(Press-News.org) Gloomy climate calculation: Scientists predict a collapse of the Atlantic ocean current to happen mid-century.
Important ocean currents that redistribute heat, cold and precipitation between the tropics and the northernmost parts of the Atlantic region will shut down around the year 2060 if current greenhouse gas emissions persist. This is the conclusion based on new calculations from the University of Copenhagen that contradict the latest report from the IPCC.
Contrary to what we may imagine about the impact of climate change in Europe, a colder future may be in store. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen’s Niels Bohr Institute and Department of Mathematical Sciences predict that the system of ocean currents which currently distributes cold and heat between the North Atlantic region and tropics will completely stop if we continue to emit the same levels of greenhouse gases as we do today.
Using advanced statistical tools and ocean temperature data from the last 150 years, the researchers calculated that the ocean current, known as the Thermohaline Circulation or the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), will collapse – with 95 percent certainty – between 2025 and 2095. This will most likely occur in 34 years, in 2057, and could result in major challenges, particularly warming in the tropics and increased storminess in the North Atlantic region.
"Shutting down the AMOC can have very serious consequences for Earth's climate, for example, by changing how heat and precipitation are distributed globally. While a cooling of Europe may seem less severe as the globe as a whole becomes warmer and heat waves occur more frequently, this shutdown will contribute to an increased warming of the tropics, where rising temperatures have already given rise to challenging living conditions," says Professor Peter Ditlevsen from the Niels Bohr Institute.
"Our result underscores the importance of reducing global greenhouse gas emissions as soon as possible," says the researcher.
The calculations, just published in the renowned scientific journal, Nature Communications, contradict the message of the latest IPCC report, which, based on climate model simulations, considers an abrupt change in the thermohaline circulation very unlikely during this century.
Early warning signals present
The researchers' prediction is based on observations of early warning signals that ocean currents exhibit as they become unstable. These Early Warning Signals for the Thermohaline Circulation have been reported previously, but only now has the development of advanced statistical methods made it possible to predict just when a collapse will occur.
The researchers analysed sea surface temperatures in a specific area of the North Atlantic from 1870 to present days. These sea surface temperatures are "fingerprints” testifying the strength of the AMOC, which has only been measured directly for the past 15 years.
"Using new and improved statistical tools, we’ve made calculations that provide a more robust estimate of when a collapse of the Thermohaline Circulation is most likely to occur, something we had not been able to do before," explains Professor Susanne Ditlevsen of UCPH’s Department of Mathematical Sciences.
The thermohaline circulation has operated in its present mode since the last ice age, where the circulation was indeed collapsed. Abrupt climate jumps between the present state of the AMOC and the collapsed state has been observed to happen 25 times in connection with iceage climate. These are the famed Dansgaard-Oeschger events first observed in ice cores from the Greenlandic ice sheet. At those events climate changes were extreme with 10-15 degrees changes over a decade, while present days climate change is 1.5 degrees warming over a century.
Facts:
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is part of a global system of ocean currents. By far, it accounts for the most significant part of heat redistribution from the tropics to the northernmost regions of the Atlantic region – not least to Western Europe.
At the northernmost latitudes, circulation ensures that surface water is converted into deep, southbound ocean currents. The transformation creates space for additional surface water to be moved northward from equatorial regions. As such, thermohaline circulation is critical for maintaining the relatively mild climate of the North Atlantic region.
The work is supported by TiPES, a joint-European research collaboration focused on tipping points of the climate system. The TiPES project is an EU Horizon 2020 interdisciplinary climate research project focused on tipping points in the climate system. END
Gloomy climate calculation: Scientists predict a collapse of the Atlantic ocean current to happen mid-century
Important ocean currents that redistribute heat, cold and precipitation between the tropics and the northernmost parts of the Atlantic region will shut down around the year 2060 if current greenhouse gas emissions persist
2023-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CiDRE renders alveolar macrophages susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 invasion
2023-07-25
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that alveolar macrophages expressing the readthrough transcript CiDRE are stimulated by interleukin-10 to express ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 receptor, and promote cytokine storm in patients with COVID-19
Tokyo, Japan – Despite intensive research since the pandemic began, much remains unknown about COVID-19, particularly why it can be so severe in some cases and relatively mild in others. Now, researchers from Japan have identified a genetic quirk that could make some patients more likely to experience severer ...
Robotic hand rotates objects using touch, not vision
2023-07-25
Inspired by the effortless way humans handle objects without seeing them, a team led by engineers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new approach that enables a robotic hand to rotate objects solely through touch, without relying on vision.
Using their technique, the researchers built a robotic hand that can smoothly rotate a wide array of objects, from small toys, cans, and even fruits and vegetables, without bruising or squishing them. The robotic hand accomplished these tasks using only information based on touch.
The work could aid in the development of robots that can manipulate objects in the ...
AI as a leader? A conversation we need to have!
