad ...
Gloomy climate calculation: Scientists predict a collapse of the Atlantic ocean current to happen mid-century
2023-07-25
Gloomy climate calculation: Scientists predict a collapse of the Atlantic ocean current to happen mid-century.
Important ocean currents that redistribute heat, cold and precipitation between the tropics and the northernmost parts of the Atlantic region will shut down around the year 2060 if current greenhouse gas emissions persist. This is the conclusion based on new calculations from the University of Copenhagen that contradict the latest report from the IPCC.
Contrary to what we may imagine about the impact ...
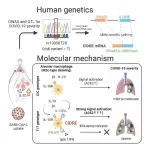
CiDRE renders alveolar macrophages susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 invasion
2023-07-25
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that alveolar macrophages expressing the readthrough transcript CiDRE are stimulated by interleukin-10 to express ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 receptor, and promote cytokine storm in patients with COVID-19
Tokyo, Japan – Despite intensive research since the pandemic began, much remains unknown about COVID-19, particularly why it can be so severe in some cases and relatively mild in others. Now, researchers from Japan have identified a genetic quirk that could make some patients more likely to experience severer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
Access to dialysis facilities in socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged communities
Dietary patterns and indicators of cognitive function
New study shows dry powder inhalers can improve patient outcomes and lower environmental impact
Plant hormone therapy could improve global food security
[Press-News.org] Physics informed supervised learning framework could make computational imaging fasterResearchers apply physics informed approach to LED microscopy and computed tomography