(Press-News.org) Arctic terns – which fly on the longest migrations of any animal on Earth – may be able to navigate the dangers posed by climate change, new research suggests.
The birds live in near-perpetual daylight, breeding in the north of our planet and flying to Antarctica for the Southern Hemisphere summer, covering enough distance in their lifetime to travel to the moon three times.
The new study, led by the University of Exeter and the Met Office, examined the likely impacts of climate change on arctic terns outside of the breeding season, investigating changes to prevailing winds, primary productivity (which affects food availability) at key sites visited by Arctic terns and Antarctic sea ice.
While poorer foraging in the North Atlantic seems likely to pose a threat for them in the future, the study concluded that the overall effects of climate change for migrating terns should be minor. They are likely to be resilient due to living their lives over such vast areas.
However, the researchers warn that multiple small effects may still harm this long-lived (up to 30 years) species – and other species may be unable to escape local and regional changes.
“Arctic terns rely on productive oceans for food, sea ice for rest and foraging, and prevailing winds during flight,” said Dr Joanne Morten, from the University of Exeter.
“Although the Arctic tern is a species of ‘least concern’ globally on the IUCN Red List, breeding numbers are declining and can be challenging to monitor.
“Climate change is a massive threat to all seabirds. Our study looked at specific aspects of this.
“So, while our findings suggest this species may be resilient, this is only part of a bigger picture for Arctic terns and many other species.
“Meeting carbon emissions targets is vital to slow these projected end-of-century climatic changes and minimise extinction risk for all species.”
The study used observations of ongoing climate change and multiple climate and Earth System Models to project changes by 2100.
It examined the impacts of two emissions scenarios: “middle-of-the-road” and “fossil-fuelled development”.
The latter led to a projected decline of primary productivity (the base level of all food chains) in the North Atlantic – a key feeding ground for millions of seabirds and other marine animals.
However, minimal changes to primary productivity were projected at three other key sites for Arctic terns: the Benguela Upwelling, the Subantarctic Indian Ocean and the Southern Ocean.
Meanwhile, the impact of likely Antarctic sea ice decline on terns is uncertain, and the projections suggested small changes to prevailing winds would have “minimal impacts” on tern migration – except in the Southern Ocean, where strengthening winds may force the birds to shift flight routes.
The study’s interdisciplinary approach began with a virtual Climate Data Challenge “hackathon” facilitated by the University of Bristol and the Met Office.
This allowed ecologists to work with climate scientists, bringing together different skills and approaches.
The research team included the universities of Liverpool, Bristol, Washington, Oxford and Iceland.
Joanne Morten’s work was funded by a NERC GW4+ Doctoral Training Partnership studentship, and a National Geographic grant funded tracking of terns.
The paper, published in the journal Global Change Biology, is entitled: “Global warming and Arctic terns: estimating climate change impacts on the world's longest migration.”
Ends
END
Arctic terns may navigate climate dangers
Arctic terns – which fly on the longest migrations of any animal on Earth – may be able to navigate the dangers posed by climate change, new research suggests.
2023-07-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
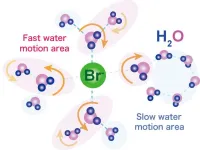
Bromide ions cause ripples in semiclathrate hydrates
2023-07-26
Osaka, Japan – The way that water molecules behave in proton conducting materials is very important for understanding—and making the most of—their properties. This means being able to look at very rapid snapshots to catch changes in the water motion. Researchers from Osaka University have taken a close look at semiclathrate hydrate crystals using quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS). Their findings are published in Applied Physics Letters.
Semiclathrate hydrates have water molecule frameworks that house other molecules or ions as ‘guests’ in their structures. The overall properties of the framework can therefore be controlled and tailored to particular ...
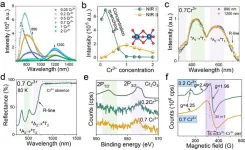
Intervalence charge transfer of Cr³⁺-Cr³⁺ aggregation for NIR-Ⅱ luminescence
2023-07-26
The near-infrared (NIR) spectrum contains characteristic vibrational absorption bands of numerous organic functional groups. NIR phosphor-converted light-emitting diodes (pc-LEDs) have gathered increasing interests in fields including non-destructive testing and night vision. In 2016, Osram reported the first NIR pc-LED, SFH4735, while with low output power (16 mW @ 350 mA) and limited wavelengths. Furthermore, luminescent contrast agents operating within the second biological imaging window (1000-1800 nm) exhibit lower tissue absorption and scattering coefficients in contrast to the traditional first window (750-950 nm), thereby ...
