(Press-News.org) How can an AI become the boss? Already during the COVID-19 pandemic, we have seen how crucial digital technologies have become for leadership. Without Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and related programs, leaders would not have been able to reach their employees easily. These tools continue to enjoy a secured place in the office today.
There is no surprise there. Anything that can be considered a competitive advantage will be utilized as such, and digital options are often quicker, more cost-efficient, or simply more convenient. Indeed, in the future, leadership as a whole is going to make giant leaps toward digitalization. The next phase is therefore only logical: digitally supported leadership, that is AI assisting human managers (e.g., for the preparation of strategic decisions or analyzing employee behavior). And the phase after that is also already on the horizon: AI substituting human leadership as opposed to merely supporting it.
Forget any romantic notions you may have about leadership
“Stop!” we hear some of you shouting. “‘Real’ leadership needs real people! How is AI supposed to motivate employees or instill in them any sense of enthusiasm for the company’s goals?” You may not like our answer: Forget any romantic notions you have about leadership. AI will likely do an even better job than (average) leaders today do. If we maintain our romantic point of view, we are going to be woefully underprepared when reality comes knocking.
How AI can be the better leader
How is it that AI, in the future, will be accepted as a leader? The AI leader of the future will most likely not be a mere chat program. It will sit on your devices with natural speech functionality (just as Siri and Alexa do now) and perhaps present itself as a human, or rather an avatar, visible through the use of VR goggles.
How effective an AI will be in its role as a true leader will be contingent on how deeply the AI used can understand the three basic psychological needs of its employees. Humans long for belonging, mastery, and autonomy – because truly fantastic leaders are good at addressing these needs. But let’s be honest for a moment: How many truly fantastic bosses have you had across your career? Many leaders are stressed out, overworked, inattentive, unwittingly unfair, or simply not very empathetic. Future AI, with the ability to record and regard any important details, would be an advantage in many situations here.
Already today, man and machine interact with one another in harmony, for instance in the field of online therapy. In fact, many people are less hesitant to open up to a computer, and some programs are so sophisticated that their communication is barely indistinguishable from humans. Why shouldn’t that apply to the field of leadership?
Don’t let your worry get in the way of constructive co-creation
Of course, regardless of all the potential benefits, this idea alone could spark fear in us. But we should have an open dialogue about this rather than fearing the worst! What does this development mean for leadership? Which leadership roles will people be able to (or need to) take on in the future? What needs to change in leadership research and education in order to help shape the ethical aspects of such man-to-machine interaction?
The way we see things? Yes, there is still a need for human leaders. But in the future, they will need to understand both what makes people tick and how AI works. Their main responsibility will be leading computers that, in turn, lead humans. In this capacity, they will have to decide upon the rules that machines will follow. We better talk about these now before machines make up their own.
More details on this topic:
Van Quaquebeke, N., & Gerpott, F. H. (2023). The Now, New, and Next of Digital Leadership: How Artificial Intelligence (AI) Will Take Over and Change Leadership as We Know It. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, online first. doi.org/10.1177/15480518231181731
About KLU
Kühne Logistics University – Wissenschaftliche Hochschule für Logistik und Unternehmensführung (KLU) – is a private university located in Hamburg’s HafenCity. The independent, state-certified university’s major research areas are Sustainability, Digital Transformation, Entrepreneurship & Value Creation in the fields of Transport, Global Logistics, and Supply Chain Management.
KLU is one of very few private universities in Germany entitled to confer their own PhDs.
With one BSc and three MSc degree programs, a structured doctoral program, and a part-time Executive MBA, KLU offers its 400 full-time students a high level of specialization and excellent learning conditions. KLU has an international team of around 30 professors who teach in English. In open, tailor-made management seminar series, industry specialists and managers alike benefit from the application of academic findings to practical issues.
► Follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter (@THE_KLU).
► KLU research, events & executive education: KLU Business Newsletter (https://www.the-klu.org/landingpages/newsletter)
► More Information: www.the-klu.org
END
AI as a leader? A conversation we need to have!
2023-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mount Sinai receives significant funding to study which coronary revascularization procedure best improves survival and quality of life for women and underserved minority groups
2023-07-25
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai will help lead and launch the first clinical trial focusing on women and minority populations to determine which coronary revascularization procedure best improves their survival and quality of life. This trial will be funded through $29.9 million from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute Award to the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Weill Cornell Medicine.
“While there have been many trials comparing coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), most have enrolled ...
Large PCORI award funds study of surgical options for coronary artery disease in underrepresented patient populations
2023-07-25
A multi-institutional team of scientists led by Dr. Mario Gaudino, the Stephen and Suzanne Weiss Professor in Cardiothoracic Surgery and assistant dean for clinical trials at Weill Cornell Medicine, has been approved for a nearly $30 million funding award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI). The award will fund the first study among women and Black and Hispanic patients comparing the effectiveness of two revascularization options used to treat coronary artery disease.
