(Press-News.org) Black Americans are 54% more likely to die of cardiovascular disease than White Americans, despite a substantial overall reduction in cardiovascular disease mortality nationwide.
Now, a new study from Tulane University published in Annals of Internal Medicine has found that this racial disparity can be attributed to social factors such as unemployment, low income, and lack of a partner rather than known factors such as hypertension and obesity.
“For so many years we have focused on smoking, diet, physical activity, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol – and we know those are important for the prevention of cardiovascular disease – but it surprised me that the Black-White difference in cardiovascular disease mortality is mainly due to social factors,” said Dr. Jiang He, lead author and Joseph S. Copes Chair in Epidemiology at Tulane’s School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine.
Using health data from more than 50,000 adults, the study examined the association between clinical risk factors (obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol), lifestyle risk factors (smoking, unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, and too little or too much sleep), and social risk factors (unemployment, low family income, food insecurity, low education, no regular access to healthcare, no private health insurance, not owning a home, and not married nor living with a partner) with cardiovascular mortality.
When the study adjusted for age and sex, Black adults had a 54% higher cardiovascular disease mortality rate compared to White adults. That dropped to 34% and 31% after adjusting for clinical and lifestyle risk factors, respectively. But the racial difference in cardiovascular mortality completely dissipated after adjusting for social risk factors.
“When we adjusted for lifestyle and clinical risk factors, the Black-White disparity in cardiovascular disease mortality was diminished but still persisted.” He said. “However, after adjusting for social risk factors, this racial difference totally disappeared.”
This study follows another recent Tulane study which similarly found Black Americans are 59% more likely to die prematurely than White Americans. That disparity was reduced to zero after adjusting for these social factors, also called social determinants of health.
Social determinants of health, while a relatively new framework, was emphasized by the CDC’s Healthy People 2030 initiative as eight areas of life critical to health and well-being.
For He, the findings emphasize the importance of well-paying jobs, health care access and social support that can come from a family or tight-knit community.
Going forward, He is putting these findings into practice with a program that aims to address hypertension in New Orleans’ Black communities by partnering with local churches to provide health screening training and free medication.
“It is essential to develop novel community-based interventions for reducing cardiovascular disease risk in Black populations,” He said.
END
Why are Black adults at greater risk of death from heart disease? Study blames social factors
2023-08-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research offers solutions to improve drinking water access in developing countries
2023-08-14
In 2020, 771 million people worldwide still lacked access to clean drinking water, according to UNICEF and the World Health Organization.
For this reason, many nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) prioritize building new water projects, including handpumps and small piped systems, to bring clean water to rural areas of developing countries.
Alfonso Pedraza-Martinez
New research from Alfonso Pedraza-Martinez, the Greg and Patty Fox Collegiate Professor of IT, Analytics and Operations in the University of Notre Dame’s Mendoza College of Business, examines the critical problem of drinking ...
UC study focus: faster, more accurate way to diagnose lung infections
2023-08-14
A federally funded study, led by University of Cincinnati researcher Nalinikanth Kotagiri, looks to develop a new imaging method that can identify certain types of lung infections — in real time — in order to speed up treatment for critically ill patients.
Kotagiri, an associate professor of pharmaceutical sciences at the UC James L. Winkle College of Pharmacy, has been awarded a five-year $3 million, R01 grant from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) to develop and study the effectiveness of different kinds of injectable probes (metallic contrast agents) that would collect at the site of the infection and immediately light up under a nuclear ...
Illinois professor describes how whaling shaped U.S. culture even after petroleum replaced it
2023-08-14
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — The whaling industry helped drive industrialization in the 19th century, with whale oil used to light lamps and lubricate machinery. Even after petroleum replaced whale oil as an energy source in the U.S., whaling continued to be part of our cultural imagination and helped develop the idea of an energy industry, said University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign English professor Jamie L. Jones.
Her new book, “Rendered Obsolete: The Afterlife of U.S. Whaling in the Petroleum Age,” examines the influence of a dying industry during the massive energy transition from the organic fuel sources of the 19th century, including whale oil and wood, to the extraction of fossil ...
