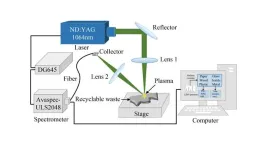
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, July 25, 2023 – Managing and classifying waste accurately for reuse is a growing challenge in environmental protection. Addressing this issue, researchers at Hefei University of Technology in China have embarked on a quest to innovate in the realm of waste management, seeking effective methods that can simplify and improve the identification and classification of recyclable waste.
Delving into the intricacies of waste management, the researchers explored the application of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technology for the identification and classification of recyclable waste and discuss their work in AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing. They collected and analyzed the spectra of 80 recyclable waste samples, classifying them into paper, plastic, glass, metal, textile, and wood based on LIBS spectra. This crucial step toward waste management optimization demonstrates a significant stride toward improving environmental sustainability and promoting resource reuse.
“We have used LIBS technology for the first time to identify and classify recyclable waste,” said author Lei Yang. “This method has accurate, reliable, fast detection results, and can achieve automatic detection.”
Given the complexities of waste materials and the importance of precise classification, the researchers further subclassified metals and plastics into subcategories. With their unique properties, each subclass of waste holds a distinct potential for specific reuse and recycling practices, making accurate identification and classification a key to unlocking efficient waste management solutions.
The research methodology employed an array of machine learning models to further advance the identification process. Among the explored models, the combination of linear discriminant analysis (LDA) and random forest (RF) emerged as the most optimal for classifying recyclable waste. Additionally, for subclassifying metals and plastics, a combination of principal component analysis and RF was deemed most effective.
Researchers were struck by the accuracy of the model of LDA with RF in classifying recyclable waste, achieving an accuracy of 100%. For subclassifying metals and plastics, the model of PCA(9D) + RF scored the highest accuracy. These results indicate the potential of this method in improving recycling efficiency and waste management practices.
“What surprised us the most was that by using LIBS technology for classification and recognition without any preprocessing of the waste object, the results are satisfactory,” Yang said.
Fueled by the promising outcomes of their research, the team is eager to expand their work in the future. They plan to enhance their studies by increasing the number of waste samples and incorporating other forms of waste such as kitchen waste. Furthermore, they hope to deepen the understanding of transparent glass detection with LIBS, opening new avenues for recycling and waste management.
###
The article “Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy identifies and classifies recyclable waste: A crucial step toward improved waste management” is authored by Lei Yang, Yong Xiang, Yinchuan Li, Wenyi Bao, Feng Ji, Jingtao Dong, Jingjing Chen, Mengjie Xu, Rongsheng Lu. It will appear in AIP Advances on July 25, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0149329). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0149329.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
AIP Advances is an open access journal publishing in all areas of physical sciences—applied, theoretical, and experimental. The inclusive scope of AIP Advances makes it an essential outlet for scientists across the physical sciences. See https://pubs.aip.org/aip/adv.
###
END
Improving recyclable waste classification with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
Coupling spectroscopy with sorting algorithms paves the way for more efficient and reliable waste segregation in the future
2023-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
State restrictions and geographic access to gender-affirming care for transgender youth
2023-07-25
About The Study: State restrictions were associated with significantly increased estimated drive times for youths seeking gender-affirming care. With more than 1 in 4 gender clinics located in states with restrictions, it is unknown whether existing clinics may have capacity to meet the increased need of out-of-state patients.
Authors: Kevin C. Chung, M.D., M.S., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.11299)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
New robot boosts solar energy research
2023-07-25
Researchers have created a robot capable of conducting experiments more efficiently and sustainably to develop a range of new semiconductor materials with desirable attributes. The researchers have already demonstrated that the new technology, called RoboMapper, can rapidly identify new perovskite materials with improved stability and solar cell efficiency.
“RoboMapper allows us to conduct materials testing more quickly, while also reducing both cost and energy overhead – making the entire process more sustainable,” ...