2023-07-25
How can an AI become the boss? Already during the COVID-19 pandemic, we have seen how crucial digital technologies have become for leadership. Without Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and related programs, leaders would not have been able to reach their employees easily. These tools continue to enjoy a secured place in the office today.
There is no surprise there. Anything that can be considered a competitive advantage will be utilized as such, and digital options are often quicker, more cost-efficient, or simply more convenient. Indeed, in the future, leadership as a whole is going to make giant leaps toward digitalization. The next phase is therefore only logical: digitally supported leadership, that ...
Mount Sinai receives significant funding to study which coronary revascularization procedure best improves survival and quality of life for women and underserved minority groups
2023-07-25
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai will help lead and launch the first clinical trial focusing on women and minority populations to determine which coronary revascularization procedure best improves their survival and quality of life. This trial will be funded through $29.9 million from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute Award to the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Weill Cornell Medicine.
“While there have been many trials comparing coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), most have enrolled ...
Large PCORI award funds study of surgical options for coronary artery disease in underrepresented patient populations
2023-07-25
A multi-institutional team of scientists led by Dr. Mario Gaudino, the Stephen and Suzanne Weiss Professor in Cardiothoracic Surgery and assistant dean for clinical trials at Weill Cornell Medicine, has been approved for a nearly $30 million funding award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI). The award will fund the first study among women and Black and Hispanic patients comparing the effectiveness of two revascularization options used to treat coronary artery disease.
Coronary artery disease, a narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries due to plaque buildup, is the leading ...
Offsetting or reducing CO2: This is what consumers want
2023-07-25
Whether it’s recycled aluminum at Apple’s MacBook Air or compensation payments from Microsoft for emissions over the life of an Xbox, climate-friendly products are becoming more and more popular. But do consumers also pay attention to how a neutral climate balance is created? Companies use two ways to accomplish this goal: reducing emissions directly or compensating them afterward. “Both approaches can make a product climate-neutral and have a positive impact on the environment, while compensatory measures are being discussed more and more critically in the public. To this end, the consumers in our study were ...
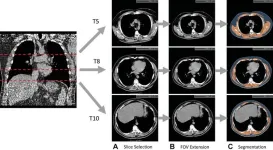
AI uses lung CT data to predict mortality risk
2023-07-25
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Artificial intelligence (AI) can use data from low-dose CT scans of the lungs to improve risk prediction for death from lung cancer, cardiovascular disease and other causes, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
The U.S Preventive Services Task Force recommends annual lung screening with low-dose CT (LDCT) of the chest for individuals ages 50 to 80 years with a high risk of lung cancer, such as longtime ...
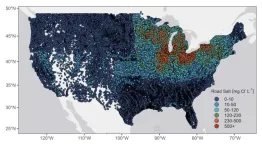
Road salt pollution in many US lakes could stabilize at or below thresholds set by the EPA
2023-07-25
Since de-icing with road salt began in the 1930s, the salinity of lakes across much of the US has been steadily increasing, posing a potential threat to aquatic life and drinking water supplies. However, a cautiously optimistic new study in Limnology and Oceanography Letters concludes that if we can hold steady or decrease road salt use, levels in many lakes could stabilize below thresholds set by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
“For the majority of US lakes, road salt pollution could be a solvable problem, if ...
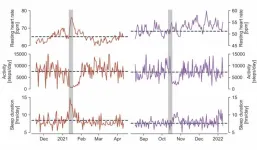
Data from wearable devices shows power of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2
2023-07-25
Data harvested from wearable devices and health apps could be valuable in public health research, according to a study. Vaccines can prevent SARS-CoV-2 infections and, in cases where the virus is able to break through, vaccination lowers the risks of severe disease, hospitalization, ICU admission, and death. Marc Wiedermann and colleagues used data from smartwatches and fitness trackers collected by the Corona Data Donation Project to investigate whether vaccination produces measurable changes in personal health and wellbeing. The Corona-Datenspende-App was launched ...
Spraying just 12% of the room kills 85% of the mosquitoes
2023-07-25
A study in a semi-natural setting finds that targeting just the very bottom of a room’s walls with insecticide will kill most of the mosquitoes, suggesting a cheaper and easier way to treat houses during disease outbreaks. The mosquito Aedes aegypti is a vector for serious diseases, including dengue, chikungunya and Zika. In Asia and Latin America, one approach taken to control mosquitoes that rest inside homes is indoor residual spraying, in which interior walls are coated with a persistent insecticide. However, the large surface area that must be coated makes the approach expensive to implement. Luca Facchinelli and colleagues sought to identify ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
[Press-News.org] Gloomy climate calculation: Scientists predict a collapse of the Atlantic ocean current to happen mid-centuryImportant ocean currents that redistribute heat, cold and precipitation between the tropics and the northernmost parts of the Atlantic region will shut down around the year 2060 if current greenhouse gas emissions persist