(Press-News.org) Future therapies to help people live healthy lives for longer could be developed from drugs that release tiny amounts of the gas hydrogen sulfide (H2S), new research has indicated.
A study from the University of Exeter, funded by the US Army and charity The United Mitochondrial Disease Foundation, found that targeting tiny amounts of H2S to specific areas of cells in adult worms using a H2S-releasing molecule called AP39, greatly improved health and activity as they aged. The research, published in PNAS, concludes that targeting H2S specifically to the energy-generating machinery of cells (mitochondria) could one day be used as a healthy aging therapeutic.
The research team administered AP39 to some worms from birth, and to others after reaching adulthood. They found that this compound improved the integrity of mitochondria – the “power house” of cells, which produces our cells’ energy, and kept the worms’ muscles active and moving, even well into old age, and when given mid-way through their life-course.
A number of age-related conditions are linked to loss of mitochondrial function, including natural ageing, neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s as well as muscular dystrophy and primary mitochondrial diseases.
The team also found a group of proteins that regulated how genes are expressed in ageing (transcription factors). There transcription factors were found to be specifically targeted by H2S. This insight may identify new targets for therapy in ageing and age-related conditions, particularly conditions affecting muscle.
Senior author Professor Tim Etheridge, of the University of Exeter, said: “Worms are a powerful genetic tool to study human health and disease and offer a strong platform to quickly identify new potential therapeutics. Diseases related to ageing take a huge toll on society. Our results indicate that H2S, administered to specific parts of the cell in tiny quantities, could one day be used to help people live healthier for longer
In previous research, the team had found that they could successfully target skeletal muscle with H2S in worms, and the new paper represents the first time this technique has been applied to natural ageing.
The University of Exeter has assigned the underlying technology to its spin-out MitoRx Therapeutics, which has developed next generation compounds with much better drug characteristics as potential medicines to combat diseases of ageing including neurodegenerative disorders such as Huntington’s disease as well as rare childhood conditions such as muscular dystrophy.
Co-author Professor Matt Whiteman, from the University of Exeter, said: “This study is not about extending life – it’s about living healthier lives well into older age. This could have huge benefits to society. We’re excited to see this research move to the next stages over the coming years, and hope it will one day form the basis of new treatments which we have the potential to develop with MitoRx.”
“We saw a small extension of lifespan in the worms that were targeted with H2S, and what’s unique here is that we extended healthspan – or the time they lived healthy lives. The worms still died, albeit later than normally expected, but they died very active and with young physiology.”
The paper is entitled ‘Mitochondrial sulfide promotes lifespan and healthspan through distinct mechanisms in developing versus adult treated Caenorhabditis elegans, and is published in PNAS.
END
Hydrogen sulfide shows promise as healthy ageing therapeutic when specifically targeted within cells
A study from the University of Exeter found that targeting tiny amounts of H2S to specific areas of cells in adult worms using a H2S-releasing molecule called AP39, improved health and activity as they aged
2023-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
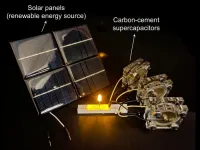
MIT engineers create an energy-storing supercapacitor from ancient materials
2023-07-31
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- Two of humanity's most ubiquitous historical materials, cement and carbon black (which resembles very fine charcoal), may form the basis for a novel, low-cost energy storage system, according to a new study. The technology could facilitate the use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and tidal power by allowing energy networks to remain stable despite fluctuations in renewable energy supply.
The two materials, the researchers found, can be combined with water to make a supercapacitor — an alternative to batteries — ...
How flies develop sight: Scientists use single-cell sequencing to identify cell types in the visual system
2023-07-31
New York University researchers have discovered new cell types in the visual system of flies, made possible by their creation of a tool that finds and labels neurons during development.
The study, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), combines single-cell sequencing data with a novel algorithm to identify pairs of genes that point to previously unknown cells in the brains of fruit flies.
Fruit flies (also known as Drosophila) have long been used as a model organism to study fundamental ...
Study reveals long-debated makeup of the molecules that help organize your cells
2023-07-31
For years, we’ve known that a special kind of molecular assembly known as a “polyelectrolyte complex” helps your cells keep themselves organized. These complexes are very good at forming interfaces to keep two liquids separated: your cells use them to create compartments. These abilities have led scientists to consider them for technological applications, including filtering water, better batteries, and even underwater glue, as well as for better pharmaceutical drugs.
