(Press-News.org) Between 7% and 15% of people in North America, between 5% and 9% of people in Europe, and between 1% and 5% of people in Asia suffer from kidney stones. Common symptoms are severe pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, and bloody urine. But kidney stones don’t just reduce the quality of life: in the long run, they may lead to infections, swollen kidneys (hydronephrosis), renal insufficiency, and end-stage renal disease. Known risk factors for developing kidney stones include being an adult male, obesity, chronic diarrhea, dehydration, and having inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, or gout.
Now, a study in Frontiers in Nutrition has shown for the first time that an elevated consumption of added sugars should probably be added to the list of risk factors for kidney stones. Added sugars occur in many processed foods, but are especially abundant in sugar-sweetened sodas, fruit drinks, candy, ice cream, cakes, and cookies.
“Ours is the first study to report an association between added sugar consumption and kidney stones,” said lead author Dr Shan Yin, a researcher at the Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China. “It suggests that limiting added sugar intake may help to prevent the formation of kidney stones.”
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yin et al. analyzed epidemiological data on 28,303 adult women and men, collected between 2007 to 2018 within the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Participants self-reported if they had a history of kidney stones. Each participant’s daily intake of added sugars was estimated from their recall of their most recent consumption of food and drinks, given twice: once in a face-to-face interview, and once in a telephone interview between three and 10 days later. For example, participants were asked if they had eaten syrups, honey, dextrose, fructose, or pure sugar during the past 24 hours.
Each participants also received a healthy eating index score (HEI-2015), which summarizes their diet in terms of the adequacy of beneficial diet components such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and moderation of potentially harmful foods, for example refined grains, sodium, and saturated fats.
The researchers adjusted the odds of developing kidney stones per year during the trial for a range of explanatory factors. These included gender, age, race or ethnicity, relative income, BMI, HEI-2015 score, smoking status, and whether the participants had a history of diabetes.
At the start of the study, participants with a higher intake of added sugar tended to have a higher current prevalence of kidney stones, a lower HEI score, and a lower education level. The overall mean intake of added sugars was 272.1 calories per day, which corresponds to 13.2% of the total daily energy intake.
Positive association between added sugars and kidney stones
The researchers showed that after adjusting for these factors, the percentage of energy intake from added sugars was positively and consistently correlated with kidney stones. For example, participants whose intake of added sugars was among the 25% highest in the population had 39% greater odds of developing kidney stones over the course of the study.
Similarly, participants who derived more than 25% of their total energy from added sugars had a 88% greater odds than those who derived less than 5% of their total energy from added sugars.
The results also indicated that participants from ‘Other’ ethnicities – for example Native American or Asian people – had higher odds of developing kidney stones when exposed to greater-than-average amounts of added sugars than Mexican American, other Hispanic, non-Hispanic White, and non-Hispanic Black people. People with a greater Poverty-Income Ratio (PIR; ie, the ratio between their income and the federal poverty level) had greater odds of developing kidney stones when exposed to more added sugars than people at or slightly above poverty level.
Possibility of confounders
The mechanisms of the relation between consuming more added sugars and a greater risk of developing kidney stones is not yet known. Because this was an uncontrolled observational trial, it can’t yet be ruled out that unknown confounding factors might drive this association.
“Further studies are needed to explore the association between added sugar and various diseases or pathological conditions in detail,” cautioned Yin. “For example, what types of kidney stones are most associated with added sugar intake? How much should we reduce our consumption of added sugars to lower the risk of kidney stone formation? Nevertheless, our findings already offer valuable insights for decision-makers.”
END
Consuming added sugars may increase risk of kidney stones
Researchers have shown for the first time that a greater intake of added sugars is associated with a greater risk of kidney stones
2023-08-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tropical plant native to China reveals antiobesity potential
2023-08-04
Obesity, a major risk factor for various lifestyle diseases such as diabetes and hypertension has become widespread worldwide, inherently demanding innovative solutions to combat it.
A multi-institutional research group led by Associate Professor Akiko Kojima of the Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology at Osaka Metropolitan University, has made significant progress in the fight against obesity. The group had previously conducted a study on the effects of the extract of Mallotus furetianus (MFE), a tropical plant native to Hainan Island, China, on the prevention of fatty liver, but the antiobesity effects of MFE and its mechanisms had not been ...
Parasites of viruses drive superbug evolution
2023-08-04
In a study published today in Cell, one of the most prominent peer-reviewed scientific journals in the field of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, scientists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) and Imperial College London have discovered a new way by which bacteria transmit their genes, enabling them to evolve much faster than previously understood. Led by Assistant Professor John Chen from the Department of Microbiology and Immunology and the Infectious Diseases Translational Research Programme at the NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine (NUS Medicine), ...
