(Press-News.org) NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has recorded breath-taking new images of the iconic Ring Nebula, also known as Messier 57.
The images, released today by an international team of astronomers led by Professor Mike Barlow (UCL, UK) and Dr Nick Cox (ACRI-ST, France), with Professor Albert Zijlstra of The University of Manchester, showcase the nebula's intricate and ethereal beauty in unprecedented detail, providing scientists and the public with a mesmerizing view of this celestial wonder.
For many sky enthusiasts, the Ring Nebula is a well-known object that is visible all summer long and is located in the constellation Lyra.
A small telescope will already reveal the characteristic donut-like structure of glowing gas that gave the Ring Nebula its name.
The Ring Nebula is a planetary nebula - objects that are the colourful remnants of dying stars that have thrown out much of their mass at the end of their lives.
Its distinct structure and its vibrant colours have long captivated the human imagination and the stunning new images captured by the JWST offer an unparalleled opportunity to study and understand the complex processes that shaped this cosmic masterpiece.
Albert Zijlstra, Professor in Astrophysics at the University of Manchester, said: “We are amazed by the details in the images, better than we have ever seen before. We always knew planetary nebulae were pretty. What we see now is spectacular.”
Dr Mike Barlow, the lead scientist of the JWST Ring Nebula Project, added: "The James Webb Space Telescope has provided us with an extraordinary view of the Ring Nebula that we've never seen before. The high-resolution images not only showcase the intricate details of the nebula's expanding shell but also reveal the inner region around the central white dwarf in exquisite clarity. We are witnessing the final chapters of a star's life, a preview of the Sun’s distant future so to speak, and JWST's observations have opened a new window into understanding these awe-inspiring cosmic events. We can use the Ring Nebula as our laboratory to study how planetary nebulae form and evolve." The Ring Nebula's mesmerizing features are a testament to the stellar life cycle.
Approximately 2,600 lightyears away from Earth, the nebula was born from a dying star that expelled its outer layers into space. What makes these nebulae truly breath-taking is their variety of shapes and patterns, that often include delicate, glowing rings, expanding bubbles or intricate, wispy clouds.
These patterns are the consequence of the complex interplay of different physical processes that are not well understood yet. Light from the hot central star now illuminates these layers.
Just like fireworks, different chemical elements in the nebula emit light of specific colours. This then results in exquisite and colourful objects, and furthermore allows astronomers to study the chemical evolution of these objects in detail.
Dr Cox, the co-lead scientist, said: "These images hold more than just aesthetic appeal; they provide a wealth of scientific insights into the processes of stellar evolution. By studying the Ring Nebula with JWST, we hope to gain a deeper understanding of the life cycles of stars and the elements they release into the cosmos.”
The international research team analysing these images is composed of researchers from the UK, France, Canada, USA, Sweden, Spain, Brazil, Ireland and Belgium.
They say that JWST/MIRI images of the Ring Nebula are coming soon.
END
James Webb Space Telescope captures stunning images of the Ring Nebula
2023-08-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wellcome Sanger Institute: Skin cancer-related mutations higher in the UK than Singapore
2023-08-03
SKIN CANCER-RELATED MUTATIONS HIGHER IN THE UK THAN SINGAPORE
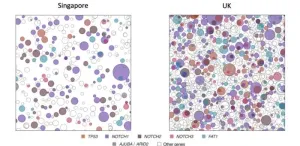
A new study has shown how, on average, people in the UK have facial skin that is far more DNA damaged from the sun than people in Singapore, explaining the far higher risk of developing the most common skin cancers in the UK.
This study looked at keratinocyte cancers - basal and squamous cell carcinomas - rather than melanoma, a rarer and sometimes fatal form of skin cancer, finding Northern European skin types in the UK were less able to protect themselves from UV damage.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and their collaborators at ...
Researchers release action plan to boost diversity in postgraduate science students
2023-08-03
UK researchers are calling on higher education institutes and research funders to adopt a new set of recommended actions to address the substantial under-representation of PhD students from ethnic minority backgrounds.
Black, Asian and minority ethnic students have a markedly lower representation in postgraduate research compared with undergraduate or taught postgraduate study in the UK. For instance, in 2020/21, around 26.5% of UK undergraduates were from ethnic minority backgrounds, compared with around 19% for postgraduate students.
The ...
