(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science (SC), announced $112 million in funding for 12 projects that focus on collaborations among fusion scientists, applied mathematicians, and computer scientists to maximize the use of high performance computing, including exascale computers.
The Scientific Discovery through Advanced Computing (SciDAC) program pairs the Fusion Energy Sciences (FES) program with the Advanced Scientific Computing Research (ASCR) program to explore solving complex problems through computing. Projects funded through this program will use computing resources to model plasmas, study turbulence, and use artificial intelligence to predict and solve problems like energy losses.
“This collaborative effort will advance our understanding of fusion as an energy source while utilizing the most powerful supercomputers in the world,” said Jean Paul Allain, DOE Associate Director of Science for Fusion Energy Sciences. “The modeling and simulation work of these partnerships will offer insight into the multitude of physical processes that plasmas experience under extreme conditions and will also guide the design of fusion pilot plants. We are also looking forward to including efforts from inertial confinement devices and stellarators in this program.”
“The SciDAC program and the FES-ASCR SciDAC partnerships have advanced scientific discovery in fusion and plasma sciences over the last two decades,” said Ceren Susut, DOE Acting Associate Director of Science for Advanced Scientific and Computing Research. “The current awards leverage this past research as well as codes developed on the ASCR Exascale Computing Project to address the new and broader 2023 portfolio.”
The projects were selected by competitive peer review under the DOE Funding Opportunity Announcement for Scientific Discovery through Advanced Computing - FES Partnerships. Total funding is $112 million for projects lasting up to four years in duration, with $28.15 million in Fiscal Year 2023 dollars and outyear funding contingent on congressional appropriations. The list of projects and more information can be found on the Fusion Energy Sciences and Advanced Scientific Computing Research program homepages.
Selection for award negotiations is not a commitment by DOE to issue an award or provide funding. Before funding is issued, DOE and the applicants will undergo a negotiation process, and DOE may cancel negotiations and rescind the selection for any reason during that time.
END
Department of Energy announces $112 million for research on computational projects in fusion energy sciences
Projects span simulation of confined plasma dynamics, materials science, whole facility modeling, and computational frameworks for fusion energy
2023-08-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cancer-infecting virus ‘warms up’ cold tumors and improves immunotherapy
2023-08-14
Equipping cancer-infecting, or oncolytic, viruses with tumor-inhibiting genetic cargo stimulates the immune system and helps immunotherapy to shrink or completely clear aggressive tumors in mice, according to a new study in the Journal of Experimental Medicine led by University of Pittsburgh and UPMC researchers. The results pave the way for clinical trials combining oncolytic viruses with immunotherapy.
Oncolytic viruses are genetically modified viruses that target rapidly dividing tumor cells while avoiding normal cells. Oncolytic viruses were originally designed to directly kill cancer cells, but researchers later ...
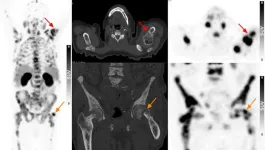
PSMA PET/CT waives the need for pre-imaging biopsy in elderly patients
2023-08-14
Reston, VA—In elderly patients with suspected prostate cancer, PSMA PET/CT can diagnose advanced disease and aid in therapy selection without the need for a biopsy. Published in the July issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, this new research demonstrates how imaging with PSMA PET/CT can potentially reduce the number of prostate biopsies and associated complications in the elderly while providing accurate staging data.
68Ga-PSMA PET/CT has gained acceptance as a highly sensitive and specific imaging modality for evaluating the extent of disease in prostate cancer patients. In general, PSMA PET/CT is indicated when intermediate ...
How did South African healthcare workers cope during the pandemic?
2023-08-14
A new study by UC Berkeley Anthropology Professor Andrew Wooyoung Kim reveals resilient coping mechanisms used by healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic in metro Johannesburg, South Africa.
Titled “Coping strategies employed by public psychiatric healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic in southern Gauteng, South Africa,”(link is external) Kim's paper was published in PLOS ONE in August. It explores the diverse coping strategies employed by public psychiatric healthcare workers during ...
