(Press-News.org) About The Study: This secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial including 19,000 older adults found a significant increase in intracranial bleeding with daily low-dose aspirin but no significant reduction of ischemic stroke. These findings may have particular relevance to older individuals prone to developing intracranial bleeding after head trauma (e.g., from falls).
Authors: John J. McNeil, Ph.D., of Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.25803)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.25803?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=072623
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Low-dose aspirin and the risk of stroke and intracerebral bleeding in healthy older people
JAMA Network Open
2023-07-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
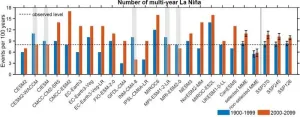
Global warming will cause more multiyear La Niña events: study
2023-07-26
The El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is the Earth's most consequential interannual climate fluctuation. Alternating irregularly between warm El Niño and cold La Niña phases, it brings shifts in ocean surface temperature and disrupts wind and rainfall patterns across the tropics.
Unlike El Niño, which usually lasts one year, La Niña tends to develop after an El Niño and lasts for two consecutive years or more. This is known as a multiyear La Niña event and exerts prolonged and aggregated impacts, such as increased wildfires, flooding, and altered ...
Earth's plate tectonics recently underwent a fundamental change
2023-07-26
Earth is truly unique among our Solar System’s planets. It has vast water oceans and abundant life. But Earth is also unique because it is the only planet with plate tectonics, which shaped its geology, climate and possibly influenced the evolution of life.
Plate tectonics describes the movement and interaction of tectonic plates on Earth’s surface. This movement is driven by the very slow creeping motion of Earth's mantle, called convection, which carry heat from the interior to our planet's ...
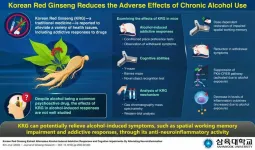
Korean Red Ginseng can alleviate addictive effects of alcohol, find Sahmyook University researchers
2023-07-26
Alcohol is one of the most commonly used psychoactive drugs, with a growing number of users in many parts of the world. Despite the awareness regarding its adverse effects, individuals can get habituated to alcohol consumption, leading to a medical condition called alcohol use disorder (AUD). AUD is characterized by the abuse, dependency, and addiction of alcohol, leading to compromised social responses and interactions of the individual. Moreover, it impairs spatial working memory (memory that allows us to orient ourselves ...
NIH-funded study explains link to increased cardiovascular risks for people with obstructive sleep apnea
2023-07-26
Researchers have found that people with obstructive sleep apnea have an increased cardiovascular risk due to reduced blood oxygen levels, largely explained by interrupted breathing. Obstructive sleep apnea has long been associated with increased risk of cardiovascular issues, including heart attack, stroke, and death, but the findings from this study, partially supported by the National Institutes of Health and published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, show the mechanism mostly responsible ...
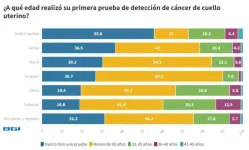
Uruguay needs to strengthen screening awareness with 69 percent of vaccinated women having cervical screening tests
2023-07-26
Research from the Registro Nacional de Cáncer notes that Uruguay has the highest cancer incidence and mortality rates in Latin America. In particular, cervical cancer is the third leading cause of cancer related morbidity among Uruguay's female population.
To further motivate action to combat cervical cancer, BGI Genomics today released its State of Cervical Cancer Awareness Report in Uruguay. This report assesses the level of knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to cervical cancer screening and the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine. By examining these key areas, this survey seeks to highlight the associated barriers and opportunities. ...
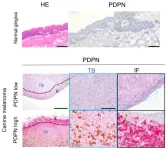
Immobilizing melanoma
2023-07-26
Although rare, mucosal melanoma in humans has a low survival rate. It has been difficult to investigate due to a lack of similar cancers in animals for study. Researchers explored a protein common to human and canine mucosal melanoma. The protein seems to be what makes this cancer so problematic, as it mobilizes the cancer cells, allowing them to spread. Researchers hope that eliminating this protein could lead to a potential treatment. The study is published in Molecular Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Melanoma is a type of cancer that begins in ...
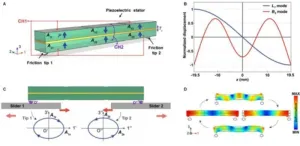
A symmetric-actuating linear piezoceramic ultrasonic motor capable of producing a scissoring effect
2023-07-26
As an electromechanical actuator, symmetric-actuating devices are often used in the fields where symmetrical motion, drive, and control are required, such as grasping or scissoring operations, and fast symmetric opening or closing of microchannels. One scenario with strong demand is minimally invasive surgery, including precision grasping and cutting tumor cells, retinal microsurgery, etc. In the field of micro electromechanical devices, the scissoring or grasping operation essentially belongs to two symmetrical actuations between two end-effectors. However, there is almost no one motor that can directly generate two symmetrical linear motions.
In general, to produce two symmetrical ...
$2.1 million awarded to research link between migraine, strokes and cardiovascular disease
2023-07-26
DALLAS, July 26, 2023 — Existing research shows certain types of migraines can increase the risk of stroke, and there is growing evidence that they may also lead to other types of cardiovascular disease (CVD). To learn more about these connections, the American Heart Association, the world's leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, is providing a total of $2.1 million in grants for seven new scientific research projects. The selected teams of scientists for the “Migraine ...
2023 Blavatnik National Awards for Young Scientists announced
2023-07-26
NEW YORK, July 26, 2023 – The Blavatnik Family Foundation and the New York Academy of Sciences announced today the 2023 laureates of the Blavatnik National Awards for Young Scientists.
Each will receive $250,000, the largest unrestricted scientific award for America’s most innovative, faculty-ranked scientists and engineers who are under the age of 42. The winners and their distinguished research:
2023 Laureate in Life Sciences: William Anderegg, Ph.D., The University of Utah (Ecology & Evolutionary ...
Metastatic breast cancer’s Trojan horse
2023-07-26
Lymph nodes are one of the body’s first lines of defense against disease. Immune cells are dispatched from these biological police stations to fight off intruders. But somehow, lymph nodes are also the first stop for most metastatic cancers.
“It’s paradoxical,” Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Assistant Professor Semir Beyaz says. “The cancer goes right in, but the immune cells aren’t doing anything. It’s important to understand what’s going on because this is how cancer takes the whole body hostage.”
Beyaz joined with collaborators from Massachusetts General Hospital to investigate. They ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
[Press-News.org] Low-dose aspirin and the risk of stroke and intracerebral bleeding in healthy older peopleJAMA Network Open