(Press-News.org) Kyoto, Japan -- Having control over how a dish is cooked is always a good idea. Taking a hint from the kitchen, scientists appear to have discovered a way to produce a true structure of the rare but naturally-occurring anti-HIV compound Lancilactone C from start to finish.
Its non-cytotoxicity in mammals could make this triterpenoid an ideal candidate for treating AIDS if its biological activity were clear -- and if only it were abundant in nature.
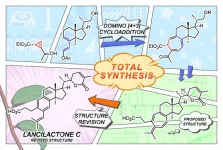
Now, a research group at Kyoto University has succeeded in creating a domino-like synthesis of Lancilactone C's unique seven-membered ring structure.
"Our synthetic method revealed that the proposed structure of Lancilactone C was initially incorrect," says Chihiro Tsukano of Kyoto University's Graduate School of Agriculture. "But we successfully derived its true structure from our spectral data and understanding of its biosynthesis."
In addition to this revelation, Tsukano realized that the electrocyclization -- a rearrangement reaction in organic chemistry -- used in the total synthesis also occurs in biosynthesis. Ironically, it remains a mystery of whether the proposed structure containing an unsaturated seven-membered ring might exist in nature as an analog -- or equivalent compound -- and how it might affect the expression of biological activity.
Tsukano's team utilized the domino-like reaction to enable the total synthesis of lancilactones and related triterpenoids. This outcome has inspired the team to further their research in optimizing compound structures, leading to possible development of novel antivirals.
The endless loop of required medication and multi-drug therapies often correlates with a lower quality of life for economically burdened patients.
"Our synthetic method for Lancilactone C, with its known efficacy, may lead to developing less problematic anti-HIV drugs," concludes Tsukano.
###
The paper "Total Synthesis and Structure Revision of (+)-Lancilactone C" appeared on 16 June 2023 in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, with doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c04124
About Kyoto University
Kyoto University is one of Japan and Asia's premier research institutions, founded in 1897 and responsible for producing numerous Nobel laureates and winners of other prestigious international prizes. A broad curriculum across the arts and sciences at undergraduate and graduate levels complements several research centers, facilities, and offices around Japan and the world. For more information, please see: http://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/en
END
Total recall on HIV
Researchers create total synthesis of HIV replication inhibitor
2023-07-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
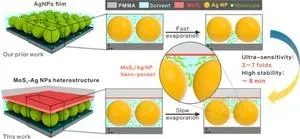
Scientists suggest AgNP/MoS2 nano-pocket for surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy scattering detection
2023-07-28
The research group of YANG Liangbao at the Institute of Health and Medical Technology, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Science (CAS) has recently developed a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERMS) method to automatically capture target molecules in AgNP/MoS2 nano-pockets, which enables highly sensitive and long-duration dynamic detection of some chemical reaction processes.
The results were published in Analytical Chemistry and selected as the front cover.
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) is a kind of molecular spectroscopy with fast, highly sensitive, ...
Solving the climate crisis requires collaboration between natural and social scientists
2023-07-28
Now that the world has experienced its hottest day in history, it is more urgent than ever for natural and social scientists to work together to address the climate crisis and keep global temperature increases below 2°C. To this end, an international group of esteemed researchers recently published an innovative research paper that highlights the importance of integrating knowledge from natural and social sciences to inform about effective climate change policies and practice. They argue that the concept of tipping points can serve as a bridge ...
A nanoprobe developed for visual quantitative detection of pesticides
2023-07-28
Recently, Prof. JIANG Changlong and his research team at the Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), developed and synthesized two highly effective ratiometric fluorescence nanoprobes. These nanoprobes, when combined with the color recognition capabilities of smartphones, enabled the visual and quantitative detection of pesticides in food and environmental water.
The research has been published in Chemical Engineering Journal and ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
Carbamate compounds ...
Retina cell breakthrough could help treat blindness
2023-07-28
Scientists have found a way to use nanotechnology to create a 3D ‘scaffold’ to grow cells from the retina –paving the way for potential new ways of treating a common cause of blindness.