Scientists outline a new strategy for understanding the origin of life
2023-08-14
Despite decades of progress, the origin of life remains one of the great unsolved problems in science. “The most basic features of biology, that organisms are made of cells, that they pass genetic information through DNA, that they use protein enzymes to run their metabolism, all emerged through specific processes in very early evolutionary history,” says Aaron Goldman, Associate Professor of Biology at Oberlin College. “Understanding how these most basic biological systems first took shape will not only give us greater insight into how life works at the most fundamental level, but what life actually is in the ...
USC Stem Cell studies tune into hearing regeneration
2023-08-14
A deafened adult cannot recover the ability to hear, because the sensory hearing cells of the inner ear don’t regenerate after damage. In two new studies, partially funded by the National Institutes of Health and published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences (PNAS), USC Stem Cell scientists explain why this is the case and how we might be able to change it.
“In the non-sensory supporting cells of the inner ear, key genes required for conversion to sensory cells are shut off through a process ...
Government regulation can effectively curb social media dangers
2023-08-14
Government legislation to flag and moderate dangerous content on social media can be effective in reducing harm, even on fast-paced platforms such as X (formerly Twitter) new research shows.
Social media posts such as those that promote terrorism and hate, dangerous challenges that put teen lives at risk, or those that glamorise suicide, pose a significant threat to society. And this harm spreads exponentially, like an infectious disease.
Dr Marian-Andrei Rizoiu from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) Behavioural Data Science Lab and Philipp J. Schneider from École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne harnessed ...
Digital puzzle games could be good for memory in older adults, study shows
2023-08-14
Older adults who play digital puzzle games have the same memory abilities as people in their 20s, a new study has shown.
The study, from the University of York, also found that adults aged 60 and over who play digital puzzle games had a greater ability to ignore irrelevant distractions, but older adults who played strategy games did not show the same improvements in memory or concentration.
It is known that as humans age, their mental abilities tend to decrease, particularly the ability to remember a number of things at a single time - known as working memory. Working ...
Inoue receives funding for Mason CARES Plus
2023-08-14
Inoue Receives Funding For Mason CARES Plus
Megumi Inoue, Associate Professor, Social Work, received funding for: "Mason CARES Plus."
Mason CARES Plus is an expansion study to Mason CARES that will focus on conducting in-depth focus groups and online semi-structured interviews to assess which specific aspects of the Stress Busting Program (SBP) and the Music and Memory program (M&M) were most (and least) impactful in reducing care partner stress and identify effective strategies to improve care partner engagement with the M&M program among Mason CARES participants.
Preliminary results from the Mason CARES study show a high ...
Behind the shower curtain: Investigating how showerhead features impact the bacteria we are exposed to
2023-08-14
Hopping in the shower, we anticipate the warm water to be cleansing and renewing after a long, hard day — but there may be something dangerous lurking in the showerhead.
Showers can expose us to many types of bacteria cells. Most are harmless, but some – called drinking water-associated pathogens of the immunocompromised (DWPIs) – can pose a serious risk to our health, especially for individuals with weakened immune systems.
Sarah Haig, Assistant Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering, received $420,000 from the National Science Foundation ...
Integrated mental health care in pediatric primary care at Federally Qualified Health Centers linked to improvements in school functioning, study finds
2023-08-14
Boston, MA - New research led by Boston Medical Center and Boston University School of Public Health found that children who received integrated mental health care showed improvements in both mental health and school performance. These findings, published in the Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics, examined changes over time in outcomes among 6-12-year-old children receiving integrated behavioral health care at three federally qualified health centers (FQHCs) that implemented the TEAM UP Model of care.
The study, which included 51 children serviced ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Department of Energy announces $112 million for research on computational projects in fusion energy sciencesProjects span simulation of confined plasma dynamics, materials science, whole facility modeling, and computational frameworks for fusion energy