(Press-News.org) What makes a brilliant scientist? Who are the people behind the greatest discoveries of our time? Connecting art and science, photographer Herlinde Koelbl seeks the answers in this English translation of the German book Fascination of Science, an indelible collection of portraits of and interviews with sixty pioneering scientists of the twenty-first century. Koelbl's approach is intimate and accessible, and her highly personal interviews with her subjects reveal the forces (as well as the personal quirks) that motivate the scientists' work; for example, one wakes up at 3 am because her mind is calm then, another says his best ideas come to him in the shower. These glimpses into the scientists' lives and thinking add untold texture in this up-to-the-minute survey of the activities and progress that are currently taking place in the broad field of the natural sciences.
Koelbl's interview subjects include Nobel Prize winners Dan Shechtman, Frances Arnold, Carolyn Bertozzi, and cover scientific fields from astronomy, biochemistry, and quantum physics to stem-cell research and AI. Beautifully bringing together art, science, and the written word, Fascination of Science is an inspiring read that shows how creativity, obsession, persistence, and passion drive the pioneering researchers of our time.
Herlinde Koelbl is a German photographic artist, author, and documentary filmmaker. She has published more than a dozen photography books, including Jewish Portraits, Targets, and Angela Merkel Portraits 1991–2021. She has received numerous awards for her work, including the Dr. Erich Salomon Prize in 2001. You can learn more about her at www.herlindekoelbl.com.
“True to its title, this is a fascinating collection of interviews. Herlinde Koelbl's insightful questions and the candid responses of her subjects offer a matchless window into the personal histories and thinking of some of the world's most successful scientists."
-- John P. Holdren, Research Professor, Harvard University; President Obama's Science Advisor, January 2009 to January 2017
Contact: Head of UK and EU Publicity, Katie Lewis, The MIT Press, (lewisk@mit.edu)
END
Fascination of Science: 60 Encounters with Pioneering Researchers of Our Time
An intimate collection of portraits of internationally renowned scientists and Nobel Prize winners, paired with interviews and personal stories
2023-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Team identifies key driver of cancer cell death pathway that activates immune cells
2023-07-31
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Scientists have identified a protein that plays a pivotal role in the action of several emerging cancer therapies. The researchers say the discovery will likely aid efforts to fine-tune the use of immunotherapies against several challenging cancers. They report their findings in the journal Cancer Research.
“Most anticancer drugs cause cancer cells to shrivel up and die in a controlled process known as apoptosis. But apoptosis does not usually strongly activate immune cells,” said David Shapiro, a professor ...
Scrambler therapy may offer lasting relief for chronic pain, review paper suggests
2023-07-31
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
A new review paper co-authored by two Johns Hopkins pain experts suggests that scrambler therapy, a noninvasive pain treatment, can yield significant relief for approximately 80%–90% of patients with chronic pain, and it may be more effective than another noninvasive therapy: transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). The write-up was published online July 13 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Scrambler therapy, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2009, administers electrical stimulation through the skin via electrodes placed in areas of the body above and below where chronic pain is felt. The goal is to capture the nerve endings ...
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai receives $11.5 million grant renewal to study the impact of psychosocial stress on cardiovascular disease
2023-07-31
New York, NY (July 31, 2023)—Psychosocial stress profoundly affects people’s lives globally, not least because it can be a critical risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Thanks to an $11.5 million award renewal from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) of the National Institutes of Health, distinguished researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and elsewhere aim to gain a deeper understanding of how stress influences cardiovascular health.
“To address residual cardiovascular risk in patients, our research program aims to bolster our mechanistic understanding ...
Way cool: UVA professor developing ‘freeze ray’ technology for the Air Force
2023-07-31
You know that freeze-ray gun that “Batman” villain Mr. Freeze uses to “ice” his enemies? A University of Virginia professor thinks he may have figured out how to make one in real life.
