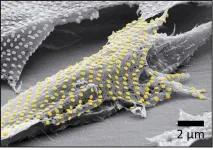
(Press-News.org) For now, cyborgs exist only in fiction, but the concept is becoming more plausible as science progresses. And now, researchers are reporting in ACS’ Nano Letters that they have developed a proof-of-concept technique to “tattoo” living cells and tissues with flexible arrays of gold nanodots and nanowires. With further refinement, this method could eventually be used to integrate smart devices with living tissue for biomedical applications, such as bionics and biosensing.
Advances in electronics have enabled manufacturers to make integrated circuits and sensors with nanoscale resolution. More recently, laser printing and other techniques have made it possible to assemble flexible devices that can mold to curved surfaces. But these processes often use harsh chemicals, high temperatures or pressure extremes that are incompatible with living cells. Other methods are too slow or have poor spatial resolution. To avoid these drawbacks, David Gracias, Luo Gu and colleagues wanted to develop a nontoxic, high-resolution, lithographic method to attach nanomaterials to living tissue and cells.
The team used nanoimprint lithography to print a pattern of nanoscale gold lines or dots on a polymer-coated silicon wafer. The polymer was then dissolved to free the gold nanoarray so it could be transferred to a thin piece of glass. Next, the gold was functionalized with cysteamine and covered with a hydrogel layer, which, when peeled away, removed the array from the glass. The patterned side of this flexible array/hydrogel layer was coated with gelatin and attached to individual live fibroblast cells. In the final step, the hydrogel was degraded to expose the gold pattern on the surface of the cells. The researchers used similar techniques to apply gold nanoarrays to sheets of fibroblasts or to rat brains. Experiments showed that the arrays were biocompatible and could guide cell orientation and migration.
The researchers say their cost-effective approach could be used to attach other nanoscale components, such as electrodes, antennas and circuits, to hydrogels or living organisms, thereby opening up opportunities for the development of biohybrid materials, bionic devices and biosensors.
The authors acknowledge funding from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the National Institute on Aging, the National Science Foundation and the Johns Hopkins University Surpass Program.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
Tattoo technique transfers gold nanopatterns onto live cells
2023-08-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Long COVID symptoms can emerge months after infection
2023-08-10
Long COVID can persist for at least a year after the acute illness has passed, or appear months later, according to the most comprehensive look yet at how symptoms play out over a year.
The multicenter study, a collaboration between UC San Francisco, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and seven other sites, expands knowledge of post-COVID-19 conditions, describing trends in more detail than previous research and highlighting significant impacts the epidemic has had on the U.S. health care system.
The study appears Aug. 10, 2023, in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), ...
PeerJ announce Professors Ute Roessner and Luis E. Eguiarte as Co-Editors-in-Chief of forthcoming new journal, PeerJ Open Advances in Plant Science
2023-08-10
Open Access publisher PeerJ have announced their second Editor-in-Chief partnership for the Open Advances series of journals. Professors Ute Roessner and Luis E. Eguiarte have agreed to take on the leadership of PeerJ Open Advances in Plant Science as Co-Editors-in-Chief.
Professors Roessner and Eguiarte are highly respected, award-winning scientists working at the forefront of their fields. As Co-Editors-in-Chief they will provide the scientific leadership for the journal, starting with recruiting an Editorial Board who will ...
NIH zebrafish research included in US Postal Service’s “Life Magnified” stamps
2023-08-10
A microscopy image created by National Institutes of Health researchers is part of the “Life Magnified” stamp panel issued today by the United States Postal Service (USPS®). The NIH zebrafish image, which was taken to understand lymphatic vessel development in the brain, merges 350 individual images to reveal a juvenile zebrafish with a fluorescently tagged skull, scales and lymphatic system.
“Zebrafish are used as a model for typical and atypical human development. It is surprising how much we have in common with ...
Novel socio-environmental vulnerability index pinpoints sustainability issues in Brazilian river basins
2023-08-10
Brazilian researchers combined environmental physical, social and economic indicators to create an index that measures a region’s vulnerability and used it to analyze the basins of the Parnaíba River and São Francisco River in the Northeast of Brazil. The index is named SEVI (for Socio-Environmental Vulnerability).
The Parnaíba and São Francisco basins are considered crucial to agricultural expansion and biodiversity conservation. They contain more than 780 municipalities and part of the semi-arid Caatinga and savanna-like Cerrado biomes, which are threatened ...
Mayo Clinic ‘mini-brain’ study reveals possible key link to autism spectrum disorder
2023-08-10
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Using human "mini-brain" models known as organoids, Mayo Clinic and Yale University scientists have discovered that the roots of autism spectrum disorder may be associated with an imbalance of specific neurons that play a critical role in how the brain communicates and functions. The specific cells are known as excitatory cortical neurons.
The new study is published in Nature Neuroscience.
Findings
The team found an abnormal imbalance of excitatory ...
Muon g-2 doubles down with latest measurement, explores uncharted territory in search of new physics
2023-08-10
Batavia, Ill., Aug. 10, 2023 – Physicists now have a brand-new measurement of a property of the muon called the anomalous magnetic moment that improves the precision of their previous result by a factor of 2.
An international collaboration of scientists working on the Muon g-2 experiment at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory announced the much-anticipated updated measurement on Aug. 10. This new value bolsters the first result they announced in April 2021 and sets up a showdown between theory and experiment over 20 years in the making.
“We’re really probing new territory. We’re determining ...
Making molecules dance to our tune reveals what drives their first movements
2023-08-10
Bringing ultrafast physics to structural biology has revealed the dance of molecular ‘coherence’ in unprecedented clarity.
How molecules change when they react to stimuli such as light is fundamental in biology, for example during photosynthesis. Scientists have been working to unravel the workings of these changes in several fields, and by combining two of these, researchers have paved the way for a new era in understanding the reactions of protein molecules fundamental for life.
The large international research team, led by Professor ...
Gut microbiome can increase risk, severity of HIV, EBV disease
2023-08-10
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Over the past decade, the gut microbiome has gained significant interest by scientists and non-scientists alike. Recent research has shown that the bacteria and other microbes in our gut play a supporting role in immunity, metabolism, digestion, and the fight against "bad bacteria" that try to invade our bodies.
However, new research published in Nature Biotechnology by Angela Wahl, PhD, Balfour Sartor, MD, J. Victor Garcia, PhD, and UNC School of Medicine colleagues others has revealed that the microbiome may not as always be protective against human pathogens.
Using a first-of-its-kind ...
YALE EMBARGOED NEWS: Yale scientists reveal two paths to autism in the developing brain
2023-08-10
New Haven, Conn. — Two distinct neurodevelopmental abnormalities that arise just weeks after the start of brain development have been associated with the emergence of autism spectrum disorder, according to a new Yale-led study in which researchers developed brain organoids from the stem cells of boys diagnosed with the disorder.
And, researchers say, the specific abnormalities seem to be dictated by the size of the child’s brain, a finding that could help doctors and researchers to diagnosis and treat autism in the future.
The findings were ...
Before reaching the skies, the Himalayas had a leg up, new study shows
2023-08-10
Mountain ranges play a key role in global climate, altering weather and shaping the flora and fauna that inhabit their slopes and the valleys below. As warm air rises windward grades and cools, moisture condenses into rain and snow. On the leeward side, it’s quite the opposite. Deserts prevail, a phenomenon known as rain shadow. Thus, the way mountain ranges form is a matter of intense interest among those who study and model climates of the past.
That debate will soon grow more heated with a new paper in the journal Nature Geoscience. A team of researchers ...