(Press-News.org) In 2022, a team of researchers at Baylor College of Medicine discovered that a little-known enzyme called MAPK4 is involved in the growth of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) and its resistance to certain therapies. Looking into the details of this novel role of MAPK4, the researchers have now identified a strategy that can potentially control MAPK4-promoted growth in TNBC and other cancers. The study, published in PLOS Biology, opens new options for treating this devastating disease.
“Some cancers depend on MAPK4 for their growth, and our team studies cellular processes or pathways that participate in MAPK4-induced cancer growth,” said corresponding author Dr. Feng Yang, associate professor of pathology and immunology and of molecular and cellular biology. He also is a member of the Dan L Duncan Comprehensive Cancer Center at Baylor.
Yang and his team knew that in some TNBC cases, MAPK4 activates an enzyme called AKT, which promotes cancer growth. They also knew that in the same cells, another enzyme called PDK1 can also promote cancer growth by activating both AKT and a series of other enzymes of the AGC group. This PDK1-mediated activation of AGC enzymes mostly depends on the amount of PDK1 in the cell.
In this study the team discovered that MAPK4 and PDK1 are not so independent in their tumor-promoting actions after all, and this led to a novel idea on how to treat these cancers. Working with TNBC cells in the lab, the researchers found that, besides directly activating AKT, MAPK4 also enhances the production of PDK1in cells, which in turn promotes tumor growth.
“We found that MAPK4 can activate both AKT and PDK1, which then work together enhancing cancer growth and resistance to therapy,” Yang said. “Eliminating MAPK4 in cells in the lab inhibited both of its actions on AKT and PDK1 and reduced tumor growth.”
However, there are no drugs that specifically block MAPK4 that could be tested to reduce tumor growth. Instead, Yang and his colleagues explored an alternative approach. “We showed that blocking both AKT and PDK1 effectively repressed MAPK4-induced cancer cell growth, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy to treat MAPK4-dependent cancers, such as a subset of TNBC, prostate and lung cancer.”
“In this study we have not only advanced our understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying the tumor-promoting activity of MAPK4, we also have found a potential novel therapeutic approach for human cancers,” Yang said.
Other contributors to this work include Dong Han, Wei Wang, Julie Heejin Jeon, Tao Shen, Xiangsheng Huang and Bingning Dong, all at Baylor, and Ping Yi at the University of Houston.
This research was supported by grants from the Department of Defense Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs (W81XWH-17-1-0043), the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (RP130651 and RP200439) and the National Institutes of Health (1R01CA276341 and postdoctoral training grant T32CA203690).
###
END
A novel strategy to suppress triple negative breast cancer growth
2023-08-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Super Radar: Breakthrough radar research overcomes a nearly century-old trade-off between wavelength and distance resolution
2023-08-02
New interference radar functions employed by a team of researchers from Chapman University and other institutions improve the distance resolution between objects using radar waves. The results may have important ramifications in military, construction, archaeology, mineralogy and many other domains of radar applications.
This first proof-of-principle experiment opens a new area of research with many possible applications that can be disruptive to the multi-billion dollar radar industry. There are many new avenues to pursue both in theory and experiment.
The ...
Study finds Black people less likely to be seen at memory clinic than white people
2023-08-02
MINNEAPOLIS – Black people and people living in less affluent neighborhoods—areas with higher poverty levels and fewer educational and employment opportunities— may be less likely to be seen at a memory care clinic compared to white people and people living in neighborhoods with fewer disadvantages, according to new research published in the August 2, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Our results are concerning, especially ...
Bullying, suicidal thoughts linked to more frequent headaches in teens
2023-08-02
MINNEAPOLIS – Teens who have been bullied by their peers, or who have considered or attempted suicide, may be more likely to have more frequent headaches than teens who have not experienced any of these problems, according to a study published in the August 2, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that bullying or thoughts of suicide cause headaches; it only shows an association.