But for decades, no one knew exactly ...
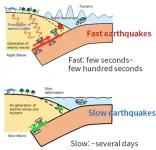
How to distinguish slow and fast earthquakes
2023-07-31
Researchers from the University of Tokyo and Stanford University show what differentiates slow and fast earthquakes and how their magnitudes vary with time.
Normally, earthquakes last up to a few minutes and radiate strong seismic waves. But around 23 years ago, scientists discovered an unusual slow-slip phenomena called slow earthquakes. Slow earthquakes last days or even months. Though they involve significant tectonic movement, you may never feel them. Since slow earthquakes could indicate future fast earthquakes, monitoring and ...
Research shows filter tip stent retrievers may allow neurointerventionalists to remove blood clots on the first try during stroke treatment
2023-07-31
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: July 31, 2023, 12:00 P.M. PDT
CONTACT: Camille Jewell
cjewell@vancomm.com or 202-248-5460
Research Shows Filter Tip Stent Retrievers May Allow Neurointerventionalists to Remove Blood Clots on the First Try During Stroke Treatment
SAN DIEGO—Research presented today at the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery’s (SNIS) 20th Annual Meeting shows that different types of stent retriever tips may result in improved patient outcomes when performing mechanical thrombectomy to treat stroke.
Ischemic stroke, one of the most common types of strokes, happens ...
Nuclear spin's impact on biological processes uncovered
2023-07-31
A research team led by Prof. Yossi Paltiel at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem with groups from HUJI, Weizmann and IST Austria new study reveals the influence of nuclear spin on biological processes. This discovery challenges long-held assumptions and opens up exciting possibilities for advancements in biotechnology and quantum biology.
Scientists have long believed that nuclear spin had no impact on biological processes. However, recent research has shown that certain isotopes behave differently due to their nuclear spin. The team focused on stable oxygen isotopes (16O, 17O, 18O) and found ...
Researchers use geospatial mapping to assist burn patients
2023-07-31
University of Texas at Dallas researchers are using geospatial mapping techniques to identify social and environmental obstacles in communities that might impede burn injury survivors’ reentry into society.
The project is designed to help patients with burn injuries better adapt to their lives after medical discharge, including improving patient access to transportation, employment, food and other necessities.
“Our study looks at how people who survive burn injuries reenter the community,” said Dr. Richard Scotch, program head of sociology and a professor of public policy and political economy in the School of ...
Diving deep: Unveiling the secrets of microalgae to cope with environmental challenges.
2023-07-31
Environmental change, such as ocean warming, alters resource competition and biodiversity. Thus, it is essential to understand how organisms respond to increased competition because changes in their size and metabolism affect the productivity of ecosystems.
Competition has long been recognized as a driving force behind rapid evolution. Still, until now, a mechanistic framework for identifying the specific traits that evolve and their trajectories has yet to be developed. Researchers at Gulbenkian and Monash University turned to metabolic theory, which explicitly predicts how competition shapes the evolution of metabolism ...
Plans to plant billions of trees threatened by massive undersupply of seedlings
2023-07-31
The REPLANT Act provides money for the US Forest Service to plant more than a billion trees in the next nine years. The World Economic Forum aims to help plant a trillion trees around the world by 2030. Many US cities have plans to shade their streets with millions of trees. Major government and private funding is being invested in planting trees as a powerful tool to fight climate change, protect water, clean air, and cool cities. In short, trees are hot.
But new research shows a troubling bottleneck that could threaten these efforts: U.S. ...
Hollings director honored as fellow of Royal College of Physicians
2023-07-31
Raymond N. DuBois, M.D., Ph.D., director of MUSC Hollings Cancer Center, has been inducted as a fellow into the Royal College of Physicians (RCP).
DuBois traveled to London, England, for the ceremony in July. He had been elected to the prestigious body prior to the COVID pandemic, which delayed the induction ceremony.
The Royal College of Physicians was established in 1518 by a royal charter from King Henry VIII. The college's founding aim was to professionalize physicians through an academic body that required a degree and an exam before ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] Hydrogen sulfide shows promise as healthy ageing therapeutic when specifically targeted within cellsA study from the University of Exeter found that targeting tiny amounts of H2S to specific areas of cells in adult worms using a H2S-releasing molecule called AP39, improved health and activity as they aged