(Press-News.org) University of Tennessee Extension and GAP Connections recently received a grant from the Southern Extension Risk Management Education Center to launch a series of workshops across the state to help agricultural producers and agribusinesses navigate the intricacies of labor management.
Tennessee’s labor-intensive farming operations are increasingly in need of agricultural labor options, creating challenges for agricultural employers that have transitioned from readily available family labor to scarce hired labor that must be sourced and managed in compliance with complex laws.
UT Extension and GAP Connections developed this workshop series to help address these issues, as well as explain best practices for managing labor and maintaining compliance, helping workshop attendees make better informed decisions for their operations.
Workshop topics include sourcing options and associated costs, agricultural laws and regulations, and practices that guide agricultural employers to move beyond compliance to implementation of best practices for recordkeeping, communication, training, housing and more.
“Ultimately, our goal is to improve the economic sustainability of labor-intensive agricultural enterprises in Tennessee by reducing the risk associated with the ability to attract, secure and retain agricultural labor,” said project co-director Margarita Velandia, professor and interim department head in UT’s Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics.
Workshop locations include Jonesborough on November 2, Clarksville on November 14, and Murfreesboro on November 16. To learn more and register for the free workshop series, visit gapconnections.com/what-we-do/labor-management or contact Margarita Velandia at mvelandi@utk.edu.
This work is supported by USDA’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture under award number 2021-70027-34722.
Through its land-grant mission of research, teaching and extension, the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture touches lives and provides Real. Life. Solutions. utia.tennessee.edu.
END
UT extension to help Tennessee farmers navigate labor management
Three workshops to be held across the state
2023-08-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
More girls started puberty early during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-08-03
WASHINGTON—The number of girls diagnosed with precocious puberty increased during the COVID-19 pandemic due to potential risk factors such as increased screen time and less physical activity, according to a new study published in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
The number of girls referred to pediatric endocrinologists for precocious puberty has increased significantly over the last two years, potentially due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Precocious puberty is when children's bodies begin to change into adult bodies too soon. They start to develop physical changes before the age of 8 such as breasts ...
It’s 2023, and coming out is, well, complicated
2023-08-03
In an era of unprecedented LGBTQ2+ visibility coupled with incredible backlash, coming out as a sexual minority can be a deeply ambivalent experience, according to new research.
In a study published in Theory and Society, sociologists Dr. Amin Ghaziani and Andy Holmes conducted in-depth interviews with 52 adult Vancouverites about their experiences coming out over the last five years.
We spoke to Dr. Ghaziani (he/him), professor in the UBC department of sociology and Canada Research Chair in Urban Sexualities, about the findings.
Why were you interested in recent experiences of coming out?
Coming out is about sharing your identity with someone, and it’s an ongoing ...
Enhanced tumor modeling using Laponite bioinks for 3D bioprinting
2023-08-03
(LOS ANGELES) – August 3, 2023 - Scientists from the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) have developed a nanoengineered bioink with improved bonding and cross-linking capabilities for 3D bioprinting of tumor models. A key component of this bioink is Laponite, highly charged, disk-shaped, crystalline nanoparticles. As explained in their recent paper in Biofabrication, these nanoparticles were shown to enhance the biological signaling that occurs in the tumor microenvironment ...
Sharing on Facebook reveals 2 very different news environments
2023-08-03
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A first-of-its-kind study examined 2.2 million news stories shared on Facebook and found that publishers create two very different news environments.
These distinct ecosystems involve low-credibility publishers – those that publish what is sometimes referred to as fake news – versus high-credibility publishers.
Findings showed that while these two types of publishers often pushed out bursts of coverage at the same time – a common feature of news coverage – they were often about different topics, said Kelly Garrett, senior author of the study and professor of communication at The Ohio State University.
“These ...
The Access to Advanced Health Institute receives $18 million award to develop a temperature stable, single-dose chikungunya RNA vaccine through a phase 1 clinical trial
2023-08-03
The Access to Advanced Health Institute Receives $18 Million Award to Develop a Temperature Stable, Single-Dose Chikungunya RNA Vaccine Through a Phase 1 Clinical Trial
KEY POINTS:
The goal of the award is to develop an effective chikungunya vaccine candidate that can reach endemic areas of the world by using AAHI’s innovative RNA platform technology.
The project will demonstrate that classic large-scale manufacturing challenges of live-attenuated vaccines can be overcome by using standard manufacturing equipment and techniques that are easy to tech transfer and scale.