“Headaches are a common problem for teenagers, but our study looked beyond the biological factors to also consider the psychological and social factors that are associated with headaches,” ...
Study defines disparities in memory care
2023-08-02
Patients who live in less affluent neighborhoods and those from underrepresented racial or ethnic groups are less likely than others to receive specialized care for dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, a new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates. Further, the research shows that Black people are more likely than white people to be diagnosed with dementia at a later, more advanced stage, which could contribute to inequities in access to new treatments.
The study appears Aug. 2 in the journal Neurology.
New medications ...
New analysis shows surgery is safe and effective for people with unruptured brain arteriovenous malformation
2023-08-02
CONTACT: Camille Jewell
cjewell@vancomm.com or 202-248-5460
SAN DIEGO—Contrary to the results of a seminal study in the field, a recent analysis presented today at the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery’s (SNIS) 20th Annual Meeting indicates that surgical approaches (embolization, microsurgery, radiosurgery) for treating selected patients with unruptured arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is safe and effective.
AVMs are tangled blood vessels with abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary ...
Researchers develop smartphone app that reliably recognizes physical signs of stroke
2023-08-02
CONTACT: Camille Jewell
cjewell@vancomm.com or 202-248-5460
SAN DIEGO—Today at the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery’s (SNIS) 20th Annual Meeting, researchers discussed a smartphone app created that reliably recognizes patients’ physical signs of stroke with the power of machine learning.
In the study, “Smartphone-Enabled Machine Learning Algorithms for Autonomous Stroke Detection,” researchers from the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine and multiple medical institutions in Bulgaria used data from 240 patients with stroke at four metropolitan stroke centers. Within 72 hours of the ...
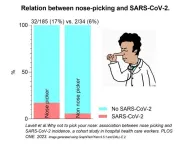
Nose-picking healthcare workers were more likely to catch COVID-19 during the pandemic than their colleagues who refrained, per Netherlands cohort study
2023-08-02
Nose-picking healthcare workers were more likely to catch COVID-19 during the pandemic than their colleagues who refrained, per Netherlands cohort study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0288352
Article Title: Why not to pick your nose: Association between nose picking and SARS-CoV-2 incidence, a cohort study in hospital health care workers
Author Countries: The Netherlands
Funding: This work was funded by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development ZonMw (S3 study, grant agreement no. 10430022010023 to M.K.B.) and the Corona ...
Half of popular TikTok videos about Baby Boomers portray older adults negatively, risking reinforcing stereotypes and creating intergenerational conflict
2023-08-02
Half of popular TikTok videos about Baby Boomers portray older adults negatively, risking reinforcing stereotypes and creating intergenerational conflict
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0285987
Article Title: Videos about older adults on TikTok
Author Countries: Singapore
Funding: We gratefully acknowledge the support of the Social Science Research Council SSHR Fellowship (MOE2018-SSHR-004). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to ...
Extreme climates may have driven Middle Pleistocene hominins towards (positive) assortative mating and evolution of bigger brains, according to economic model of climate change impacts
2023-08-02
Extreme climates may have driven Middle Pleistocene hominins towards (positive) assortative mating and evolution of bigger brains, according to economic model of climate change impacts
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287964
Article Title: An economic model and evidence of the evolution of human intelligence in the Middle Pleistocene: Climate change and assortative mating
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The author received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Interest in bird feeding surged in over 100 countries worldwide during the COVID-19 lockdowns
2023-08-02
Interest in local bird feeding appears to have ramped up in countries all over the world during the pandemic lockdowns, even in countries not historically noted for bird feeding practices, according to a study published August 2, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Jacqueline Doremus from California Polytechnic State University and Liqing Li from Texas A&M University College Station, US, and Darryl Jones from Griffith University, Australia.
Feeding wild birds is a popular nature-based pastime because of its simplicity, low cost, and accessibility in even urban environments. ...