(Press-News.org) Paleoclimate evidence shows that around 1.1 million years ago, the southern European climate cooled significantly and likely caused an extinction of early humans on the continent, according to a new study led by UCL researchers.
Published in the journal Science, the team of researchers discovered the occurrence of previously unknown extreme glacial conditions around 1.1 million years ago. The glacial cooling pushed the European climate to levels beyond what archaic humans could tolerate, emptying the continent of human populations.
The oldest known human remains in Europe have previously been recovered from Iberia and suggest that early humans had arrived from southwest Αsia by about 1.4 million years ago. The climate around that time would have generally been warm and wet, punctuated by mild cold periods. Up to now, the prevailing theory has been that once humans arrived, they were able to survive through multiple climate cycles and adapt to increasingly harsh conditions after 900,000 years ago.
Senior author Professor Chronis Tzedakis (UCL Geography) said: “Our discovery of an extreme glacial cooling event around 1.1 million years ago challenges the idea of continuous early human occupation of Europe.”
Paleoclimate scientists from UCL, University of Cambridge and CSIC Barcelona analysed the chemical composition of marine micro-organisms and examined the pollen content in a deep-sea sediment core recovered from off the coast of Portugal. This revealed the presence of abrupt climate changes that culminated in an extreme glacial cooling, with ocean surface temperatures off Lisbon dropping below 6°C and semi-deserts expanding on the adjacent land.
Lead author Dr Vasiliki Margari (UCL Geography) said: “To our surprise, we found that this cooling at 1.1 million years ago was comparable to some of the most severe events of recent ice ages.”
Co-author Professor Nick Ashton of the British Museum said: “A cooling of this magnitude would have placed small hunter-gatherer bands under considerable stress, especially since early humans may have lacked adaptations such as sufficient fat insulation and also the means to make fire, effective clothing or shelters.”
To assess the climate impact on early human populations, co-corresponding author Professor Axel Timmermann and his team from the IBS Center for Climate Physics at Pusan National University ran a climate simulation on their supercomputer Aleph to capture the extreme conditions during this time. Combining the output of the simulation with fossil and archaeological evidence of human occupation in southwest Eurasia, the team then developed a human habitat model, which predicts how suitable the environment was for early human occupation.
Professor Axel Timmermann said: “The results showed that 1.1 million years ago climate around the Mediterranean became too hostile for archaic humans.”
Together, the paleoclimate data and human habitat model results indicate that Iberia, and more generally southern Europe, was depopulated during the Early Pleistocene. An apparent lack of stone tools and human remains over the next 200,000 years further raises the possibility of a long-lasting hiatus in European occupation.
Co-author Professor Chris Stringer of the Natural History Museum in London said: “According to this scenario, Europe may have been recolonized around 900,000 years ago by more resilient humans with evolutionary or behavioural changes that allowed survival in the increasing intensity of glacial conditions.”
The research was led by scientists at UCL Geography and the IBS Center for Climate Physics, Pusan National University, South Korea in partnership with researchers from the Cambridge University, CSIC Barcelona, the Natural History Museum, London, the British Museum and the UCL Institute of Archaeology.
Notes to Editors
For more information or to speak to the researchers involved or to get a copy of the paper, please contact Michael Lucibella, UCL Media Relations. T: +44 (0)753 941 0389, E: m.lucibella@ucl.ac.uk
Margari, V., Hodell, D.A., Parfitt, S.A., Ashton, N.M., Grimalt, J.O., Kim, H., Yun, K.-S., Gibbard, P.L., Stringer, C.B., Timmermann, A. & Tzedakis, P.C. (2023) ‘Extreme glacial cooling likely led to hominin depopulation of Europe in the Early Pleistocene’ will be published in Science on Thursday 10 August 2023, at 19:00 (7:00 pm) British Summer Time / 14:00 (2:00 pm) U.S. Eastern Time and is under a strict embargo until this time.
The DOI for this paper will be: 10.1126/science.adf4445
Additional material
Video: https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fi/by3uu2i4rb5hd05grtw2k/UCL-Vas-v9.mp4?rlkey=kpchx03auqvkmpde4p7iyqqpn&dl=0
More information, including a copy of the paper, can be found online at the Science press package at https://www.eurekalert.org/press/scipak/
About UCL – London’s Global University
UCL is a diverse community with the freedom to challenge and think differently.
Our community of more than 41,500 students from 150 countries and over 12,500 staff pursues academic excellence, breaks boundaries and makes a positive impact on real world problems.
We are consistently ranked among the top 10 universities in the world and are one of only a handful of institutions rated as having the strongest academic reputation and the broadest research impact.
We have a progressive and integrated approach to our teaching and research – championing innovation, creativity and cross-disciplinary working. We teach our students how to think, not what to think, and see them as partners, collaborators and contributors.
For almost 200 years, we are proud to have opened higher education to students from a wide range of backgrounds and to change the way we create and share knowledge.
We were the first in England to welcome women to university education and that courageous attitude and disruptive spirit is still alive today. We are UCL.
www.ucl.ac.uk| Follow @uclnews on Twitter | Watch our YouTube channel | Listen to UCL podcasts on SoundCloud | Find out what’s on at UCL Minds | #MadeAtUCL
Find out how UCL is helping lead the global fight against COVID-19 www.ucl.ac.uk/covid-19-research
END
Extreme cooling ended the first human occupation of Europe
2023-08-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
An unexpected way to upcycle: Plastic waste transforms into soap
2023-08-10
A team led by Virginia Tech researchers has developed a new method for upcycling plastics into high-value chemicals known as surfactants, which are used to create soap, detergent, and more.