New photocatalytic system converts carbon dioxide to valuable fuel more efficiently than natural photosynthesis
2023-08-03
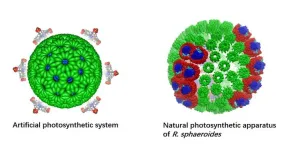
A joint research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) and collaborators recently developed a stable artificial photocatalytic system that is more efficient than natural photosynthesis. The new system mimics a natural chloroplast to convert carbon dioxide in water into methane, a valuable fuel, very efficiently using light. This is a promising discovery, which could contribute to the goal of carbon neutrality.
Photosynthesis is the process by which chloroplasts in plants and some organisms use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to create food or energy. In past decades, many scientists have tried to develop artificial photosynthesis processes to turn ...
Association of pregnancy-specific alcohol policies with infant morbidities and maltreatment
2023-08-03
About The Study: In this study of 1.4 million birthing person–infant pairs in the U.S., most pregnancy-specific alcohol policies were not associated with decreased odds of infant injuries or morbidities. Policy makers should not assume that pregnancy-specific alcohol policies improve infant health.
Authors: Sarah C. M. Roberts, Dr.P.H., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.27138)
Editor’s ...
Nottingham Trent University chooses Digital Science to measure social impact of research
2023-08-03
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that Nottingham Trent University has chosen Altmetric Explorer from Digital Science’s flagship products to improve the measurement and reporting of social media and alternative metrics.
Nottingham Trent University (NTU) has signed a deal to utilise Altmetric to report on societal impact and dissemination of research.
Using Digital Science’s products and tools, NTU will be able to support its research strategy, impact development, dissemination ...
Seven entrepreneurs join Innovation Crossroads seventh cohort
2023-08-03
Seven entrepreneurs will embark on a two-year fellowship as the seventh cohort of Innovation Crossroads kicks off this month at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Representing a range of transformative energy technologies, Cohort 7 is a diverse class of innovators with promising new companies.
New to Innovation Crossroads’ sponsorship this year are DOE’s Office of Electricity and Office of Science Advanced Scientific Computing Research program, which join DOE’s Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies Office, DOE’s Building Technologies Office, and the Tennessee ...
After 7 years, generative AI succeeds in predicting clinical trial outcomes
2023-08-03
Highlights:
Since its inception in 2014, Insilico Medicine has developed multiple AI models for predicting the probability of success of clinical trials focusing on Phase II to Phase III transition probabilities.
To validate the models, it pursued three strategies - retrospective, quasi-prospective, and prospective validation.
In 2016, it deposited on a preprint server the first date-stamped article with the predictions of clinical trials.
The publication titled “Prediction of clinical trials outcomes based on target choice and clinical trial design with multi‐modal artificial intelligence” ...
Study highlights importance of mineral iron in ocean ecosystems
2023-08-03
New research published today in Nature has revealed the importance of mineral forms of iron in regulating the cycling of this bio-essential nutrient in the ocean.
The findings pave the way for new work on the relationship between the iron and carbon cycles and how changing ocean oxygen levels may interact.
The study, led by the University of Liverpool and involving collaborators in the United States, Australia and France, addresses a knowledge gap in ocean research.
Principal Investigator Professor Alessandro Tagliabue said: “To date we have not fully appreciated ...
NUS study: A patchwork of Wnt signalling ligands and receptors pattern the colours on the wings of butterflies
2023-08-03
Wnt signalling is a well-known mode of cell-to-cell communication in multicellular biological organisms. It involves the secretion of small Wnt glycoproteins, by signalling cells, that bind to receptor proteins in the membrane of receiving cells. This signal modifies proteins on the inside of these receiving cells to make cells grow, divide or differentiate. This mode of communication is fundamental in both normal and altered cellular development, such as in cancer and wound healing, and has remained in the limelight ...
University of Ottawa research team finds window into mechanisms of rare disease
2023-08-03
A University of Ottawa-led research team has published rigorous new research that advances a quest to understand a puzzling – and heartbreaking – ultra-rare disease that’s found almost exclusively in boys.
XLP-2 is a genetic X-linked lymphoproliferative disease first described in 2006. It typically has severe complications among patients who become infected with the Epstein-Barr virus, an exceedingly common virus that infects most people without problems in their teenage years or young adulthood. But when the few individuals with XLP-2 encounter the Epstein-Barr virus the experience is often fatal ...