(Press-News.org) Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that all persons planning to or who could become pregnant take a daily supplement containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid. Neural tube defects are among the most common congenital malformations in the U.S., with an estimated 3,000 pregnancies affected each year. Many of these neural tube defects are caused by low folate levels in the body. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this recommendation is a reaffirmation of its 2017 recommendation statement.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.12876)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
Note: More information about the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, its process, and its recommendations can be found on the newsroom page of its website.
# # #
Media advisory: To contact the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, email the Media Coordinator at Newsroom@USPSTF.net or call 301-951-9203.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time and all USPSTF articles remain free indefinitely https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2023.12876?guestAccessKey=a80a001a-3225-4474-bd26-3d7bc115b3f6&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=080123
END
USPSTF recommendation statement on folic acid supplementation to prevent neural tube defects
JAMA
2023-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Race and treatment outcomes in patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer
2023-08-01
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that providing fair and equal access to health care may reduce the disparities in treatment outcomes between Black and white patients with advanced prostate cancer.
Authors: Neeraj Agarwal, M.D., of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.26546)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Effect of exercise on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy among patients treated for ovarian cancer
2023-08-01
About The Study: The findings of this secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial suggest that exercise is a promising treatment for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) and incorporating exercise program referrals into the standard oncology care may reduce CIPN symptoms and increase quality of life for survivors of ovarian cancer.
Authors: Anlan Cao, M.B.B.S., of the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.26463)
Editor’s ...
City of Hope scientists develop targeted chemotherapy able to kill all solid tumors in preclinical research
2023-08-01
LOS ANGELES — Researchers at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, today published a new study explaining how they took a protein once thought to be too challenging for targeted therapy, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and developed a targeted chemotherapy that appears to annihilate all solid tumors in preclinical research. As the scientists continue to investigate the foundational mechanisms that make this cancer-stopping pill work in animal models, they note that ...
Millions of long-term smokers have lung disease that defies diagnosis
2023-08-01
Millions of Americans with tobacco-related lung disease have symptoms that do not fit any existing tobacco-related disease criteria – including the most common of those, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) – according to a new study led by researchers at UC San Francisco.
In a study publishing Aug. 1, 2023, in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), the research team found that half of the participants with extensive tobacco exposure had a persistently high level of respiratory symptoms, including shortness of breath, daily cough and ...
Research team identifies human odorant receptor for horse stable odor
2023-08-01
Para-cresol is an aromatic compound with a strong horse stable-like odor. It contributes to the off-flavor of some foods, but it is also detectable as a characteristic odorant in whiskey and tobacco, as well as in the urine of various mammals. A research team led by the Leibniz Institute of Food Systems Biology at the Technical University of Munich has now discovered which odorant receptor humans use to perceive para-cresol.
Para-cresol (4-methylphenol) is formed during the microbial degradation of certain amino acids, but also during thermal ...
A natural experiment provides evidence of link between air pollution and childhood obesity
2023-08-01
A large natural experiment in Catalonia shows that moving to areas with higher levels of air pollution is associated with weight gain in young children. The study, led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by ”la Caixa Foundation”, in collaboration with the IDIAP Jordi Gol, provides further evidence to support efforts to reduce air pollution.
Overweight and obesity in childhood result from the interaction of genes, lifestyle behaviours, physiological and social factors. Environmental exposures such as air pollution may ...
Cracking in lithium-ion batteries speeds up electric vehicle charging
2023-08-01
Aug. 1, 2023
Contact: Derek Smith, 734-546-3632, smitdere@umich.edu
Katherine McAlpine, 734-647-7087, kmca@umich.edu
Images
Cracking in lithium-ion batteries speeds up electric vehicle charging
Cracks in predominant lithium-ion electrodes shorten battery lifespans, but a neuroscience-inspired technique shows that they have an upside
ANN ARBOR—Rather than being solely detrimental, cracks in the positive electrode of lithium-ion batteries reduce battery charge time, research done at the University of Michigan shows.
This runs counter to the view of many ...
Tracking periodontal disease to improve diagnosis and treatment
2023-08-01
INDIANAPOLIS – Periodontal disease is a growing public health issue in the United States as the nation’s population ages, yet it’s underdiagnosed and undertreated. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 47 percent of adults aged 30 years and older and 79 percent of adults 65 years and older have some form of periodontal disease.
Researchers from Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Dentistry have developed computer algorithms to track periodontal disease change, which could help dentists and periodontists follow disease progression. They also have developed tools to ...
Frank J. Malina Astronautics Medal awarded to Klaus Schilling
2023-08-01
The International Astronautical Federation (IAF) selected Würzburg space expert Professor Klaus Schilling for the Frank J. Malina Astronautics Medal 2023. This medal is a top award in the space sector for innovative research and for commitment to education.
According to a statement by the IAF, the medal is awarded each year to a personality who has provided outstanding services to space education and research. This applies to Professor Schilling without reservation: "He has provided numerous students with practical experience in satellite construction and has been involved in a wide ...
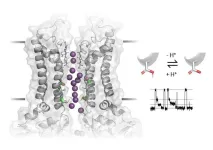
New study sheds light on the gating mechanism of ion channels
2023-08-01
Ion channels play a crucial role in many cellular processes, including neuronal communication, muscle contraction or cell proliferation. Most multi subunit ion channels exist in two functional states, either closed or open. During gating, one should expect that all subunits undergo conformational changes. The absence of intermediate conduction levels is surprising and asks for an explanation. A team of researchers from the University of Vienna and the Washington University in St. Louis created a smart model system to answer this important question. The study is currently published in Nature ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] USPSTF recommendation statement on folic acid supplementation to prevent neural tube defectsJAMA