Trinity research looks to Latin America for clues on healthy brain ageing
Researchers at Trinity College Dublin study the factors influencing healthy brain ageing in Latin American and Caribbean (LAC) countries and find the lessons learned there, can also be applied to home.
2023-08-10
(Press-News.org)
Researchers at Trinity College Dublin study the factors influencing healthy brain ageing in Latin American and Caribbean (LAC) countries and find the lessons learned there, can also be applied to home.
Ageing is not a uniform process across the globe. Most research into cognitive and functional ageing has been conducted in the US and Europe, in high-income settings. Researchers from the Global Brain Health Institute (GBHI) at Trinity College are filling the knowledge gap that exists for Latin American populations on the factors associated with healthy ageing. Their findings are published today [Thursday, 10th August 2023] in the journal Nature Medicine.
The study found that social/health disparities significantly influence healthy ageing differentially across countries and regions. Researchers believe the same can be expected of other countries and regions, including Ireland.
Researchers set out to investigate the combined impact of social determinants of health (SDH), lifestyle factors, cardiometabolic factors, mental health symptoms and demographics (age, sex) on healthy brain ageing across Latin American and Caribbean (LAC) countries with different levels of socioeconomic development. In LAC countries, there is an urgent need to assess regional diversity and deliver tailored evidence for diverse populations.
Previous studies in high-income countries (US and Europe) that capture risk factors of healthy and pathological brain ageing were not accurate for low-income and middle-income countries. Assessing specific risk factors in LAC countries constitutes a critical priority for understanding healthy ageing globally.
Speaking on how the study and its findings pertain to our understanding of ageing brain health, Dr Augustin Ibanez, co-lead author of the study, GBHI Faculty at Trinity College and Director of the Latin American Brain Health Institute (BrainLat), said:
“This study emphasizes that ageing is influenced by more than just biological factors such as age and sex. It suggests that other factors, such as social determinants of health, mental health symptoms, and cardiometabolic risks, profoundly impact healthy ageing. While the study is specific to Latin American countries, it considers a new perspective for understanding ageing in Ireland, encouraging a more holistic approach in considering all these factors.”
Researchers employed machine-learning models to analyse the complex interplay of factors associated with ageing. The study’s findings suggest that a one-size-fits-all approach to understanding healthy ageing is insufficient. So, while the specific results in the Latin American context may not be directly applicable to Ireland due to cultural, socioeconomic, and environmental differences; the research methodology and overarching themes can be utilized to study ageing in the Irish demographics. The use of machine learning models to analyze the complex interplay of factors can be applied to understand Ireland's unique challenges and risks.
Dr Ibanez, said:
“This study provides a valuable lens to reconsider how we approach healthy ageing in Ireland and highlights the need for region-specific, data-driven health strategies.”
Professor Brian Lawlor, Site Director, Global Brain Health Institute and Professor of Old Age Psychiatry, Trinity College, said:
“This study enhances our understanding of the importance of inequities and the social determinants of health as drivers of brain health and ageing, which is core to the mission of the Global Brain Health Institute (GBHI) based at Trinity College Dublin. This research, led by Atlantic Fellow at GBHI and Trinity Faculty member Agustin Ibanez, highlights why we need to adopt diverse perspectives and avoid simplistic models of ageing if we are to successfully tackle the challenges of ageing and brain health on a global scale”.
You can read the study: Factors associated with healthy aging in Latin American populations in Nature Medicine at the following link: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-023-02495-1
Ends/
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-10
Key Takeaways
Lung and heart transplant recipients experienced diminished and delayed antibody responses to the first two COVID-19 mRNA vaccine doses, but most developed stronger responses following a third dose
A third dose also boosted cross-protection against SARS-CoV-2 viral variants
For lung and heart transplant recipients, vaccine doses beyond the third dose are likely important for maintaining immunity
BOSTON – Transplant recipients must take life-long immunosuppressive medications to prevent rejection, but these drugs ...
2023-08-10
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $11 million in funding for 15 projects in exploratory research for extreme-scale science that will leverage emerging trends and advances in high-end computing, massive datasets, scientific machine learning, artificial intelligence, and novel computing architectures.
“There is a wide expanse of exciting opportunities as we reach beyond exascale computing,” said Ceren Susut, DOE Acting Associate Director of Science for Advanced Scientific Computing Research. “These ...
