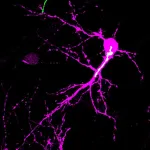
(Press-News.org) Research from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago found that direct injection of neonatal mesenchymal stem cells, derived from heart tissue discarded during surgery, reduces intestinal inflammation and promotes wound healing in a mouse model of Crohn’s disease-like ileitis, an illness marked by chronic intestinal inflammation and progressive tissue damage.
The study, published in the journal Advanced Therapeutics, offers a promising new and alternative treatment approach that avoids the pitfalls of current Crohn’s disease medications, including diminishing effectiveness, severe side effects and increased risk of gastrointestinal dysfunction.
“Neonatal cardiac-derived mesenchymal stem cells have been used in a clinical trial to repair an injured heart, but this is the first time these potent cells have been studied in an inflammatory intestinal disease model,” said senior author Arun Sharma, PhD, from Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute at Lurie Children’s who is the Director of Pediatric Urological Regenerative Medicine and Surgical Research, and Research Associate Professor of Urology and Biomedical Engineering at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and the McCormick School of Engineering, Northwestern University. “Our results are encouraging and definitely provide a new platform to potentially treat aspects of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases.”
Dr. Sharma explains that before it would be feasible to use these stem cells clinically to treat Crohn’s disease, his team needs to overcome the hurdle of how they are administered. In the current animal model study, the stem cells were injected directly into the inflammatory lesions in the small intestine, which requires surgical procedures. The next step then is to develop a safe way to inject them into the body through a vein, similar to performing a blood draw in the arm of a patient. More animal studies will be needed before this novel treatment approach can progress to clinical trials.
“Ultimately our goal is to utilize this cell type as treatment, but also as a preventive measure, before signs and symptoms of Crohn’s disease develop,” said Dr. Sharma. “We also might be able to apply this approach to other inflammatory diseases. The potential is enormous, and we are excited to move forward.”
Research at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago is conducted through Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute. The Manne Research Institute is focused on improving child health, transforming pediatric medicine and ensuring healthier futures through the relentless pursuit of knowledge. Lurie Children’s is a nonprofit organization committed to providing access to exceptional care for every child. It is ranked as one of the nation’s top children’s hospitals by U.S. News & World Report. Lurie Children’s is the pediatric training ground for Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine.
END
Neonatal stem cells from the heart could treat Crohn’s disease
Study found reduced intestinal inflammation and wound healing in a mouse model
2023-07-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
China, Indonesia, and Vietnam lead global growth for coming decade in new Harvard Growth Lab projections
2023-07-28
Cambridge, MA – China, India, Indonesia, Uganda, and Vietnam are projected to be among the fastest-growing economies for the coming decade, according to researchers at the Growth Lab at Harvard University. The new growth projections presented in The Atlas of Economic Complexity include the first detailed look at 2021 trade data, which reveal continued disruptions from the uneven economic recovery to the global pandemic. China is expected to be the fastest-growing economy per capita, although its growth rate is smaller than gains seen over the past decade.
Growth over the coming decade is projected to take off in three growth poles, East Asia, Eastern ...
Researchers tickle rats to identify part of the brain critical for laughter and playfulness
2023-07-28
To study play behaviors in animals, scientists must be able to authentically simulate play-conducive environments in the laboratory. Animals like rats are less inclined to play if they are anxious or restrained, and there is minimal data on the brain activity of rats that are free to play. After getting rats comfortable with a human playmate, tickling them under controlled conditions, then measuring the rats’ squeaks and brain activity, a research team reports on July 27 in the journal Neuron that a structure in rat brains called the periaqueductal gray is essential for play and laughter.
“We know that vocalizations such as laughter are very ...
Scientists discover secret of virgin birth, and switch on the ability in female flies
2023-07-28
Scientists have pinpointed a genetic cause for virgin birth for the first time, and once switched on the ability is passed down through generations of females.
For the first time, scientists have managed to induce virgin birth in an animal that usually reproduces sexually: the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster.
