(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Tokyo and Stanford University show what differentiates slow and fast earthquakes and how their magnitudes vary with time.
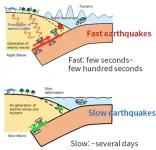
Normally, earthquakes last up to a few minutes and radiate strong seismic waves. But around 23 years ago, scientists discovered an unusual slow-slip phenomena called slow earthquakes. Slow earthquakes last days or even months. Though they involve significant tectonic movement, you may never feel them. Since slow earthquakes could indicate future fast earthquakes, monitoring and understanding them helps accurately forecast devastating earthquakes and tsunamis.
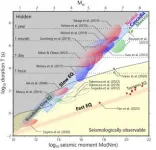
Understanding them requires knowing how they change over time. For that, researchers use scaling laws which define the relationship between two quantities over a wide interval. In 2007, researchers proposed a controversial scaling law relating the magnitude and duration of earthquakes, which can help differentiate slow and fast earthquakes.
According to the scaling law, for slow earthquakes, as its magnitude (measured by a quantity called seismic moment) increases, the duration of the earthquake increases proportionately. For fast earthquakes, the relation is not linearly but cubically proportionate, which means the seismic moment increases very rapidly in a short time.
The scaling law received criticism from other researchers and raised questions about the likelihood of events in between slow and fast earthquakes that do not fall within the law. Seismologists Satoshi Ide of the University of Tokyo and Gregory Beroza of Stanford University now bolster the scaling law with more data, reinterpret the scaling relation, and address the controversy.
“Most of the challenges to the scaling law were problematic, but we have had no chance to disprove their challenges,” says Ide. “A surprise was that totally erratic results were published in Nature, and believed by many scientists, who made further problematic numerical models.”
With the advent of new seismic detection technology and data accumulated over 16 years, Ide and Beroza now reason that most arguments against the law had improper data calculations and were inconsistent given their data constraints. They suggest the presence of a speed limit to slow earthquakes and reveal physical processes that differentiate slow and fast earthquakes.
Many, but all the same
Since slow earthquakes include phenomena with different frequency bands, they are more diverse than fast earthquakes. They were named differently, such as low-frequency earthquakes, tectonic tremors, very low-frequency earthquakes, and slow slip events. So researchers observing one type of slow earthquake considered other types irrelevant. “Our study confirmed that all these phenomena are mutually connected, or rather regarded as a single phenomenon that radiates various signals,” explains Ide.
Slow slips, but not so fast
Slow earthquakes are so subtle and inaccessible that detecting and monitoring them is challenging. Due to the detection bias, only large enough slow earthquakes are observed. That prompted Ide and Beroza to propose an upper limit to the speed of slow earthquakes. Based on that, the duo redefined the 2007 scaling law with the maximum value constraint. As they showed continuous evidence for the scaling law over a broad time scale of less than a second to more than a year, they put an end to the debate.
How are slow and fast earthquakes different?
When Ide’s group proposed the scaling law in 2007, they were unsure of what makes these two earthquake types different. Now, with more data and theoretical models, Ide and Beroza show that their scaling differences dictate physical movement processes governing the events. Diffusion processes govern slow earthquakes, whereas seismic wave propagation dictates fast earthquakes. Because of this difference, the magnitude of slow earthquakes cannot be as large as fast earthquakes when the event lasts longer.
“We pointed out that ‘diffusion’ is important in slow earthquakes, but what is physically diffusing is not well understood,” says Ide.
Experts still don't know what kind of forecast information they can provide based on slow earthquake monitoring. This study will be a foundation for building appropriate numerical models, making predictions, and taking countermeasures.
###
Useful resources for journalists:
A leaflet explaining slow and fast earthquakes:
https://www.eri.u-tokyo.ac.jp/project/sloweq/en/newsletters/pdf/leaflet_EN.pdf
About the School of Science, the University of Tokyo: https://www.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/overview/
Researcher website: http://www-solid.eps.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ide/en/
About the project: https://en.slow-to-fast-eq.org/project-overview/
Journal article: Satoshi Ide and Gregory Beroza. 2023. Slow earthquake scaling reconsidered as a boundary between distinct modes of rupture propagation. PNAS.
Expert contact:
Satoshi Ide, PhD
School of Science, The University of Tokyo
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033
Phone: +81-3-5841-4653
Email: ide@eps.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Press Office contact:
Ravindra Palavalli-Nettimi, PhD
School of Science, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033
Email: ravindra.pn@mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
@Utokyo_science
END
How to distinguish slow and fast earthquakes
New data analysis bolsters a controversial law defining the scale of slow earthquakes, allows reinterpretation, and offers a potential for forecasting fast earthquakes.
2023-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research shows filter tip stent retrievers may allow neurointerventionalists to remove blood clots on the first try during stroke treatment
2023-07-31
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: July 31, 2023, 12:00 P.M. PDT
CONTACT: Camille Jewell
cjewell@vancomm.com or 202-248-5460
Research Shows Filter Tip Stent Retrievers May Allow Neurointerventionalists to Remove Blood Clots on the First Try During Stroke Treatment
SAN DIEGO—Research presented today at the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery’s (SNIS) 20th Annual Meeting shows that different types of stent retriever tips may result in improved patient outcomes when performing mechanical thrombectomy to treat stroke.