Only 60% of at-risk women report getting counseled on heart health at their postpartum visit
2023-07-25
Heart disease risk factors (being overweight, having diabetes or high blood pressure) increased among birthing adults between 2016 and 2020
Postpartum visits are crucial for checking mom’s heart health after delivery
Each year, 90% of women in the U.S. attend at least one postpartum visit
‘We must take advantage of this prime opportunity when we have a captive audience’
CHICAGO --- Despite having risk factors for heart disease, only 60% of women reported receiving counseling on optimizing their heart health, which includes healthy eating, exercise and losing weight gained during pregnancy at their six-week ...
Vegetarian dietary patterns and cardiometabolic risk in people with or at high risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-07-25
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that consuming a vegetarian diet may modestly but significantly improve cardiometabolic outcomes beyond standard pharmacological therapy in individuals at high risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), highlighting the potential protective and synergistic effects of vegetarian diets for the primary prevention of CVD.
Authors: Tian Wang, A.P.D., R.D., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.25658)
Editor’s ...
DNA testing before tissue diagnosis and time to treatment in lung cancer
2023-07-25
About The Study: The use of plasma circulating tumor DNA testing before tissue diagnosis among patients with suspected advanced lung cancer may expedite biomarker testing and accelerate time to treatment.
Authors: Natasha B. Leighl, M.D., of the University Health Network in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.25332)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
Origins of glioma brain cancer found to be in the epigenome
2023-07-25
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Study Title: Modeling Epigenetic Lesions that Cause Gliomas
Publication: Cell, Tuesday, July 25, 2023 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.06.022)
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Authors: Gilbert J. Rahme, PhD; Nauman M. Javed, MD, PhD; Kaitlyn L. Puorro; Volker Hovestadt, PhD; Sarah E. Johnstone, MD, PhD; Bradley E. Bernstein, MD, PhD
Summary:
While cancers often originate from mutations and other alterations of cells' DNA, researchers in the Bernstein Laboratory at Dana-Farber and the Broad ...
Gloomy climate calculation: Scientists predict a collapse of the Atlantic ocean current to happen mid-century
2023-07-25
Gloomy climate calculation: Scientists predict a collapse of the Atlantic ocean current to happen mid-century.
Important ocean currents that redistribute heat, cold and precipitation between the tropics and the northernmost parts of the Atlantic region will shut down around the year 2060 if current greenhouse gas emissions persist. This is the conclusion based on new calculations from the University of Copenhagen that contradict the latest report from the IPCC.
Contrary to what we may imagine about the impact ...
CiDRE renders alveolar macrophages susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 invasion
2023-07-25
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that alveolar macrophages expressing the readthrough transcript CiDRE are stimulated by interleukin-10 to express ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 receptor, and promote cytokine storm in patients with COVID-19
Tokyo, Japan – Despite intensive research since the pandemic began, much remains unknown about COVID-19, particularly why it can be so severe in some cases and relatively mild in others. Now, researchers from Japan have identified a genetic quirk that could make some patients more likely to experience severer ...
Robotic hand rotates objects using touch, not vision
2023-07-25
Inspired by the effortless way humans handle objects without seeing them, a team led by engineers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new approach that enables a robotic hand to rotate objects solely through touch, without relying on vision.
Using their technique, the researchers built a robotic hand that can smoothly rotate a wide array of objects, from small toys, cans, and even fruits and vegetables, without bruising or squishing them. The robotic hand accomplished these tasks using only information based on touch.
The work could aid in the development of robots that can manipulate objects in the ...
AI as a leader? A conversation we need to have!
2023-07-25
How can an AI become the boss? Already during the COVID-19 pandemic, we have seen how crucial digital technologies have become for leadership. Without Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and related programs, leaders would not have been able to reach their employees easily. These tools continue to enjoy a secured place in the office today.
There is no surprise there. Anything that can be considered a competitive advantage will be utilized as such, and digital options are often quicker, more cost-efficient, or simply more convenient. Indeed, in the future, leadership as a whole is going to make giant leaps toward digitalization. The next phase is therefore only logical: digitally supported leadership, that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
[Press-News.org] Improving recyclable waste classification with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopyCoupling spectroscopy with sorting algorithms paves the way for more efficient and reliable waste segregation in the future