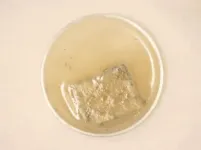
(Press-News.org) Plastic waste is a problem. Most plastics can’t be recycled, and many use finite, polluting petrochemicals as the basic ingredients. But that’s changing. In a study published today in Nature Sustainability, researchers successfully engineered microbes to make biological alternatives for the starting ingredients in an infinitely recyclable plastic known as poly(diketoenamine), or PDK.
The finding comes from collaboration among experts at three facilities at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab): the Molecular Foundry, the Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI), and the Advanced Light Source.
“This is the first time that bioproducts have been integrated to make a PDK that is predominantly bio-based,” said Brett Helms, staff scientist at the Molecular Foundry who led the project. “And it’s the first time that you see a bio-advantage over using petrochemicals, both with respect to the material’s properties and the cost of producing it at scale.”
Unlike traditional plastics, PDK can be repeatedly deconstructed into pristine building blocks and formed into new products with no loss in quality. PDKs initially used building blocks derived from petrochemicals, but those ingredients can be redesigned and produced with microbes instead. Now, after four years of effort, collaborators have manipulated E. coli to turn sugars from plants into some of the starting materials – a molecule known as triacetic acid lactone, or bioTAL – and produced a PDK with roughly 80% bio-content.
“We’ve demonstrated that the pathway to 100% bio-content in recyclable plastics is feasible,” said Jeremy Demarteau, a project scientist on the team contributing to biopolymer development. “You’ll see that from us in the future.”
PDKs can be used for a variety of products, including adhesives, flexible items like computer cables or watch bands, building materials, and “tough thermosets,” rigid plastics made through a curing process. Researchers were surprised to find that incorporating the bioTAL into the material expanded its working temperature range by up to 60 degrees Celsius compared to the petrochemical version. This opens the door to using PDKs in items that need specific working temperatures, including sports gear and automotive parts such as bumpers or dashboards.
Solving the plastic waste problem
The United Nations Environment Program estimates that we globally produce about 400 million tons of plastic waste every year, and that number is predicted to climb to more than 1 billion tons by 2050. Of the 7 billion tons of plastic waste already created, only about 10 percent has been recycled, while most is discarded into landfills or burned.
“We can’t keep using our dwindling supply of fossil fuels to feed this insatiable desire for plastics,” said Jay Keasling, a professor at UC Berkeley, senior faculty scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Biosciences Area, and the CEO of JBEI. “We want to help solve the plastic waste problem by creating materials that are both biorenewable and circular – and providing an incentive for companies to use them. Then people could have the products they need for the time they need them, before those items are transformed into something new.”
The study released today also builds on a 2021 environmental and technological analysis, which showed that PDK plastic could be commercially competitive with conventional plastics if produced at a large scale.
“Our new results are extremely encouraging,” said Corinne Scown, a staff scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Energy Technologies Area and a vice president at JBEI. “We found that with even modest improvements to the production process, we could soon be making bio-based PDK plastics that are both cheaper and emit less CO2 than those made with fossil fuels.”
Those improvements would include speeding up the rate at which microbes convert sugars to bioTAL, using bacteria that can transform a wider variety of plant-derived sugars and other compounds, and powering the facility with renewable energy.
This work was supported by the Department of Energy’s Bioenergy Technologies Office. The Molecular Foundry is a DOE Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences user facility that specializes in nanoscale science. JBEI is a Bioenergy Research Center funded by DOE’s Office of Science. The Advanced Light Source is a DOE Office of Science user facility.
PDK technology is available for licensing and collaboration. If interested, please contact Berkeley Lab’s Intellectual Property Office, ipo@lbl.gov.
###
Founded in 1931 on the belief that the biggest scientific challenges are best addressed by teams, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and its scientists have been recognized with 16 Nobel Prizes. Today, Berkeley Lab researchers develop sustainable energy and environmental solutions, create useful new materials, advance the frontiers of computing, and probe the mysteries of life, matter, and the universe. Scientists from around the world rely on the Lab’s facilities for their own discovery science. Berkeley Lab is a multiprogram national laboratory, managed by the University of California for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.
END
Promising new research suggests a total of just 4.5 minutes of vigorous activity that makes you huff and puff during daily tasks could reduce the risk of some cancers by up to 32 percent.
Published in JAMA Oncology and led by the University of Sydney, Australia, the study used data from wearable devices to track the daily activity of over 22,000 ‘non-exercisers’. Researchers then followed the group’s clinical health records for close to seven years to monitor for cancer.
