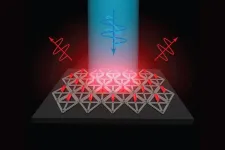
(Press-News.org) Cambridge, MA – Flat screen TVs that incorporate quantum dots are now commercially available, but it has been more difficult to create arrays of their elongated cousins, quantum rods, for commercial devices. Quantum rods can control both the polarization and color of light, to generate 3D images for virtual reality devices.
Using scaffolds made of folded DNA, MIT engineers have come up with a new way to precisely assemble arrays of quantum rods. By depositing quantum rods onto a DNA scaffold in a highly controlled way, the researchers can regulate their orientation, which is a key factor in determining the polarization of light emitted by the array. This makes it easier to add depth and dimensionality to a virtual scene.
“One of the challenges with quantum rods is: How do you align them all at the nanoscale so they’re all pointing in the same direction?” says Mark Bathe, an MIT professor of biological engineering and the senior author of the new study. “When they’re all pointing in the same direction on a 2D surface, then they all have the same properties of how they interact with light and control its polarization.”
MIT postdocs Chi Chen and Xin Luo are the lead authors of the paper, which appears today in Science Advances. Robert Macfarlane, an associate professor of materials science and engineering; Alexander Kaplan PhD ’23; and Moungi Bawendi, the Lester Wolfe Professor of Chemistry, are also authors of the study.
Nanoscale structures
Over the past 15 years, Bathe and others have led in the design and fabrication of nanoscale structures made of DNA, also known as DNA origami. DNA, a highly stable and programmable molecule, is an ideal building material for tiny structures that could be used for a variety of applications, including delivering drugs, acting as biosensors, or forming scaffolds for light-harvesting materials.
Bathe’s lab has developed computational methods that allow researchers to simply enter a target nanoscale shape they want to create, and the program will calculate the sequences of DNA that will self-assemble into the right shape. They also developed scalable fabrication methods that incorporate quantum dots into these DNA-based materials.
In a 2022 paper, Bathe and Chen showed that they could use DNA to scaffold quantum dots in precise positions using scalable biological fabrication. Building on that work, they teamed up with Macfarlane’s lab to tackle the challenge of arranging quantum rods into 2D arrays, which is more difficult because the rods need to be aligned in the same direction.
Existing approaches that create aligned arrays of quantum rods using mechanical rubbing with a fabric or an electric field to sweep the rods into one direction have had only limited success. This is because high-efficiency light-emission requires the rods to be kept at least 10 nanometers from each other, so that they won’t “quench,” or suppress, their neighbors’ light-emitting activity.
To achieve that, the researchers devised a way to attach quantum rods to diamond-shaped DNA origami structures, which can be built at the right size to maintain that distance. These DNA structures are then attached to a surface, where they fit together like puzzle pieces.
“The quantum rods sit on the origami in the same direction, so now you have patterned all these quantum rods through self-assembly on 2D surfaces, and you can do that over the micron scale needed for different applications like microLEDs,” Bathe says. “You can orient them in specific directions that are controllable and keep them well-separated because the origamis are packed and naturally fit together, as puzzle pieces would.”
Assembling the puzzle
As the first step in getting this approach to work, the researchers had to come up with a way to attach DNA strands to the quantum rods. To do that, Chen developed a process that involves emulsifying DNA into a mixture with the quantum rods, then rapidly dehydrating the mixture, which allows the DNA molecules to form a dense layer on the surface of the rods.
This process takes only a few minutes, much faster than any existing method for attaching DNA to nanoscale particles, which may be key to enabling commercial applications.
“The unique aspect of this method lies in its near-universal applicability to any water-loving ligand with affinity to the nanoparticle surface, allowing them to be instantly pushed onto the surface of the nanoscale particles. By harnessing this method, we achieved a significant reduction in manufacturing time from several days to just a few minutes,” Chen says.
These DNA strands then act like Velcro, helping the quantum rods stick to a DNA origami template, which forms a thin film that coats a silicate surface. This thin film of DNA is first formed via self-assembly by joining neighboring DNA templates together via overhanging strands of DNA along their edges.
The researchers now hope to create wafer-scale surfaces with etched patterns, which could allow them to scale their design to device-scale arrangements of quantum rods for numerous applications, beyond only microLEDs or augmented reality/virtual reality.
“The method that we describe in this paper is great because it provides good spatial and orientational control of how the quantum rods are positioned. The next steps are going to be making arrays that are more hierarchical, with programmed structure at many different length scales. The ability to control the sizes, shapes, and placement of these quantum rod arrays is a gateway to all sorts of different electronics applications,” Macfarlane says.
“DNA is particularly attractive as a manufacturing material because it can be biologically produced, which is both scalable and sustainable, in line with the emerging U.S. bioeconomy. Translating this work towards commercial devices by solving several remaining bottlenecks, including switching to environmentally safe quantum rods, is what we’re focused on next,” Bathe adds.
###
The research was funded by the Office of Naval Research, the National Science Foundation, the Army Research Office, the Department of Energy, and the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences.
END
Arrays of quantum rods could enhance TVs or virtual reality devices
MIT engineers developed a new way to create these arrays, by scaffolding quantum rods onto patterned DNA.