Plastics and soaps tend to have little in common when it comes to texture, appearance, and, most importantly, how they are used. But there is a surprising connection between the two on a molecular level: The chemical structure of polyethylene — one of the most commonly used plastics in the world today — is strikingly similar ...
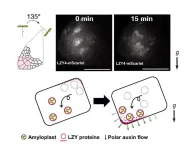
The positional transmitter of statoliths unveiled: It keeps plants from getting lazy
2023-08-10
Plants orient their organs in response to the gravity vector, with roots growing towards gravity and shoots growing in the opposite direction. The movement of statoliths responding to the inclination relative to the gravity vector is employed for gravity sensing in both plants and animals. However, in plants, the statolith takes the form of a high-density organelle, known as an amyloplast, which settles toward gravity within the gravity sensing cell. Despite the significance of this gravity sensing mechanism, the exact process behind it has eluded scientists ...
City of Hope researchers develop a CAR T cell therapy for advanced ovarian cancer
2023-08-10
LOS ANGELES — There are currently few effective treatment options for patients with recurrent ovarian cancer and other solid tumors, but City of Hope researchers are trying to change that.
Researchers with City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the nation, have published preclinical research in Nature Communications demonstrating that a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered T cell therapy worked against ovarian cancer in the laboratory and in preclinical models.
“City of Hope’s ...
Threatened grey-necked rockfowl's habitat even smaller than expected, study finds
2023-08-10
SAN DIEGO (AUG. 10, 2023) — A new study on gray-necked rockfowl has found a much smaller range of suitable habitat for this elusive African bird than was previously assumed, and may warrant a downgrade in its conservation status.
Scientists from the Cameroon Biodiversity Association (CAMBIO) in Cameroon, in partnership with San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance, set out to better understand how much suitable habitat remains for the rockfowl, and where the birds can still be found.
Understanding suitable habitat and its extent is crucial for protecting species. However, scientists have limited knowledge ...
Louisiana Obesity Society to host inaugural conference on Aug. 12 in New Orleans
2023-08-10
Physicians, psychologists, advanced practice providers, dietitians, and others who are committed to treating and preventing obesity in Louisiana have come together to formally launch the Louisiana Obesity Society, a new statewide professional organization. The Louisiana Obesity Society will be hosting its inaugural annual conference in conjunction with the Louisiana Chapter of American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery on Saturday, Aug. 12, at the Renaissance New Orleans Arts Warehouse District Hotel in New Orleans.
The Louisiana Obesity Society was created to support providers treating obesity through education and networking. The society will also advocate ...
Poverty alleviation breakthrough: How a switch to a 'growth mindset' empowers entrepreneurs in developing nations
2023-08-10
Although millions are spent each year on entrepreneurship training that is intended to help alleviate poverty and elevate the quality of life of entrepreneurs in developing nations, these programs often fail to make an impact.
Brigham Young University professors Shad Morris and Chad Carlos, along with three other colleagues, were invited by the Tanzania Social Action Fund (“TASAF”) to see if they could help figure out why TASAF’s entrepreneurship trainings were not producing the results they were hoping for.
In order to assist TASAF, Morris, Carlos, and colleagues Geoff Kistruck, Elly Tumsifu and Bob Lount, carried out an extensive ...
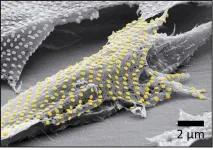
Tattoo technique transfers gold nanopatterns onto live cells
2023-08-10
For now, cyborgs exist only in fiction, but the concept is becoming more plausible as science progresses. And now, researchers are reporting in ACS’ Nano Letters that they have developed a proof-of-concept technique to “tattoo” living cells and tissues with flexible arrays of gold nanodots and nanowires. With further refinement, this method could eventually be used to integrate smart devices with living tissue for biomedical applications, such as bionics and biosensing.
Advances in electronics have enabled manufacturers ...
Long COVID symptoms can emerge months after infection
2023-08-10
Long COVID can persist for at least a year after the acute illness has passed, or appear months later, according to the most comprehensive look yet at how symptoms play out over a year.
The multicenter study, a collaboration between UC San Francisco, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and seven other sites, expands knowledge of post-COVID-19 conditions, describing trends in more detail than previous research and highlighting significant impacts the epidemic has had on the U.S. health care system.
The study appears Aug. 10, 2023, in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), ...
PeerJ announce Professors Ute Roessner and Luis E. Eguiarte as Co-Editors-in-Chief of forthcoming new journal, PeerJ Open Advances in Plant Science
2023-08-10
Open Access publisher PeerJ have announced their second Editor-in-Chief partnership for the Open Advances series of journals. Professors Ute Roessner and Luis E. Eguiarte have agreed to take on the leadership of PeerJ Open Advances in Plant Science as Co-Editors-in-Chief.
Professors Roessner and Eguiarte are highly respected, award-winning scientists working at the forefront of their fields. As Co-Editors-in-Chief they will provide the scientific leadership for the journal, starting with recruiting an Editorial Board who will ...
NIH zebrafish research included in US Postal Service’s “Life Magnified” stamps
2023-08-10
A microscopy image created by National Institutes of Health researchers is part of the “Life Magnified” stamp panel issued today by the United States Postal Service (USPS®). The NIH zebrafish image, which was taken to understand lymphatic vessel development in the brain, merges 350 individual images to reveal a juvenile zebrafish with a fluorescently tagged skull, scales and lymphatic system.
“Zebrafish are used as a model for typical and atypical human development. It is surprising how much we have in common with ...