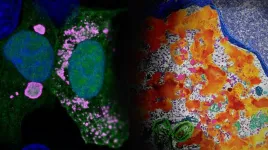
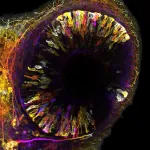
Carpets retain a stubborn grip on pollutants from tobacco smoke
Study finds ozone generators are only partially effective at cleaning
2023-08-09
(Press-News.org)
– By Christina Nunez
In rooms where smoking has taken place regularly, tobacco's imprint lingers on indoor surfaces, even long after regular smoking has stopped. The leftover residues, known as thirdhand smoke, can be a long-term source of indoor pollutants. New research from a team led by the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) zeroes in on carpets as an especially potent – and difficult to clean – reservoir of tobacco contaminants.
When thirdhand smoke settles into surfaces, it doesn't stay there. Chemicals re-enter the air, sometimes transforming into new types of contaminants. Carpet is a major sink for thirdhand smoke. In this study, the researchers evaluated the effects of ozonation, a common cleaning method, on smoke-exposed carpet.
The study, which was recently published in the journal Environmental Science and Technology, examined smoke-contaminated aged carpets that had been retrieved from homes in the San Diego area, as well as new carpet exposed to fresh smoke in the lab.
The team found that while ozonation partially removed a group of compounds named polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from both aged and fresh carpet samples, it was relatively ineffective at removing deeply embedded nicotine, because the fibers and other chemical constituents in the material serve as a chemical shield. They evaluated the samples in a room-size environmental chamber at Berkeley Lab’s Air Quality Testing Laboratory, with additional tests carried out at the Molecular Foundry, a DOE Office of Science user facility at Berkeley Lab.
The research, which was supported by grants from the University of California Tobacco-Related Disease Research Program, highlights carpets as a common and important reservoir and source of contaminants from thirdhand smoke.
"Because it does not reach deeply into materials, ozone has a limited ability to 'clean' permanently," said Berkeley Lab researcher Xiaochen Tang, the study’s lead author. "In the case of carpet, the best solution may be replacing it with a new one."
The work builds on a previous study from Berkeley Lab’s Indoor Environment Group, which found that ozonation could remove tobacco contaminants from a room. In that 2021 study, the ozonation was conducted only on freshly generated thirdhand smoke.
Ozone generators release ozone gas so that it can react with harmful compounds and remove them from the air and from surfaces. But the generator also creates a burst of contaminants when running, the previous study showed, pointing to the need for ventilation and a waiting period before people can re-enter a space after ozonation.
Berkeley Lab Senior Scientist Hugo Destaillats noted that ozonation has been used as a remediation method for years because it is good at removing odors – but that can create a false sense of efficacy.
"Ozone generators are also used to remediate fire damage and mold, but they have limitations, as we saw in this study," Destaillats said. "The lack of a detectable smell does not mean that all of the contaminants we are concerned about have been eliminated." Next steps in this research will evaluate the role of other indoor reservoirs, such as drywall and upholstery.
###
Founded in 1931 on the belief that the biggest scientific challenges are best addressed by teams, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and its scientists have been recognized with 16 Nobel Prizes. Today, Berkeley Lab researchers develop sustainable energy and environmental solutions, create useful new materials, advance the frontiers of computing, and probe the mysteries of life, matter, and the universe. Scientists from around the world rely on the Lab’s facilities for their own discovery science. Berkeley Lab is a multiprogram national laboratory, managed by the University of California for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-09
A telecommunications fiber optic cable deployed offshore of Oliktok Point, Alaska recorded ambient seismic noise that can be used to finely track the formation and retreat of sea ice in the area, researchers report in The Seismic Record.
Andres Felipe Peña Castro of the University of New Mexico and colleagues used distributed acoustic sensing, or DAS, to identify seismic signals related to the motion of waves on open water and the sea ice that suppresses that wave action. The technique offers a way to track sea ice with increasing spatial and temporal resolution—on the scale of hours and kilometers--compared to satellite images that are updated ...
