(Press-News.org) Each year, more than 200 million people fall sick with malaria and more than half a million of these infections lead to death. The World Health Organization recommends parasite-based diagnosis before starting treatment for the disease caused by Plasmodium parasites. There are various diagnostic methods, including conventional light microscopy, rapid diagnostic tests and PCR.
The standard for malaria diagnosis, however, remains manual light microscopy, during which a specialist examines blood films with a microscope to confirm the presence of malaria parasites. Yet, the accuracy of the results depends critically on the skills of the microscopist and can be hampered by fatigue caused by excessive workloads of the professionals doing the testing.
Now, writing in Frontiers in Malaria, an international team of researchers has assessed whether a fully automated system, combining AI detection software and an automated microscope, can diagnose malaria with clinically useful accuracy.
“At an 88% diagnostic accuracy rate relative to microscopists, the AI system identified malaria parasites almost, though not quite, as well as experts,” said Dr Roxanne Rees-Channer, a researcher at The Hospital for Tropical Diseases at UCLH in the UK, where the study was performed. “This level of performance in a clinical setting is a major achievement for AI algorithms targeting malaria. It indicates that the system can indeed be a clinically useful tool for malaria diagnosis in appropriate settings.”
AI delivers accurate diagnosis
The researchers sampled more than 1,200 blood samples of travelers who had returned to the UK from malaria-endemic countries. The study tested the accuracy of the AI and automated microscope system in a true clinical setting under ideal conditions.
They evaluated samples using both manual light microscopy and the AI-microscope system. By hand, 113 samples were diagnosed as malaria parasite positive, whereas the AI-system correctly identified 99 samples as positive, which corresponds to an 88% accuracy rate.
“AI for medicine often posts rosy preliminary results on internal datasets, but then falls flat in real clinical settings. This study independently assessed whether the AI system could succeed in a true clinical use case,” said Rees-Channer, who is also the lead author of the study.
Automated vs manual
The fully automated malaria diagnostic system the researchers put to the test includes hard- as well as software. An automated microscopy platform scans blood films and malaria detection algorithms process the image to detect parasites and the quantity present.
Automated malaria diagnosis has several potential benefits, the scientists pointed out. “Even expert microscopists can become fatigued and make mistakes, especially under a heavy workload,” Rees-Channer explained. “Automated diagnosis of malaria using AI could reduce this burden for microscopists and thus increase the feasible patient load.” Furthermore, these systems deliver reproducible results and can be widely deployed, the scientists wrote.
Despite the 88% accuracy rate, the automated system also falsely identified 122 samples as positive, which can lead to patients receiving unnecessary anti-malarial drugs. “The AI software is still not as accurate as an expert microscopist. This study represents a promising datapoint rather than a decisive proof of fitness,” Rees-Channer concluded.
END
New high-tech microscope using AI successfully detects malaria in returning travelers
Researchers have tested the accuracy of an automated microscope combined with AI software to identify malaria parasites in blood samples – an additional diagnostic approach to disease detection
2023-08-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
HKUST researchers pioneers technique to self-assemble high-performance biomolecular films
2023-08-10
A research team led by The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has developed a novel technique to self-assemble a thin layer of amino acids with ordered orientation over a large area that demonstrates high piezoelectric strength, making the manufacturing of biocompatible and biodegradable medical microdevices, such as pacemaker and implantable biosensor, in the near future possible.
The generation of bioelectricity from the piezoelectric effect – reversible conversion between mechanical and electrical energies – has physiological significance in living systems. ...
A platform for integrated spectrometers based on solution-processable semiconductors
2023-08-10
Acquiring real-time spectral information in point-of-care diagnosis, internet-of-thing, and other lab-on-chip applications require spectrometers with hetero-integration capability and miniaturized feature. Compared to conventional semiconductors integrated by heteroepitaxy, solution-processable semiconductors provide a much-flexible integration platform due to their solution-processability, and, therefore, more suitable for the multi-material integrated system. However, solution-processable semiconductors are usually incompatible with the micro-fabrication processes, making them far from practical use in various lab-on-chip applications.
In a new paper published ...
Researchers develop novel technology to quantify protein critical to blood clot formation through breath gas analysis
2023-08-10
Immunothrombosis, or the formation of microscopic blood clots during inflammation, is a major cause of morbidity among patients with sepsis or severe COVID-19. A key enzyme in this process is thrombin. To date, no method exists for early detection of immunothrombosis in a living organism.