Geomagnetic field protects Earth from electron showers
2023-08-04
Understanding the ionosphere high in the Earth's atmosphere is important due to its effects on communications systems, satellites and crucial chemical features including the ozone layer. New insights into the activity of high energy electrons have come from a simulation study led by geophysicist Yuto Katoh at Tohoku University, reported in the journal Earth, Planets and Space.
"Our results clarify the unexpected role of the geomagnetic field surrounding the Earth in protecting the atmosphere from high energy electrons," says Katoh.
The ionosphere is a wide region between roughly ...
Displaying the design of DNA
2023-08-04
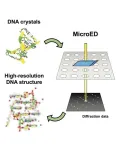
Function and form are deeply intertwined in biology. Knowing how organisms grow, adapt and reproduce requires understanding their physical structures. Hence the transformative power of the microscope across the past four centuries of science.
Microscopy, or the field of microscope use, can now reveal the tiniest of structures through techniques such as microcrystal electron diffraction, or MicroED. Instead of passing light through a cell like an optical microscope, MicroED bombards crystalline samples with a stream of electrons to produce detailed information about their atomic configuration.
“The method was developed ...
Unveiling a new mechanism that accelerates aging of adipose tissues
2023-08-04
Korean researchers have unveiled a novel signaling pathway that fosters aging-related chronic metabolic disorders.
A research team led by Professor Jong Kyoung Kim from the Department of Life Sciences at POSTECH along with Professor Seung-Hoi Koo from the Division of Life Sciences at Korea University and principal researcher Geum-Sook Hwang from Korea Basic Science Institute (KBSI) announced the discovery of a new mechanism where BCAA metabolic pathway becomes impaired due to aging, resulting in dysfunctions of adipose cells and chronic metabolic disorders. The research findings were published in Nature Aging (IF=16.6) ...
Diagnosing pediatric Crohn disease with radiomic and clinical data
2023-08-04
Leesburg, VA, August 4, 2023—An accepted manuscript published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) found that deploying a radiomic-based model with T2-weighted MRI data could increase diagnostic accuracy for pediatric Crohn disease (CD).
Noting that ileal-wall radiomic features were strongly predictive of CD—and that model performance improved when ensembled with clinical data—“a radiomic machine learning model predicted CD diagnosis with better performance than two of three expert radiologists,” wrote corresponding author and AJR Pediatric Imaging Section Editor Jonathan R. Dillman, MD, MSc.
Dillman et al.’s manuscript ...
Childhood trauma may heighten subsequent risk of pregnancy complications
2023-08-04
Childhood trauma, such as abuse, emotional neglect, and exposure to domestic violence, may heighten a woman’s subsequent risk of pregnancy complications, and of giving birth to a low birthweight or premature baby, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
The risks of pregnancy related diabetes, high blood pressure, depression/anxiety and of giving birth to underweight and or premature babies may all be significantly higher, the analysis suggests.
While previously ...
Peppermint oil aromatherapy may ease pain severity after heart surgery
2023-08-04
The use of essential peppermint oil aromatherapy may ease pain severity after open heart surgery and enhance sleep quality as well, suggest the results of a small comparative clinical trial, published online in the journal BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care.
Heart surgery is a major procedure, necessitating the separation of the breastbone (sternum) as well as mechanical breathing support, both of which are associated with a high risk of severe pain, stress, and sleeplessness, note the researchers.
Effective pain relief allows patients to recover more quickly and may reduce the risk of postoperative complications, ...
Mortality gap exists in 3,110 counties, 5 racial-ethnic groups, 19 causes, 20 years
2023-08-04
SEATTLE, Wash. August 3, 2023 – An analysis of 19 causes of death in the United States revealed persistent disparities and a familiar pattern across five racial-ethnic groups and 3,110 counties from 2000 to 2019. That’s according to the most comprehensive peer-reviewed research published today in The Lancet.
The mortality rates among American Indian or Alaska Native (AIAN) and Black populations were substantially higher than among White populations nationally and in most counties. For example, mortality was higher among the AIAN population than the White population in nearly all counties for skin and ...
Walking 25 mins/day enough to counter physical impact of bedrest on older hospital patients
2023-08-04
As little as 25 minutes a day of slow walking seems to be enough to counter the detrimental physical effects of bedrest on older hospital patients, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
And for optimal improvements in physical function, around 50 mins/day of slow walking or around 40 mins of combined physical activities, such as 20 mins of resistance bands with around 20 mins of aerobic activity, are the most effective, the analysis indicates.
But there may be a threshold effect, with no clear benefit for ‘doses’ of more than 90 mins/day ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
[Press-News.org] Consuming added sugars may increase risk of kidney stonesResearchers have shown for the first time that a greater intake of added sugars is associated with a greater risk of kidney stones