Coronary artery disease, a narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries due to plaque buildup, is the leading ...
Offsetting or reducing CO2: This is what consumers want
2023-07-25
Whether it’s recycled aluminum at Apple’s MacBook Air or compensation payments from Microsoft for emissions over the life of an Xbox, climate-friendly products are becoming more and more popular. But do consumers also pay attention to how a neutral climate balance is created? Companies use two ways to accomplish this goal: reducing emissions directly or compensating them afterward. “Both approaches can make a product climate-neutral and have a positive impact on the environment, while compensatory measures are being discussed more and more critically in the public. To this end, the consumers in our study were ...
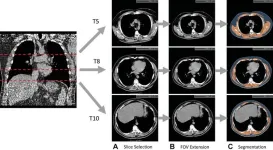
AI uses lung CT data to predict mortality risk
2023-07-25
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Artificial intelligence (AI) can use data from low-dose CT scans of the lungs to improve risk prediction for death from lung cancer, cardiovascular disease and other causes, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
The U.S Preventive Services Task Force recommends annual lung screening with low-dose CT (LDCT) of the chest for individuals ages 50 to 80 years with a high risk of lung cancer, such as longtime ...
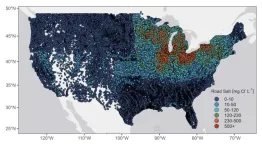
Road salt pollution in many US lakes could stabilize at or below thresholds set by the EPA
2023-07-25
Since de-icing with road salt began in the 1930s, the salinity of lakes across much of the US has been steadily increasing, posing a potential threat to aquatic life and drinking water supplies. However, a cautiously optimistic new study in Limnology and Oceanography Letters concludes that if we can hold steady or decrease road salt use, levels in many lakes could stabilize below thresholds set by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
“For the majority of US lakes, road salt pollution could be a solvable problem, if ...
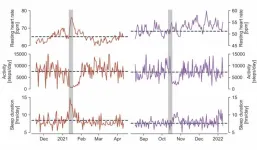
Data from wearable devices shows power of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2
2023-07-25
Data harvested from wearable devices and health apps could be valuable in public health research, according to a study. Vaccines can prevent SARS-CoV-2 infections and, in cases where the virus is able to break through, vaccination lowers the risks of severe disease, hospitalization, ICU admission, and death. Marc Wiedermann and colleagues used data from smartwatches and fitness trackers collected by the Corona Data Donation Project to investigate whether vaccination produces measurable changes in personal health and wellbeing. The Corona-Datenspende-App was launched ...
Spraying just 12% of the room kills 85% of the mosquitoes
2023-07-25
A study in a semi-natural setting finds that targeting just the very bottom of a room’s walls with insecticide will kill most of the mosquitoes, suggesting a cheaper and easier way to treat houses during disease outbreaks. The mosquito Aedes aegypti is a vector for serious diseases, including dengue, chikungunya and Zika. In Asia and Latin America, one approach taken to control mosquitoes that rest inside homes is indoor residual spraying, in which interior walls are coated with a persistent insecticide. However, the large surface area that must be coated makes the approach expensive to implement. Luca Facchinelli and colleagues sought to identify ...
Deep Longevity and House of Gaia announce strategic partnership to advance longevity research and wellness solutions
2023-07-25
Deep Longevity is at the forefront of AI-based longevity science, using deep learning techniques to analyse multiple data types and develop accurate aging clocks. These clocks provide valuable insights into an individual's biological age, offering a holistic understanding of their health and longevity potential. By partnering with House of Gaia, Deep Longevity seeks to bring their cutting- edge technologies and expertise to a wider audience, empowering individuals to take control of their well-being.
House of Gaia is a respected name in the wellness industry, known for its comprehensive range of holistic health services and programs. By ...
SwRI developing advanced electronic warfare system for U.S. Air Force
2023-07-25
SAN ANTONIO — July 25, 2023 —The U.S. Air Force awarded Southwest Research Institute a $4.8 million contract to further develop an adaptable, “continuously staring,” next-generation electronic warfare system capable of detecting advanced enemy radar signals. Using cutting-edge algorithms in a congested signal test environment, the system demonstrated more than 99% probability of intercepting signals with no false detections in a USAF verified simulated environment, a software model loaded with enemy radar.
“Eliminating ...
Food allergy in infancy linked to childhood asthma and reduced lung function
2023-07-25
Having a food allergy as a baby is linked to asthma and reduced lung function later in childhood, according to a world first study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute and published in the Lancet Child & Adolescent Health, found that early life food allergy was associated with an increased risk of both asthma and reduced lung growth at six years of age.
Murdoch Children’s Associate Professor Rachel Peters said this was the first study to examine the relationship between challenge-confirmed food allergy in infancy and asthma and poorer lung health ...