Once induced in this fruit fly, this ability is passed on through the generations: the offspring can reproduce either sexually if there are males around, or by virgin birth if there aren’t.
For most animals, reproduction is sexual - it involves a female’s egg being fertilised by a male’s sperm. ...
Uncovering how the Golgi apparatus impacts early postnatal neuron development
2023-07-28
Neurons are the cells that constitute neural circuits and use chemicals and electricity to receive and send messages that allow the body to do everything, including thinking, sensing, moving, and more. Neurons have a long fiber called an axon that sends information to the subsequent neurons. Information from axons is received by branch-like structures that fan out from the cell body, called dendrites.
Dendritic refinement is an important part of early postnatal brain development during which dendrites are tailored to make specific connections with appropriate axons. In a recently published paper, researchers present evidence showing how a mechanism within the neurons of a rodent involving ...
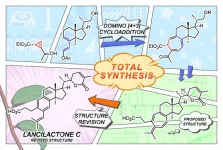
Total recall on HIV
2023-07-28
Kyoto, Japan -- Having control over how a dish is cooked is always a good idea. Taking a hint from the kitchen, scientists appear to have discovered a way to produce a true structure of the rare but naturally-occurring anti-HIV compound Lancilactone C from start to finish.
Its non-cytotoxicity in mammals could make this triterpenoid an ideal candidate for treating AIDS if its biological activity were clear -- and if only it were abundant in nature.
Now, a research group at Kyoto University has succeeded in ...
Scientists suggest AgNP/MoS2 nano-pocket for surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy scattering detection
2023-07-28
The research group of YANG Liangbao at the Institute of Health and Medical Technology, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Science (CAS) has recently developed a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERMS) method to automatically capture target molecules in AgNP/MoS2 nano-pockets, which enables highly sensitive and long-duration dynamic detection of some chemical reaction processes.
The results were published in Analytical Chemistry and selected as the front cover.
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) is a kind of molecular spectroscopy with fast, highly sensitive, ...
Solving the climate crisis requires collaboration between natural and social scientists
2023-07-28
Now that the world has experienced its hottest day in history, it is more urgent than ever for natural and social scientists to work together to address the climate crisis and keep global temperature increases below 2°C. To this end, an international group of esteemed researchers recently published an innovative research paper that highlights the importance of integrating knowledge from natural and social sciences to inform about effective climate change policies and practice. They argue that the concept of tipping points can serve as a bridge ...
A nanoprobe developed for visual quantitative detection of pesticides
2023-07-28
Recently, Prof. JIANG Changlong and his research team at the Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), developed and synthesized two highly effective ratiometric fluorescence nanoprobes. These nanoprobes, when combined with the color recognition capabilities of smartphones, enabled the visual and quantitative detection of pesticides in food and environmental water.
The research has been published in Chemical Engineering Journal and ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
Carbamate compounds ...
Retina cell breakthrough could help treat blindness
2023-07-28
Scientists have found a way to use nanotechnology to create a 3D ‘scaffold’ to grow cells from the retina –paving the way for potential new ways of treating a common cause of blindness.
Researchers, led by Professor Barbara Pierscionek from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), have been working on a way to successfully grow retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells that stay healthy and viable for up to 150 days. RPE cells sit just outside the neural part of the retina and, when damaged, can cause vision to deteriorate.
It ...
The approaches to achieve high-performance wearable sensors with hydrogels
2023-07-28
This review is written by Dr. Weixing Song from the Department of Chemistry, Capital Normal University. The paper reviewed the toughness and conductive network of existing hydrogel sensors. It emphasized the development status of various hydrogel sensors and highlighted strategies to enhance their mechanical and electrical performance. The findings are valuable for designing components and structures of high-performance wearable hydrogel sensors.
The increasing demand for healthcare IoT devices drives the development of wearable electronics. Electronic skins possess softness, stretchability, and self-healing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
[Press-News.org] Neonatal stem cells from the heart could treat Crohn’s diseaseStudy found reduced intestinal inflammation and wound healing in a mouse model