The discovery – which, unexpectedly, relies on heat-generating plasma – is not meant for weaponry, however. Mechanical and aerospace engineering professor Patrick Hopkins wants to create on-demand surface cooling for electronics inside spacecraft and high-altitude jets.
“That’s the primary problem right now,” Hopkins said. “A lot of electronics on board heat up, but they have no way to cool down.”
The U.S. Air Force likes the prospect of a freeze ...
Bees likely evolved from ancient supercontinent, earlier than suspected
2023-07-31
PULLMAN, Wash. –The origin of bees is tens of millions of years older than most previous estimates, a new study shows.
A team led by Washington State University researchers traced the bee genealogy back more than 120 million years to an ancient supercontinent, Gondwana, which included today’s continents of Africa and South America.
In a study that proposes a new evolutionary history of bees, the researchers found evidence that bees originated earlier, diversified faster and spread wider than many scientists previously suspected. They published their findings in the journal Current ...
Routinely drinking alcohol may raise blood pressure even in adults without hypertension
2023-07-31
Research Highlights:
An analysis of data from seven studies involving more than 19,000 adults in the United States, Korea and Japan found a clear association between increases in systolic (top-number) blood pressure and the number of alcoholic beverages consumed daily.
Even people who drank one alcoholic beverage per day showed a link to higher blood pressure when compared to non-drinkers, reinforcing the American Heart Association’s advice to limit alcohol intake and to not start drinking alcohol if you do not already.
Embargoed until ...
This disease can be caused by a food allergy and prevent children from eating. A new study may show how to treat it
2023-07-31
A new study from Tulane University has identified a new treatment for a chronic immune system disease that can prevent children from eating.
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is triggered by food allergies or airborne allergens which causes a type of white blood cell, eosinophils, to build up in the lining of the esophagus. This causes the esophagus to shorten and the esophageal wall to thicken, making swallowing difficult and causing food to get stuck in the throat.
The disease occurs in an estimated 1 in 2,000 adults but more frequently affects children (1 in 1,500) where symptoms can be harder to diagnose and pose greater risks as difficulty feeding can lead to malnutrition, weight loss and ...
Oxycodone prescriptions after delivery not linked to longer-term opioid use compared to codeine prescriptions
2023-07-31
Postpartum prescriptions for oxycodone were not associated with increased risk of longer-term opioid use compared to codeine prescriptions, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221351.
Over the last 10 years, there has been a shift to fewer codeine prescriptions and an increase in prescriptions for stronger opioids, such as hydrocodone, hydromorphone and oxycodone for patients postpartum.
“This occurred in part ...
Novel vaccine may hold key to prevent or reduce the impact of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-07-30
Research Highlights:
A novel vaccine that targets a protein involved in Alzheimer’s disease helped eliminate toxic cells in mice with the condition.
After vaccination, the mice had fewer amyloid plaques and less inflammation in brain tissue and showed improvement in behavior and awareness.
Embargoed until 12 p.m. CT/1 p.m. ET, Sunday, July 30, 2023
BOSTON, July 30, 2023 — A novel vaccine that targets inflamed brain cells associated with Alzheimer’s disease may hold the key to potentially preventing or modifying the course of the disease, according to preliminary research presented at the American Heart Association’s Basic Cardiovascular Sciences Scientific ...
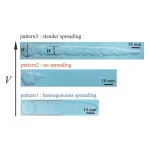
To spread or slide? Scientists uncover how foams are spread on surfaces
2023-07-29
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have uncovered the physics behind how foams are spread on surfaces. Balls of foam placed on a flat substrate were scraped across with a plate and observed. They identified different patterns which strongly depend on the scraping speed, governed by competing physical phenomena. Their findings apply to all kinds of soft materials that need to be spread evenly on surfaces, from mayonnaise on bread to insulation on walls.
Whether ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
[Press-News.org] Fascination of Science: 60 Encounters with Pioneering Researchers of Our TimeAn intimate collection of portraits of internationally renowned scientists and Nobel Prize winners, paired with interviews and personal stories