A team of investigators led by Ali Hafezi-Moghadam, MD, PhD, director of the Molecular Biomarkers Nano-Imaging Laboratory (MBNI) at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of Mass General Brigham healthcare system, and an associate professor of Radiology at Harvard Medical School, developed a novel technology to diagnose immunothrombosis by measuring ...
C-Path welcomes Sanofi to its Type 1 Diabetes Consortium to help advance drug development
2023-08-10
TUCSON, Ariz., August 9, 2023 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) announced today that Sanofi, a global leader in immunology and diabetes care, has joined its Type 1 Diabetes Consortium (T1DC). Sanofi joins T1DC as part of its commitment to push the boundaries of innovation to improve the lives of those with diabetes.
T1DC was established in 2017 with the goal to significantly advance the drug development landscape for T1D prevention and treatment. The consortium achieves this by fostering ...
How sure is sure? Incorporating human error into machine learning
2023-08-10
Researchers are developing a way to incorporate one of the most human of characteristics – uncertainty – into machine learning systems.
Human error and uncertainty are concepts that many artificial intelligence systems fail to grasp, particularly in systems where a human provides feedback to a machine learning model. Many of these systems are programmed to assume that humans are always certain and correct, but real-world decision-making includes occasional mistakes and uncertainty.
Researchers from the University of Cambridge, along with The Alan Turing Institute, Princeton, and Google DeepMind, have been attempting ...
Large study suggests people with low levels of vitamin K have less healthy lungs
2023-08-10
People with low levels of vitamin K in their blood are more likely to have poor lung function and to say they suffer with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and wheezing, according to a study published today (Thursday) in ERJ Open Research [1].
Vitamin K is found in leafy green vegetables, vegetable oils and cereal grains. It plays a role in blood clotting, and so helps the body to heal wounds, but researchers know very little about its role in lung health.
Researchers say their new findings do not alter the current advice on vitamin K intake, but they do support further research to ...
Sanford Burnham Prebys Cancer Center earns merit extension from NCI
2023-08-10
Sanford Burnham Prebys’ Cancer Center has received a rare and prestigious Merit Extension Award from the National Cancer Institute (NCI), recognizing and rewarding its earlier accomplishments as well as current research plans. The award extends the center’s current 5-year Cancer Center Support Grant (CCSG) for an additional two years.
There are only seven Basic Laboratory Cancer Centers in the NCI’s national network. These centers focus primarily on laboratory research: developing, conducting, translating and advancing fundamental discoveries to clinical testing and, ultimately, ...
Stem cell therapy rescues symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-08-09
In the ongoing search for a cure for Alzheimer’s disease, a burgeoning branch of medicine is bringing new hope. Stem cell therapies are already being used to treat various cancers and disorders of the blood and immune system. In a new proof-of-concept study, scientists at University of California San Diego show stem cell transplants may also be a promising therapeutic against Alzheimer’s.
In the study, publishing this month in Cell Reports, the researchers demonstrate that transplanting hematopoietic ...
Penn Medicine neuroscientists identify brain mechanism that drives focus despite distractions
2023-08-09
PHILADELPHIA—Trying to finish your homework while the big game is on TV? “Visual-movement” neurons in the front of your brain can help you stay focused, according to a new study from neuroscientists in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
In the study, published recently in Neuron, the scientists sought to illuminate the neural mechanism that helps the brain decide whether to focus visual attention on a rewarding task or an alluring distraction. By analyzing neuron activity in animal models as they faced this kind of attentional ...
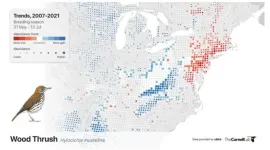
Novel machine-learning method produces detailed population trend maps for 550 bird species
2023-08-09
Scientists at the Cornell Lab of Ornithology have developed a novel way to model whether the populations of more than 500 bird species are increasing or decreasing. The method solves a nagging statistical problem by accounting for year-to-year changes in the behavior of people collecting the data. The result is detailed trend maps for each species down to an eight-mile radius--a major boost for local conservation efforts. Scientists used an approach called Double Machine Learning. Details are published in the journal Methods in Ecology and Evolution.
“Changing human behavior presents a problem for statistical analysis ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Enzymes work as Maxwell's demon by using memory stored as motion
Methane’s missing emissions: The underestimated impact of small sources
Beating cancer by eating cancer
How sleep disruption impairs social memory: Oxytocin circuits reveal mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
[Press-News.org] New high-tech microscope using AI successfully detects malaria in returning travelersResearchers have tested the accuracy of an automated microscope combined with AI software to identify malaria parasites in blood samples – an additional diagnostic approach to disease detection