In battle against pancreatic cancer, grant-funded H-FIRE study offers hope
2023-08-14
Only about 10 percent of patients survive as long as five years after a diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
“Pancreatic cancer is very hard to treat,” said Irving Coy Allen, professor of inflammatory diseases in the Department of Biomedical Sciences and Pathology at the Virginia-Maryland College of Veterinary Medicine. “It's one of the top five deadliest cancers in the U.S. And it's deadly because by the time you find out that you have a tumor, it's usually metastasized. You can usually treat the local tumor, but how do you treat the metastatic lesions?”
The National Institutes of Health has awarded $2.6 million to a Virginia Tech team ...
Consumers who buy cannabis products containing HHCs could be getting less than they hoped for
2023-08-14
Key takeaways
In the fast-growing marketplace for recreational marijuana and related products, products containing cannabinoids called HHCs are gaining popularity.
The neurological and physiological effects of HHCs are not well understood.
A new study by UCLA chemists is the first to explain how well HHCs bind to receptors in the human body; the scientists also devised a safer way to produce HHCs than the current standard process.
As more of the nation has adopted legal marijuana, a glut of products has emerged in dispensaries that contain the psychoactive ingredient in marijuana, ...
A new way to evaluate the impact of medical research
2023-08-14
Scientific journals and research papers are evaluated by a metric known as their “impact factor,” which is based on how many times a given paper is cited by other papers. However, a new study from MIT and other institutions suggests that this measure does not accurately capture the impact of medical papers on health outcomes for all patients, particularly those in low- or middle-income countries.
To more fully capture a paper’s impact on health, metrics should take into account the demographics of the researchers who performed the ...
Department of Energy announces $112 million for research on computational projects in fusion energy sciences
2023-08-14
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science (SC), announced $112 million in funding for 12 projects that focus on collaborations among fusion scientists, applied mathematicians, and computer scientists to maximize the use of high performance computing, including exascale computers.
The Scientific Discovery through Advanced Computing (SciDAC) program pairs the Fusion Energy Sciences (FES) program with the Advanced Scientific Computing Research (ASCR) program to explore solving complex ...
Cancer-infecting virus ‘warms up’ cold tumors and improves immunotherapy
2023-08-14
Equipping cancer-infecting, or oncolytic, viruses with tumor-inhibiting genetic cargo stimulates the immune system and helps immunotherapy to shrink or completely clear aggressive tumors in mice, according to a new study in the Journal of Experimental Medicine led by University of Pittsburgh and UPMC researchers. The results pave the way for clinical trials combining oncolytic viruses with immunotherapy.
Oncolytic viruses are genetically modified viruses that target rapidly dividing tumor cells while avoiding normal cells. Oncolytic viruses were originally designed to directly kill cancer cells, but researchers later ...
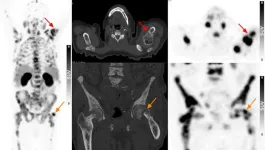
PSMA PET/CT waives the need for pre-imaging biopsy in elderly patients
2023-08-14
Reston, VA—In elderly patients with suspected prostate cancer, PSMA PET/CT can diagnose advanced disease and aid in therapy selection without the need for a biopsy. Published in the July issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, this new research demonstrates how imaging with PSMA PET/CT can potentially reduce the number of prostate biopsies and associated complications in the elderly while providing accurate staging data.
68Ga-PSMA PET/CT has gained acceptance as a highly sensitive and specific imaging modality for evaluating the extent of disease in prostate cancer patients. In general, PSMA PET/CT is indicated when intermediate ...
How did South African healthcare workers cope during the pandemic?
2023-08-14
A new study by UC Berkeley Anthropology Professor Andrew Wooyoung Kim reveals resilient coping mechanisms used by healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic in metro Johannesburg, South Africa.
Titled “Coping strategies employed by public psychiatric healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic in southern Gauteng, South Africa,”(link is external) Kim's paper was published in PLOS ONE in August. It explores the diverse coping strategies employed by public psychiatric healthcare workers during ...