As few as four to five minutes of vigorous intermittent lifestyle physical activity or ‘VILPA’ was associated with a substantially lower cancer risk compared to those who undertook no ...
Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) researchers have developed one of the world’s smallest, most intense and fastest refrigeration devices, the wearable thin-film thermoelectric cooler (TFTEC), and teamed with neuroscientists to help amputees perceive a sense of temperature with their phantom limbs. This advancement, one of the first of its kind, enables a useful new capability for a variety of applications, including improved prostheses, haptics for new modalities in augmented reality (AR) and thermally-modulated therapeutics for applications such as pain management. The technology also has a variety ...
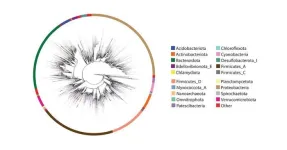
Two leading sequencing techniques are no longer at odds, thanks to an international effort led by scientists at University of California San Diego. In a study published July 27, 2023 in Nature Biotechnology, the researchers debuted a new reference database called Greengenes2, which makes it possible to compare and combine microbiome data derived from either 16S ribosomal RNA gene amplicon (16S) or shotgun metagenomics sequencing techniques.
“This is a significant moment in microbiome research, as we’ve effectively rescued over a decade’s worth of 16S data that might have otherwise become obsolete in the modern world ...
There’s no doubt that Aussies love a good celebration. We’re all in when it comes to the weekend, and most of us can’t go past a Christmas celebration without a little bit of overindulging. But all this comes at a cost, and it’s taking a massive toll on our waistline.
Now, a world-first study from the University of South Australia exposes the real weight gains of everyday Australians, in a move to tackle overweight and obesity.
Funded by the NHMRC, and published in JAMA Open Network today, the study explored how weight changes across a 12-month period, finding that weight fluctuated throughout the year.
Specifically, ...
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy aim to destroy cancer cells by inducing DNA double-strand breaks – damage that, once inflicted, usually causes the cells to die. But damage to a cell’s genetic material also activates a signaling pathway called IKK/NF-κB that helps prevent cell death, thus limiting the success of these treatments in patients.
NF-κB is a family of gene regulators that controls a wide variety of cellular processes – from immune responses to embryonic development – and is activated by the enzyme complex ...
Over the last decade, advances in 3D printing have unlocked new possibilities for bioengineers to build heart tissues and structures. Their goals include creating better in vitro platforms for discovering new therapeutics for heart disease, the leading cause of death in the United States, responsible for about one in every five deaths nationally, and using 3D-printed cardiac tissues to evaluate which treatments might work best in individual patients. A more distant aim is to fabricate implantable tissues that can heal or replace faulty or diseased structures inside a patient’s heart.
In a paper published in Nature Materials, researchers ...
QUT researchers have developed a new approach for designing molecular ON-OFF switches based on proteins which can be used in a multitude of biotechnological, biomedical and bioengineering applications.
The research team demonstrated that this novel approach allows them to design and build faster and more accurate diagnostic tests for detecting diseases, monitoring water quality and detecting environmental pollutants.
Professor Kirill Alexandrov, of the QUT School of Biology and Environmental ...
(Memphis, Tenn. – July 27, 2023) St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital proudly announces that Jinghui Zhang, Ph.D., Member of the Department of Computational Biology, has been elected as a Fellow of the International Society for Computational Biology.
Zhang is one of 15 scientists given this distinction in 2023. She’s being honored for the development and application of innovative computational methods, discovering novel targets and accelerating research and genomic data sharing to advance the diagnosis, treatment and surveillance of pediatric cancers and survivors.
“I ...
Dr. Raymond Chan's team from the Institute of Psychology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and his collaborators have recently shown that amotivation and anhedonia, rather than expressive dysfunction, play a crucial role in determining the social functioning of schizophrenia patients.
The study was published in Nature Mental Health.
Negative symptoms refer to the loss of normal functioning, including anhedonia, avolition, alogia, asociality, and affective blunting, and have been shown to be the most important predictors ...
Conventional wisdom holds that storing fat around your belly puts you at increased risk for type 2 diabetes. But surprising new findings from the University of Virginia School of Medicine suggest that naturally occurring variations in our genes can lead some people to store fat at the waist but also protect them from diabetes.
The unexpected discovery provides a more nuanced view of the role of obesity in diabetes and related health conditions. It also could pave the way for more personalized medicine – treatments tailored to the individual. ...