2023-08-09
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Whether it’s work or play that prevents us from getting enough shut-eye during the week, assuming we can make up for it by sleeping in over the weekend is a mistake. New research led by Penn State reveals that cardiovascular health measures, including heart rate and blood pressure, worsen over the course of the week when sleep is restricted to five hours per night, and attempting to catch up on sleep over the weekend is insufficient to return these measures to normal.
“Only 65% of adults in the U.S. regularly sleep the recommended seven hours per night, ...
2023-08-09
LA JOLLA, CA—New research in the journal Nature Communications gives scientists an important window into how Ebola virus replicates inside host cells. The study, led by scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI), reveals the inner workings of "viral factories," clusters of viral proteins and genomes that form in host cells.
The research team, which included experts from Scripps Research and UC San Diego School of Medicine, found that Ebola virus's replication machinery forms fascinating microscopic ...
2023-08-09
Simple home workouts using exercise apps can effectively reduce depressive symptoms in healthcare workers and could be a major tool to combat the global mental health crisis in the sector, says new University of British Columbia research.
The study, published today in JAMA Psychiatry, divided participants into either a waitlisted control group or an exercise group who were given free access to a suite of home exercise apps called DownDog, that included yoga, cardio and strength training. They were asked to aim for at least 80 minutes of moderate-intensity ...
2023-08-09
New research suggests that the Horn of Africa is likely to become even drier, not wetter in the future as predicted by most climate models.
‘Wet gets wetter, dry gets drier’. That mantra has been used for decennia to predict how global warming will affect the hydrological cycle in different world regions. But if climate models predict that much of tropical Africa will enjoy a future with wetter weather, then why does it keep getting drier in certain parts of the African tropics, like the Horn of Africa? An international team of researchers ...
2023-08-09
First study to measure resilience in biomedical scientists during the pandemic
Sixty-one percent of study participants said they experienced a setback during pandemic
‘You can be as resilient as you want, but certain structural factors can hinder your professional advancement’
CHICAGO --- When COVID-19 presented the world with the greatest health challenge in modern history, it was biomedical scientists who stepped up to develop diagnostic testing and vaccines to slow the spread of the disease.
But how did these in-demand scientists fare psychologically and in their careers amid pandemic pressures such as juggling ...
2023-08-09
Brigham researchers are working on a new approach to target autoimmunity in the brain leverages designer bacteria to make treatment safer and more effective
Researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, have designed a probiotic to suppress autoimmunity in the brain, which occurs when the immune system attacks the cells of the central nervous system. Autoimmunity in the brain is at the core of several diseases, including multiple sclerosis. In a new study, researchers demonstrated the treatment’s potential using preclinical models of these diseases, finding that the technique offered a more precise ...
2023-08-09
To function properly, organs require a precise number of cells and a functional architecture, which are established during embryogenesis. Embryos are proficient multitaskers; they grow, and acquire shape and functional architecture all at once. Despite a lot of research on embryo development, scientists do not yetfully grasp how embryos orchestrate all these different tasks in space and time to ensure the formation of healthy organs. This was ...
2023-08-09
The rare moss Takakia has adapted over millions of years to a life at high altitudes. An international research team led by Prof. Dr. Ralf Reski from the University of Freiburg and Prof. Dr. Yikun He from the Capital Normal University / China has now discovered exactly how it has developed the ability to survive frost and life-threatening high UV radiation. In the renowned journal Cell, they describe the genetic traits that protect the moss from extreme environmental conditions. At the same time, they document how climate change greatly altered the natural habitat of this highly specialized species within just a few years.
The ...
2023-08-09
A Kaiser Permanente study provides new information that may help oncologists answer one of the most common questions they hear from breast cancer survivors: Is it safe to drink alcohol?
The new study, published August 9 in Cancer, is the largest prospective study to look at short-term alcohol use after breast cancer. The findings suggest drinking alcohol is not associated with an increased risk of breast cancer recurrence or dying from the disease.
“We know that women who drink alcohol are at increased ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Carpets retain a stubborn grip on pollutants from tobacco smoke
Study finds ozone generators are only partially effective at cleaning