International trial shows that interferon could help reduce the spread of COVID-19
2023-07-26
Results of an innovative clinical trial led by Perth researchers have shown that the drug interferon could help reduce the spread of COVID-19 from a positive person to their household contacts, with the study helping to inform treatment options for a future pandemic.
The trial - CONCORD-19 - tracked 1,172 participants in 341 households in Santiago, Chile where there was a positive COVID-19 case between December 2020 and June 2021.
Researchers tested the effectiveness of treating the infected people and their uninfected household contacts with interferon, with the aim of evaluating whether this drug reduces the severity of the disease and the spread of COVID-19 within ...
Dune restoration could increase the resilience of Southern California's urban beaches to sea level rise
2023-07-26
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Over the last several years, the residents of Santa Monica, a coastal city on the edge of Los Angeles, saw something neither they, their parents, or perhaps even their grandparents had ever seen before: a three-foot-tall dune system rising gently from the flat, groomed expanse of one of the world’s most famous urban beaches. It’s a six year alliance between sand, wind and vegetation, and, according to UC Santa Barbara researchers, it’s one way to enlist nature to help protect the coast from the impacts of climate change.
“The project was really to assess whether we could naturally grow dunes on a heavily ...
How to stop obese children having heart disease in adulthood
2023-07-26
Sophia Antipolis, 26 July 2023: Childhood is a window of opportunity to tackle obesity before the damage it causes is irreversible, according to a scientific statement by experts on heart disease and childhood obesity published today in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 The document was produced by the Task Force for Childhood Health of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC) of the ESC and the European Childhood Obesity Group (ECOG).
Childhood obesity is on the rise. According to the World Health Organization, while less than 1% of children and adolescents aged 5-19 were obese in 1975, ...
Static isometric exercise, such as wall sits, best for lowering blood pressure
2023-07-26
Static isometric exercises—the sort that involve engaging muscles without movement, such as wall sits and planks—are best for lowering blood pressure, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence from clinical trials, published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
But ‘cardio’ (aerobic exercise); dynamic resistance training, such as squats, press-ups, and weights; high intensity interval training or HIIT for short (episodic short bouts of high intensity exercise ...
Consequences of premature parental death seemingly greater for boys than for girls
2023-07-26
The cumulative health and economic consequences of the premature loss of a parent may be greater for boys than for girls, suggest the findings of a large long term study published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Experiencing the death of a parent before the age of 21, however, is strongly linked to poor mental health and lower earnings/unemployment in adulthood for both sexes, the data indicate.
Previously published research has pointed to a link between premature parental death and the child’s subsequent health and prosperity. But no studies have drawn ...
Study finds ‘startling’ levels of hidden mental health symptoms among people living with long term autoimmune diseases
2023-07-26
More than half of patients with auto-immune conditions experience mental health conditions such as depression or anxiety, yet the majority are rarely or never asked in clinic about mental health symptoms, according to new research from the University of Cambridge and King’s College London.
In a study published today in Rheumatology, researchers found that over half of the patients had rarely or never reported their mental health symptoms to a clinician, and that the range of possible mental health and neurological symptoms is much wider than has been previously reported.
The team surveyed neurological and psychiatric symptoms amongst 1,853 patients with systemic auto-immune ...
Egg ‘signatures’ will allow drongos to identify cuckoo ‘forgeries’ almost every time, study finds
2023-07-26
Images and paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1mPYnFKIEArlXUAaFk5H7YTepezntqerj?usp=sharing
African cuckoos may have met their match with the fork-tailed drongo, which scientists predict can detect and reject cuckoo eggs from their nest on almost every occasion, despite them on average looking almost identical to drongo eggs.
Fork-tailed drongos, belligerent birds from sub-Saharan Africa, lay eggs with a staggering diversity of colours and patterns. All these colours and patterns are forged by the African cuckoo.
African cuckoos lay their eggs in drongos’ nests to avoid rearing their chick themselves (an example of so-called ...
A novel approach for balancing properties in composite materials
2023-07-26
Dr. Amir Asadi, an assistant professor in the Department of Engineering Technology and Industrial Distribution at Texas A&M University, is making groundbreaking strides in the field of composite materials. His research explores embedding patterned nanostructures composed of multiple materials into high-performance composites to achieve the desired multifunctionality without sacrificing any other properties. This could lead to advancements in various fields, including electronics, energy storage, transportation and consumer products.
Asadi's work has significant implications, as it addresses the challenge of simultaneously enhancing two properties — multifunctionality ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Arctic terns may navigate climate dangersArctic terns – which fly on the longest migrations of any animal on Earth – may be able to navigate the dangers posed by climate change, new research suggests.