The award supports a first-in-human clinical trial of a dried (lyophilized) ...
A path to defeating crop-killing gray mold without toxic chemicals
2023-08-03
It’s a mold that causes billions in crop losses every year, infecting berries, tomatoes and most other fruits and vegetables. Now, researchers have found a way to defeat the mold without showering toxic chemicals on the crops.
If you’ve ever seen a fuzzy gray strawberry, you’ve seen gray mold. It affects more than 1,400 different plant species, and there is no real cure for it. Being able to control it may hinge on the discovery of lipid “bubbles” secreted by the ...
Disparities in Black adults’ stroke risk factors persist; risk factor control reduced gap
2023-08-03
Research Highlights:
In a retrospective analysis of stroke patients, Black adults who had a stroke due to a severe blockage of a major artery in the brain (intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis) were younger, had higher rates of high blood pressure and Type 2 diabetes, and had lower physical activity scores compared to non-Black adults.
After one year of aggressive, individualized medical management, including lifestyle coaching and regular follow-up care, diastolic blood pressure and physical activity scores improved among Black adults.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET, Thursday, Aug. 3, 2023
DALLAS, Aug. 3, 2023 — Significant stroke risk factor disparities ...
Ear today, gone tomorrow? A new discovery in a cause of inner-ear bone loss
2023-08-03
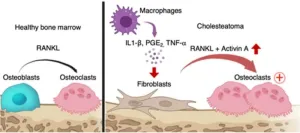
Osaka, Japan – Chronic inflammation of the middle ear can cause several problems and complications that can affect a person’s hearing and balance. One such problem is the formation of a cholesteatoma, which is an abnormal collection of cells in the ear that can cause bone erosion if left untreated. In turn, this can cause symptoms such as hearing loss, dizziness, facial paralysis, and even a brain infection.
In a study published recently in Nature Communications, researchers from Osaka University have revealed the cause of cholesteatomas, which may help in developing new therapies for patients who are suffering ...
TENS machine provides cheaper and non-invasive treatment for sleep apnoea
2023-08-03
A machine commonly used for pain relief has shown to improve breathing in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea, a clinical trial has found.
Results of the TESLA trial, published today in eClinical Medicine by researchers from King’s College London and Guy’s & St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, shows the potential of a new therapeutic option for patients using a transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS) machine.
Sleep apnoea affects about 1 billion people worldwide, and millions in the UK. The condition can be frequently associated with snoring; ...
Better coaching to promote a person’s growth
2023-08-03
CLEVELAND—What if there was a more effective way to coach and inspire your employees? Athletes? Students? Even your kids?
A new study by a team of researchers from Case Western Reserve University suggests there is.
Their newly published work used neuroimaging to peer into the brains of participants as they responded to two different styles of coaching. The researchers wanted to see what happens in the brain that either helps people grow or causes them to resist change.
“You could say it’s about how we get around the problem that you can lead a horse to water, but you can't make it drink,” said Anthony “Tony” ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brainwaves of mothers and children synchronize when playing together – even in an acquired language
A holiday to better recovery
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
Cost of copper must rise double to meet basic copper needs
A gel for wounds that won’t heal
Iron, carbon, and the art of toxic cleanup
Organic soil amendments work together to help sandy soils hold water longer, study finds
Hidden carbon in mangrove soils may play a larger role in climate regulation than previously thought
Weight-loss wonder pills prompt scrutiny of key ingredient
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
Combining AI with OCT shows potential for detecting lipid-rich plaques in coronary arteries
SeaCast revolutionizes Mediterranean Sea forecasting with AI-powered speed and accuracy
JMIR Publications’ JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology invites submissions on Bridging Data, AI, and Innovation to Transform Health
Honey bees navigate more precisely than previously thought
Air pollution may directly contribute to Alzheimer’s disease
Study finds early imaging after pediatric UTIs may do more harm than good
UC San Diego Health joins national research for maternal-fetal care
New biomarker predicts chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer
Treatment algorithms featured in Brain Trauma Foundation’s update of guidelines for care of patients with penetrating traumatic brain injury
Over 40% of musicians experience tinnitus; hearing loss and hyperacusis also significantly elevated
Artificial intelligence predicts colorectal cancer risk in ulcerative colitis patients
Mayo Clinic installs first magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia system for cancer research in the US
[Press-News.org] UT extension to help Tennessee farmers navigate labor managementThree workshops to be held across the state