2023-08-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Artificial intelligence designs advanced materials
2023-08-11
In a world where annual economic losses from corrosion surpass 2.5 trillion US Dollars, the quest for corrosion-resistant alloys and protective coatings is unbroken. Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly pivotal role in designing new alloys. Yet, the predictive power of AI models in foreseeing corrosion behaviour and suggesting optimal alloy formulas has remained elusive. Scientists of the Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung (MPIE) have now developed a machine learning model that enhances the predictive accuracy by up to 15% compared to existing frameworks. This model uncovers new, but realistic corrosion-resistant alloy compositions. ...
Even treated wastewater affects our rivers
2023-08-11
Effluents from wastewater treatment plants have a dual effect: Some species disappear, while others benefit. Especially certain insect orders, such as stonefly and caddisfly larvae, are decimated. Certain worms and crustaceans, by contrast, can increase in number. A team from Goethe University Frankfurt led by Daniel Enns and Dr. Jonas Jourdan has corroborated this in a comprehensive study, which has now been published in the journal Water Research. They examined 170 wastewater treatment plants in Hesse in relation to species composition.
Wastewater treatment plants are ...
Study: Infant formula safety checks can be improved with stratified sampling
2023-08-11
URBANA, Ill. – Producers of infant formula employ comprehensive food safety systems, including product testing to ensure those systems are working. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign finds that some testing methods are more powerful at catching contaminants than others.
Spacing out samples over time in a stratified sampling pattern is better at catching risky pathogens like Cronobacter than randomly sampling from the product as it is being produced, the researchers found. Furthermore, while taking more samples of product generally increases the chance to catch the pathogen, there is a point after which it ...
UTEP launches new research partnerships with Chihuahua universities
2023-08-11
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 11, 2023) – How are our region’s pecan farms affected by drought? Is there a better way to address domestic violence in Ciudad Juárez? These are a few of the big questions scientists are asking as they prepare to embark on a new cross-border research collaboration.
Created by The University of Texas at El Paso, the U.S.-Mexico Faculty Collaboration Fellowship program will support research projects with higher education institutions in the State of Chihuahua to spur studies on issues ...
Behind the rind: new genomic insights into watermelon evolution, quality, and resilience
2023-08-11
Watermelon is a globally significant agricultural product, both in terms of the total amount produced and the total economic value generated.
Scientists at the Boyce Thompson Institute have constructed a comprehensive "super-pangenome" for watermelon and its wild relatives, uncovering beneficial genes lost during domestication that could improve disease resistance and fruit quality of this vital fruit crop.
"We aimed to delve deeper into the genetic variations that make watermelons so diverse and unique," stated ...
Arctic monitoring program plays vital role in global pollution reduction efforts
2023-08-11
Historically, the Arctic was considered a pristine region, but scientific research spanning the last three decades has revealed the harsh reality of long-range transported pollutants reaching the Arctic from different corners of the world. In response to this alarming discovery, AMAP was created with the mission to monitor pollution and its effects on the Arctic environment and human health.
In a new article published on 26 July 2023, in the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers from Arctic Knowledge Ltd, presents the initiation and implementation of a systematic scientific and political cooperation in the Arctic related to environmental ...
University of Chicago scientists invent smallest known way to guide light
2023-08-11
Directing light from place to the place is the backbone of our modern world. Beneath the oceans and across continents, fiber optic cables carry light that encodes everything from YouTube videos to banking transmissions—all inside strands about the size of a hair.
University of Chicago Prof. Jiwoong Park, however, wondered what would happen if you made even thinner and flatter strands—in effect, so thin that they’re actually 2D instead of 3D. What would happen to the light?
Through a series of innovative experiments, he and his team found ...
Malaria vaccine candidate appears safe and produces promising immune response in a cohort of Tanzanian infants
2023-08-11
An experimental malaria vaccine appears safe and promotes an immune response in African infants, one of the groups most vulnerable to severe malaria disease. There is currently only one malaria vaccine, “RTS,S” that is approved by the World Health Organization and offers partial disease protection. However, in the results of the early-stage phase Ib trial conducted in Tanzania and published on August 11th in the journal Med, researchers find that targeting RH5 – a protein that the malaria pathogen Plasmodium falciparum uses to invade red blood cells – can generate a promising immune response ...
A roadmap to help AI technologies speak African languages
2023-08-11
From text-generating ChatGPT to voice-activated Siri, artificial intelligence-powered tools are designed to aid our everyday life — as long as you speak a language they support. These technologies are out of reach for billions of people who don’t use English, French, Spanish or other mainstream languages, but researchers in Africa are looking to change that. In a study published August 11 in the journal Patterns, scientists draw a roadmap to develop better AI-driven tools for African languages.
“It doesn’t ...
Synthetic extracellular matrix supports endometrial organoids
2023-08-11
Scientists have developed a synthetic extracellular matrix (ECM) that can support the growth of a mini endometrium in a dish for at least two weeks. The endometrium—the mucosal lining of the uterus—has been historically hard to model in the lab, which has limited scientists’ ability to study its role in healthy and diseased states like endometriosis. The matrix, described on August 11 in the journal Med, allows cells to interact in an environment that recapitulates human physiology which could help researchers better simulate the healthy and pathological response to menstrual cycles.
“With this matrix, we can begin to extrapolate and utilize ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Arrays of quantum rods could enhance TVs or virtual reality devicesMIT engineers developed a new way to create these arrays, by scaffolding quantum rods onto patterned DNA.