Ischemic stroke, one of the most common types of strokes, happens ...
Nuclear spin's impact on biological processes uncovered
2023-07-31
A research team led by Prof. Yossi Paltiel at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem with groups from HUJI, Weizmann and IST Austria new study reveals the influence of nuclear spin on biological processes. This discovery challenges long-held assumptions and opens up exciting possibilities for advancements in biotechnology and quantum biology.
Scientists have long believed that nuclear spin had no impact on biological processes. However, recent research has shown that certain isotopes behave differently due to their nuclear spin. The team focused on stable oxygen isotopes (16O, 17O, 18O) and found ...
Researchers use geospatial mapping to assist burn patients
2023-07-31
University of Texas at Dallas researchers are using geospatial mapping techniques to identify social and environmental obstacles in communities that might impede burn injury survivors’ reentry into society.
The project is designed to help patients with burn injuries better adapt to their lives after medical discharge, including improving patient access to transportation, employment, food and other necessities.
“Our study looks at how people who survive burn injuries reenter the community,” said Dr. Richard Scotch, program head of sociology and a professor of public policy and political economy in the School of ...
Diving deep: Unveiling the secrets of microalgae to cope with environmental challenges.
2023-07-31
Environmental change, such as ocean warming, alters resource competition and biodiversity. Thus, it is essential to understand how organisms respond to increased competition because changes in their size and metabolism affect the productivity of ecosystems.
Competition has long been recognized as a driving force behind rapid evolution. Still, until now, a mechanistic framework for identifying the specific traits that evolve and their trajectories has yet to be developed. Researchers at Gulbenkian and Monash University turned to metabolic theory, which explicitly predicts how competition shapes the evolution of metabolism ...
Plans to plant billions of trees threatened by massive undersupply of seedlings
2023-07-31
The REPLANT Act provides money for the US Forest Service to plant more than a billion trees in the next nine years. The World Economic Forum aims to help plant a trillion trees around the world by 2030. Many US cities have plans to shade their streets with millions of trees. Major government and private funding is being invested in planting trees as a powerful tool to fight climate change, protect water, clean air, and cool cities. In short, trees are hot.
But new research shows a troubling bottleneck that could threaten these efforts: U.S. ...
Hollings director honored as fellow of Royal College of Physicians
2023-07-31
Raymond N. DuBois, M.D., Ph.D., director of MUSC Hollings Cancer Center, has been inducted as a fellow into the Royal College of Physicians (RCP).
DuBois traveled to London, England, for the ceremony in July. He had been elected to the prestigious body prior to the COVID pandemic, which delayed the induction ceremony.
The Royal College of Physicians was established in 1518 by a royal charter from King Henry VIII. The college's founding aim was to professionalize physicians through an academic body that required a degree and an exam before ...
NIH launches long COVID clinical trials through RECOVER Initiative, opening enrollment
2023-07-31
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE
Monday, July 31, 2023
Noon EDT
Contact
NIH Office of Communications and Public Liaison
NIH News Media Branch
301-496-5787
NIH launches long COVID clinical trials through RECOVER Initiative, opening enrollment
Today, the National Institutes of Health launched and is opening enrollment for phase 2 clinical trials that will evaluate at least four potential treatments for long COVID, with additional clinical trials to test at least seven more treatments expected in the coming months. Treatments ...
Johnson-Matthews receives funding for conference: VL/HCC 2023 Graduate Consortium
2023-07-31
Brittany Johnson-Matthews, Assistant Professor, Computer Science, received funding from the National Science Foundation for: "Conference: VL/HCC 2023 Graduate Consortium."
This award will support the Graduate Consortium at this year's IEEE Conference on Visual Languages and Human-Centric Computing (VL/HCC), which will be held in Washington, D.C. October 2-6, 2023.
Johnson-Matthews said, "This funding will support the ability for students across the country to come together, network, share their research, and curate advice on completing their PhD from senior members of the VL/HCC community."
VL/HCC ...
Wang conducting finite temperature simulation of non-Markovian quantum dynamics
2023-07-31
Wang Conducting Finite Temperature Simulation Of Non-Markovian Quantum Dynamics
Fei Wang, Assistant Professor, Chemistry and Biochemistry, received funding from the National Science Foundation for the project: "Finite temperature simulation of non-Markovian quantum dynamics in condensed phase using quantum computers."
For this research, Wang will develop efficient quantum algorithms to perform condensed phase quantum dynamics simulations on quantum computers.
Many important physical and chemical processes occur in the condensed phase, spanning chemical reactions in solutions, charge transfer at semiconductor interfaces, ...
Study demonstrates efficacy of new short-term resistant TB treatment
2023-07-31
(Boston) – Tuberculosis (TB) disproportionately affects vulnerable populations including those with limited economic resources, HIV patients, those whose diet is deficient in nutrients and others. Resistant TB (MDR TB) does not respond to first line medications and is difficult to treat, requiring long regimens of 15-20 months that are associated with significant side effects and poor outcomes.
Recently, new six-month regimens have been shown to have better results than the long-term treatments, with improved quality of life and health equity. But these novel regimens have not yet been adopted widely in the United States. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] How to distinguish slow and fast earthquakesNew data analysis bolsters a controversial law defining the scale of slow earthquakes, allows reinterpretation, and offers a potential for forecasting fast earthquakes.