Overlooked CO2 emissions induced by air pollution control devices in China's coal-fired power plants
2023-08-08
(Press-News.org)
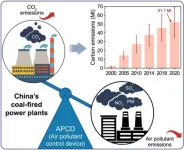
To combat this issue, China has implemented various environmental regulations, including the widespread use of air pollution control devices (APCDs) in CFPPs. While APCDs have successfully reduced air pollutants, their electricity consumption has led to indirect carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. The extent of these CO2 emissions has remained uncertain, prompting researchers to delve deeper into this overlooked environmental concern.
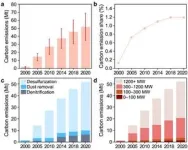
In a new study published in Volume 17 of the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers from Shandong University conducted a study revealing that the proportion of APCD CO2 emissions in total emissions from CFPPs surged from 0.12% in 2000 to 1.19% in 2020. Notably, desulfurization devices were the primary contributors, accounting for approximately 80% of APCD CO2 emissions in 2020, followed by dust removal and denitration devices. The researchers also projected future APCD CO2 emissions under different scenarios, highlighting the significant impact of CFPPs' lifespan on emissions. They identified Nei Mongol, Shanxi, and Shandong provinces as potential hotspots for high emissions due to large-scale newly built CFPPs. To tackle this emerging environmental issue, the researchers proposed various measures, including enhancing APCD energy efficiency and providing low-carbon electricity through photovoltaic power or biomass co-firing with coal. They emphasized the need for comprehensive environmental impact assessments to ensure that policies aimed at reducing air pollutants do not inadvertently increase CO2 emissions. Furthermore, the study's analysis framework offers valuable insights for other emission-intensive sectors, such as steel production and waste incineration.
Highlights
CO2 emissions induced by air pollution control devices are quantified.
A plant-level CO2 emission inventory is compiled.
Future emissions under diverse climate targets are simulated.
Hotspots of future emissions are identified.
The study's findings have emphasized the importance of adopting integrated strategies to balance the reduction of both air pollutants and carbon emissions. The findings are expected to inform policymakers, industry stakeholders, and environmentalists alike, paving the way for more informed and holistic approaches to addressing China's environmental challenges.
###
References
Funding information
The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFC3105304),
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (72348001),
The National Social Science Fund of China (22&ZD108).
DOI
10.1016/j.ese.2023.100295
About Environmental Science and Ecotechnology
Environmental Science and Ecotechnology (ISSN 2666-4984) is an international, peer-reviewed, and open-access journal published by Elsevier. The journal publishes significant views and research across the full spectrum of ecology and environmental sciences, such as climate change, sustainability, biodiversity conservation, environment & health, green catalysis/processing for pollution control, and AI-driven environmental engineering. The latest impact factor of ESE is 12.6, according to the Journal Citation ReportTM 2022.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-08
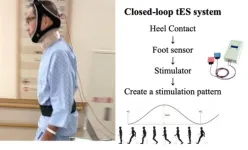
Gait-related disturbances adversely affect the quality of life of patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), a condition affecting millions worldwide. Although various pharmacological, surgical, and rehabilitative treatments exist, their effectiveness is limited. Now, a team of researchers from Japan has successfully addressed this limitation. Using a novel neuromodulation approach that incorporates gait-combined closed-loop transcranial electrical stimulation, the team demonstrated significant gait improvements in patients with various neurological disorders including PD.
Parkinson’s disease ...
2023-08-08
Pollinosis, or hay fever, makes people miserable around the world, and Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) pollen is a significant cause of the suffering in the 38.8% of Japanese people who are allergic. Japanese cedar is also the country's most important timber species. A single mature tree produces on the order of three hundred million grains of pollen. Saneyoshi Ueno and colleagues investigated the genes required to produce this massive amount of genetic material. Previous research by Ueno’s team identified ...
2023-08-08
SAN ANTONIO — August 8, 2023 – Southwest Research Institute is launching its new Engine for Automatic Biomechanical Evaluation (ENABLE™) markerless biomechanics system during the American Society of Biomechanics (ABS) Annual Conference, August 8-11, in Knoxville, Tennessee. ABS attendees can see a demonstration by visiting Booth No. 11.
