(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON —On a hot summer day, white clothing feels cooler than other colors due to reflecting—not absorbing—sunlight. Other colors like blue or black, will undergo a heating effect as they absorb light. To circumvent this heating effect in colored cooling films, researchers drew inspiration from nanostructures in butterfly wings.
The new films, which don’t absorb any light, could be used on the outside of buildings, vehicles and equipment to reduce the energy needed for cooling while preserving vivid color properties.
“In buildings, large amounts of energy are used for cooling and ventilation, and running the air conditioner in electric cars can reduce the driving range by more than half,” said research team leader Wanlin Wang from Shenzhen University in China. “Our cooling films could help advance energy sustainability and carbon neutrality.”
In Optica, Optica Publishing Group’s journal for high-impact research, the researchers show that the films they developed lower the temperature of colorful objects to about 2 °C below the ambient temperature. They also found that when left outside all day, the blue version of the films was approximately 26℃ cooler than traditional blue car paint. This represents an annual energy savings of approximately 1377 MJ/m2 per year.
“With our new films, excellent cooling performance can be achieved, no matter the desired color, saturation or brightness,” said Wang. “They could even be used on textiles to create clothes of any color that are comfortable in hot temperatures.”
Inspired by nature
A car with blue paint appears blue because it absorbs yellow light and reflects blue light. The large amount of light that is absorbed heats the car. Morpho butterflies, however, produce their highly saturated blue color based on the nanostructure of their wings. The design of the cooling nanofilm mimics these structures to produce vibrant colors that don’t absorb light like traditional paint.
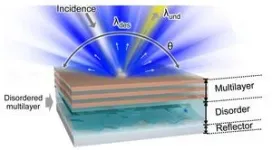
To create their Morpho-inspired nanofilms, the researchers placed a disordered material (rough frosted glass) under a multilayer material made of titanium dioxide and aluminum dioxide. They then placed this structure on a silver layer that reflects all light, thus preventing the absorption of solar radiation and the heating associated with that absorption.
The film’s color is determined by how components within its multilayered structure reflect light. To create blue, for example, the multilayer material is designed to reflect yellow light in a very narrow range of angles while the disordered structure diffuses the blue light across a broad area.
Although this type of passive photonic thermal management has been accomplished before, it has only been used with white or clear objects because it is difficult to maintain a wide viewing angle and high color saturation.
Passive cooling of colorful objects
“Thanks to the layered structure we developed, we were able to extend the passive cooling method from colorless objects to colorful ones while preserving color performance,” said Wang. “In other words, our blue film looks blue across a large range of viewing angles and doesn’t heat up because it reflects all the light. In addition, high saturation and brightness can be achieved by optimizing the structure.”
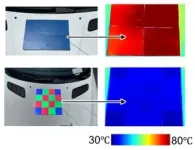
To test the new technology, the researchers created blue, yellow and colorless films, which they placed outdoors at Shenzhen University, on surfaces such as roofs, cars, cloth and cell phones, from 9 a.m. to 4 p.m. in both winter and summer. Using thermocouple sensors and infrared cameras to measure temperature, they found that the cooling films were more than about 15 ℃ cooler than the surfaces they were placed on in the winter and about 35 ℃ cooler in the summer.
The researchers point out that replacing the silver film with an aluminum film would make the films less expensive and manufacturable by a scalable fabrication method such as electron beam evaporation and magnetron sputtering. Now that they have demonstrated the cooling and color performance of the films, the researchers plan to study and optimize other properties such as mechanical and chemical robustness.
Paper: W. Wang, H. Xing, X. Shu, X. Zhao, X. Yan, B. Hong, L. Sun, W. Zhang, G. P. Wang, “Cooling colors below the ambient temperature 10, 8 (2023).
DOI: doi.org/10.1364/OPTICA.487561.
About Optica
Optica is an open-access journal dedicated to the rapid dissemination of high-impact peer-reviewed research across the entire spectrum of optics and photonics. Published monthly by Optica Publishing Group, the Journal provides a forum for pioneering research to be swiftly accessed by the international community, whether that research is theoretical or experimental, fundamental or applied. Optica maintains a distinguished editorial board of more than 60 associate editors from around the world and is overseen by Editor-in-Chief Prem Kumar, Northwestern University, USA. For more information, visit Optica.
About Optica Publishing Group (formerly OSA)
Optica Publishing Group is a division of Optica (formerly OSA), Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide. It publishes the largest collection of peer-reviewed content in optics and photonics, including 18 prestigious journals, the society’s flagship member magazine, and papers from more than 835 conferences, including 6,500+ associated videos. With over 400,000 journal articles, conference papers and videos to search, discover and access, Optica Publishing Group represents the full range of research in the field from around the globe.
END
Butterfly-inspired films create vibrant colors while passively cooling objects
New nanofilms could significantly reduce the energy needed for cooling buildings or vehicles
2023-08-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MIT Press's Direct to Open (D2O) achieves second year goal, opens access to 82 new books in 2023
2023-08-03
Thanks to the support of libraries participating in Direct to Open (D2O), the MIT Press will publish its full list (see below) of 2023 scholarly monographs and edited collections open access on the MIT Press Direct platform.