Researchers, led by Professor Barbara Pierscionek from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), have been working on a way to successfully grow retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells that stay healthy and viable for up to 150 days. RPE cells sit just outside the neural part of the retina and, when damaged, can cause vision to deteriorate.
It ...
The approaches to achieve high-performance wearable sensors with hydrogels
2023-07-28
This review is written by Dr. Weixing Song from the Department of Chemistry, Capital Normal University. The paper reviewed the toughness and conductive network of existing hydrogel sensors. It emphasized the development status of various hydrogel sensors and highlighted strategies to enhance their mechanical and electrical performance. The findings are valuable for designing components and structures of high-performance wearable hydrogel sensors.
The increasing demand for healthcare IoT devices drives the development of wearable electronics. Electronic skins possess softness, stretchability, and self-healing ...
Enhanced light sensitivity may contribute to Alzheimer's 'sundowning,' disease progression
2023-07-28
New Alzheimer’s research from UVA Health suggests that enhanced light sensitivity may contribute to “sundowning” – the worsening of symptoms late in the day – and spur sleep disruptions thought to contribute to the disease’s progression.
The new insights into the disruptions of the biological clock seen in Alzheimer’s could have important potential both for the development of treatments and for symptom management, the researchers say. For example, caregivers often struggle with the erratic sleep patterns caused by Alzheimer’s ...
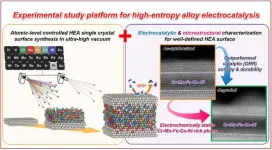
Researchers reveal a powerful platform for studying high-entropy alloy electrocatalysis
2023-07-28
Introduced in 2004, high-entropy alloys (HEAs) are alloys composed of multiple principal elements in nearly equiatomic proportions. Their unique chemical composition results in a high degree of chemical disorder, i.e. entropy, and produces remarkable properties such as high strength, ductility, and strong wear-and-tear resistance even at high temperatures. Scientists have dedicated a significant amount of attention to developing novel HEAs to help improve the performance of various electrocatalyst materials.
Because they are made up of differing constituent elements, HEAs' atomic-level surface designs can be complex. But unravelling this complexity is crucial, since the surface ...
San Diego family shares recent tragedy of losing daughter to necrotizing enterocolitis, as NEC Society prepares for the NEC Symposium in San Diego
2023-07-28
San Diego, CA - The NEC Society and Cincinnati Children’s have teamed up to present the NEC Symposium, the only conference in North America dedicated to understanding and preventing necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). NEC is a devastating intestinal disease that affects medically fragile infants in their first weeks and months of life. Every year in the United States, thousands of babies are diagnosed with NEC and at least one baby dies from NEC every day. The NEC Symposium will transform the NEC Research ...
Citizen science inspires kids to take local action
2023-07-28
North Carolina State University researchers recently found that a program designed to get Girl Scouts involved in citizen science – programs where members of the public can participate in real scientific research – not only taught girls about the process of science, but also motivated them to tackle scientific or environmental problems in their communities.
The findings demonstrate the impacts citizen science projects can have on their participants and offer lessons for other organizations on how to structure STEM-focused learning opportunities using citizen science.
“We’ve found that after participating ...
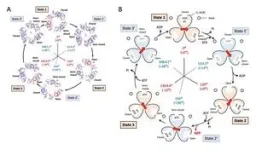
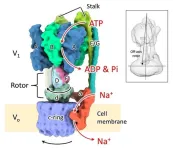
The structures of six states of a rotary sodium ion pump are revealed
2023-07-28
Six structures exhibited by the rotating sodium ion pump were reconstructed in 3D using cryo-electron microscopy. This analysis revealed that (1) the rotor exhibits non-uniform rotation behavior due to partial structural interference with the stator component, and (2) the rotor interacts with one edge of the large ion transport ring causing it to rotate. The study showed a unique molecular mechanism of the rotary sodium ion pump.
The results will be published on July 28 in Communications Biology.
“In previous single-molecule imaging ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
[Press-News.org] Total recall on HIVResearchers create total synthesis of HIV replication inhibitor