ENABLE is a user-friendly markerless motion capture system that leverages artificial intelligence, computer vision algorithms and biomechanical modeling. The key advantage of ENABLE is it efficiently captures ...
2023-08-08
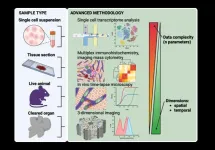
This review manuscript highlights the relevance of spatially-resolved macrophage phenotyping in liver disease-related research.
The liver is a vital organ heavily populated with macrophages, which represent key players of the innate immune response but also hold key functions in the maintenance of a healthy organ. Liver macrophages are mostly distributed across two populations of different origins and functions during homeostasis and disease: liver resident macrophages (referred to as Kupffer cells, KCs), and monocytic macrophages derived from the bone-marrow (MoMFs). The KC: MoMF ratio, as well as their respective spatial distribution through the liver, are increasingly ...
2023-08-08
A study looks at the mechanisms behind genetic variation in the bacteria that cause Lyme disease. Lyme disease is the most common vector-transmitted disease in the United States, with around 476,000 human cases annually. Most Lyme disease is caused by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb), which is transmitted by ticks and can infect a wide range of mammals and birds. Matthew Combs and colleagues analyzed the genetic diversity of Bb, specifically focusing on the pathogen’s outer surface protein C (ospC) gene, a well-known virulence factor that is essential for survival of the pathogen inside the tick and the early stages of infection in vertebrates. ...
2023-08-08
***Embargo 14:00 UK / 10:00 BRT / 9:00 ET / 6:00 PT Tuesday, August 8, 2023***
SEATTLE, Wash. August 8, 2023 – 569,000 deaths were linked to bacterial antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in all 35 countries of the WHO Region of the Americas, according to a new peer-reviewed paper published in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas. This analysis on the burden of AMR in the Americas is the most comprehensive yet for the region, providing data for 35 countries, 23 bacterial pathogens, and 88 pathogen-drug combinations.
The ...
2023-08-08
Humans are social creatures and learn from each other, even from a young age. Infants keenly observe their parents, siblings or caregivers. They watch, imitate and replay what they see to learn skills and behaviors.
The way babies learn and explore their surroundings inspired researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and Meta to develop a new way to teach robots how to simultaneously learn multiple skills and leverage them to tackle unseen, everyday tasks. The researchers set out to develop a robotic AI agent with manipulation abilities equivalent to a 3-year-old child.
The team has announced RoboAgent, an artificial intelligence agent that leverages passive observations and active ...
2023-08-08
Every year in the United States, about 1.7 million youth run away from home, which places them at risk for sex trafficking and prostitution. Sadly, most youth tend to fall victim to sex trafficking between the ages of 12 to 14.
While federal and state laws have been enacted to protect these runaway youth, they continue to be arrested, charged and detained for prostitution. Detaining youth who should not legally be considered offenders and who have extensive histories of victimization and mental health issues only exacerbates their underlying vulnerabilities that may have led them to run away or be sexually exploited in the first place.
There is ...
2023-08-08
Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical stage generative artificial intelligence (AI) drug discovery company, has announced that it is now a member of the Chamber of Commerce of Metropolitan Montreal, demonstrating its commitment to the vibrant business community of Montreal and to fostering economic growth in the region. Insilico will officially launch its AI R&D Center in Montreal later this fall.
As a new member of the Chamber of Commerce of Metropolitan Montreal, Insilico brings its innovative expertise ...
2023-08-08
NEW YORK, August 8, 2023 — CUNY ASRC researcher Adam Braunschweig’s lab is part of a newly awarded $20 million center from the U.S. National Science Foundation to understand the atomic-scale mysteries of "crushing" chemistry. The multi-institutional award will establish the Center for the Mechanical Control of Chemistry (CMCC), which will conduct work to understand how the mechanical application of force can enable new advances in chemistry and make industrial processes cheaper and more environmentally friendly.
“I’m excited that my lab is playing a part in research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Overlooked CO2 emissions induced by air pollution control devices in China's coal-fired power plants