Launched in 2021, D2O is a sustainable framework that harnesses the collective power of libraries to support open and equitable access to vital, leading scholarship. D2O moves scholarly books from a solely market-based, purchase model, where individuals and libraries buy ...
CMS Innovation Center new care, payment model influenced by Eskenazi Health, Regenstrief Institute, IU School of Medicine
2023-08-03
INDIANAPOLIS -- A team including Eskenazi Health, Indiana University School of Medicine and Regenstrief Institute has helped guide a new dementia care and payment model announced by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Innovation Center.
Guiding an Improved Dementia Experience (GUIDE) is the first model established by the Innovation Center that directly addresses the needs of unpaid caregivers, usually family, of individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementia. The model will provide a comprehensive ...
Scientists warn about decoupling warming trend when detecting marine heat waves
2023-08-03
The climate crisis is severely affecting marine ecosystems around the world and the Mediterranean is not an exception. Marine heat waves associated with this crisis are causing massive mortality events throughout the basin. Given this scenario, their correct definition and characterization become a key element in defining possible future scenarios.
Now, a new study by the Institut de Ciències del Mar (ICM-CSIC) and the Institute of Marine Sciences of the National Research Council (CNR-ISMAR) has revealed how decoupling global warming trends affects the definition of marine heat waves characteristics. ...
On-off switch for enzymes
2023-08-03
Light affects living organisms in many different ways: for example, plants orient their growth direction towards the sun, while circadian rhythms in humans are controlled by daylight. These processes always involve photoreceptors, which are proteins that can sense different colours and intensities of light.
10,000-fold increase in enzymatic activity
Now, researchers at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) have deciphered the function of a highly efficient photoreceptor. Their findings have been published in the journal Science Advances. The research ...
New-generation geostationary satellite reveals widespread midday depression in dryland photosynthesis during 2020 western US heatwave
2023-08-03
The western U.S., particularly the Southwest, has experienced a notable increase in record-breaking high temperatures over recent decades, with recurring drought and heatwaves. These conditions have resulted in severe consequences for both human and nature systems, including dire water shortages, rampant wildfires, substantial agricultural losses, and increased human mortality. These regions, dominated by water-limited ecosystems, face exacerbated water stress due to more frequent and protracted droughts and heatwaves, which can profoundly impair ecosystem ...
Nanorings: New building blocks for chemistry
2023-08-03
Sandwich complexes were developed about 70 years ago and have a sandwich-like structure. Two flat aromatic organic rings (the “slices of bread”) are filled with a single, central metal atom in between. Like the slices of bread, both rings are arranged in parallel. Adding further layers of ‘bread’ and ‘filling’ produces triple or multiple sandwiches. “These compounds are among the most important complexes used in modern organometallic chemistry,” says Professor Peter ...
Rural environment supports children’s immune systems
2023-08-03
Children raised in rural environments who spend a lot of time outdoors with some exposure to animals grow to have better regulated immune systems than children living in urban environments, a new study has found.
Research led by APC Microbiome Ireland (APC), a world-leading SFI research centre and University College Cork (UCC), has shown that early life immune development is highly dependent on a child’s living environment and lifestyle factors. Researchers say that the immune system needs to learn how not to over-respond ...
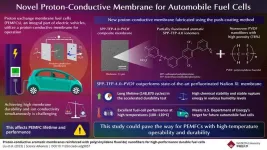
Novel proton-conductive membranes for automobile fuel cells
2023-08-03
Fuel cells are compact energy conversion units that utilize clean energy sources like hydrogen and convert them into electricity through a series of oxidation–reduction reactions. Specifically, proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs), an integral part of electric vehicles, utilize proton-conductive membranes for operation. Unfortunately, these membranes suffer from a trade-off between high durability and high ion conductivity, affecting the lifetime and performance of PEMFCs.
To overcome this issue, scientists ...
UT extension to help Tennessee farmers navigate labor management
2023-08-03
University of Tennessee Extension and GAP Connections recently received a grant from the Southern Extension Risk Management Education Center to launch a series of workshops across the state to help agricultural producers and agribusinesses navigate the intricacies of labor management.
Tennessee’s labor-intensive farming operations are increasingly in need of agricultural labor options, creating challenges for agricultural employers that have transitioned from readily available family labor to scarce hired labor that ...
More girls started puberty early during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-08-03
WASHINGTON—The number of girls diagnosed with precocious puberty increased during the COVID-19 pandemic due to potential risk factors such as increased screen time and less physical activity, according to a new study published in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
The number of girls referred to pediatric endocrinologists for precocious puberty has increased significantly over the last two years, potentially due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Precocious puberty is when children's bodies begin to change into adult bodies too soon. They start to develop physical changes before the age of 8 such as breasts ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists discover “bacterial constipation,” a new disease caused by gut-drying bacteria
DGIST identifies “magic blueprint” for converting carbon dioxide into resources through atom-level catalyst design
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
[Press-News.org] Butterfly-inspired films create vibrant colors while passively cooling objectsNew nanofilms could significantly reduce the energy needed for cooling buildings or vehicles