2023-08-10
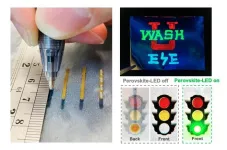
Researchers working with Chuan Wang, an associate professor of electrical and systems engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, have developed ink pens that allow individuals to handwrite flexible, stretchable optoelectronic devices on everyday materials including paper, textiles, rubber, plastics and 3D objects.
In a paper published Aug. 7 in Nature Photonics, the team reports their simple and versatile fabrication approach to allow anyone to make a custom light-emitting diode (LED) or photodetector ...
2023-08-10
URBANA, Ill. – Madagascar is one of the poorest countries in the world and access to health care is limited for many people. Childhood vaccinations are a crucial component of preventative care, but vaccination rates remain below the World Health Organization’s goal of reaching 95% of children. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign examines the effectiveness of a health intervention program that enlists community-based health workers to promote child vaccination uptake.
“Childhood vaccinations are a cost-effective investment that can have large ripple effects. Vaccines can reduce child mortality ...
2023-08-10
It is now almost a rule of thumb: As soon as an athlete falls to the ground with a sudden cardiac arrest, social media is awash with claims that COVID-19 vaccinations are to blame. This was the case with English footballer Charlie Wyke, cyclist Sonny Colbrelli and, most recently, with college basketballer, and son of LeBron, Bronny James. In the view of Harald Jorstad, Sports Cardiologist at Amsterdam UMC, there is no evidence to support these claims, but timing of the vaccination can be structured to not ...
2023-08-10
BEAUFORT, N.C. – Microscopic plastic particles have been found in the fats and lungs of two-thirds of the marine mammals in a graduate student’s study of ocean microplastics. The presence of polymer particles and fibers in these animals suggests that microplastics can travel out of the digestive tract and lodge in the tissues.
The study, slated for the Oct. 15 edition of Environmental Pollution, appeared online this week.
Harms that embedded microplastics might cause to marine mammals are yet to be determined, ...
2023-08-10
Text-to-image (T2I) generative artificial intelligence tools are increasingly powerful and widespread tools that can create nearly any image based on just a few inputted words. T2I generative AI can create convincingly realistic photos and videos which are being used more and more for a multitude of purposes, from art to political campaigning.
However, the algorithmic models that power these tools are trained on data from humans, and can replicate human biases in the images they produce, such as biases around gender and skin tone. These biases can harm marginalized populations, reinforcing stereotypes and potentially leading to discrimination.
To address these implicit biases, ...
2023-08-10
Sodium, Potassium and zinc have all been promising contenders for lithium’s place in rechargeable batteries of the future, but researchers at Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) have added an unusual and more abundant competitor to the mix: chloride, the richest negatively charged ions in seawater.
Xiaowei Teng, the James H. Manning professor of Chemical Engineering at WPI, has discovered a new redox chemistry empowered by chloride ions for the development of seawater green batteries.
Modern lithium-ion batteries used in various applications, including electric vehicles, can be problematic for grid storage, given their ...
2023-08-10
A new analysis shows that infectious bacteria exposed to the antibiotic albicidin rapidly develop up to a 1,000-fold increase in resistance via a gene amplification mechanism. Mareike Saathoff of Freie Universität Berlin, Germany, and colleagues present these findings August 10th in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a growing problem associated with millions of deaths around the world every year. Understanding how bacteria evolve resistance is key to developing more effective antibiotics and strategies for using them.
In recent years, albicidin has emerged as a promising antibiotic capable of killing a wide range of bacterial species ...
2023-08-10
Pushing into a new chapter of technologically advanced biological sensors, scientists from the University of California San Diego and their colleagues in Australia have engineered bacteria that can detect the presence of tumor DNA in a live organism.
Their innovation, which detected cancer in the colons of mice, could pave the way to new biosensors capable of identifying various infections, cancers and other diseases.
The advancement is described Aug. 11, 2023, in the journal Science. Bacteria previously have been designed to carry out various diagnostic and therapeutic functions, but lacked the ability to identify specific DNA sequences and mutations outside ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Trinity research looks to Latin America for clues on healthy brain ageing
Researchers at Trinity College Dublin study the factors influencing healthy brain ageing in Latin American and Caribbean (LAC) countries and find the lessons learned there, can also be applied to home.