(Press-News.org) Most infants admitted to the intensive care or high acuity unit for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections during fall 2022 were previously healthy and born at term, according to a new study reported in JAMA Network Open.
The findings from this study support the use of preventative interventions in all infants to protect them from RSV, the leading cause of lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI) and hospitalizations worldwide.
RSV accounts for about 57,000-80,000 hospitalizations in children younger than 5 years with 1 in 5 RSV-positive hospitalized children being admitted to intensive care units, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
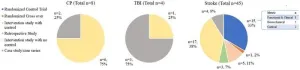
Researchers across the United States evaluated the characteristics and outcomes of RSV-related critical illness in 600 infants from 39 hospitals across 27 states as part of the RSV Pediatric Intensive Care registry.
The registry conducted prospective surveillance during the RSV seasonal peak in 2022. During the two-month period, the investigators found:
The median age for infants requiring intensive care was 2.6 months.
169 (28%) were premature.
487 (81%) had no underlying medical conditions.
143 (24%) received invasive mechanical ventilation.
“Most of the infants in our study receiving ICU-level care were young, healthy and born at term,” said lead investigator Natasha Halasa, MD, MPH, Craig Weaver Professor of Pediatrics in the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt. “Although mortality was rare, our findings emphasize the significant illness caused by RSV in young infants.”
Children with a history of prematurity or certain underlying medical conditions such as congenital heart disease, neurologic or neurodevelopmental/neuromuscular disorders, chronic lung disease and immunocompromising conditions are at higher risk for life-threatening RSV disease, according to Halasa and co-corresponding author Angela Campbell, MD, MPH, from the CDC.
High-risk infants are the only eligible population approved to receive a monoclonal antibody to prevent RSV-associated LRTI called palivizumab.
“However, most infants in our study admitted to the ICU with severe RSV did not have an underlying medical condition. Therefore, our data support the need for RSV preventative interventions targeting all infants to reduce the burden of severe RSV illness, including nirsevimab, the long-acting RSV-neutralizing monoclonal antibody. The drug was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration, and a maternal vaccine for RSV prevention is under consideration,” Halasa said.
“These products may protect both high-risk and healthy infants from medically attended RSV-associated LRTI.”
On Aug. 3, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) unanimously recommended nirsevimab for all infants younger than 8 months, born during or entering their first RSV season and for children ages 8-19 months who are at increased risk of severe RSV disease and entering their second RSV season. Additionally, ACIP unanimously recommended inclusion of nirsevimab in the Vaccines for Children program.
The current study found that only 2 of 17 infants eligible for palivizumab received the treatment, which highlights administration barriers and emphasizes the need to ensure that all eligible patients receive therapeutic interventions in a timely manner. Since nirsevimab requires only one shot versus monthly shots, it is believed that uptake and compliance will be improved.
“We hope that our study findings will aid in the design of future RSV prophylactic and maternal RSV vaccine effectiveness and usage studies and recommendations,” Halasa said.
The study was supported by the CDC.
END
Study finds most infants receiving ICU-level care for RSV had no underlying medical condition
2023-08-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Making sense of life’s random rhythms
2023-08-15
CLEVELAND–Life’s random rhythms surround us–from the hypnotic, synchronized blinking of fireflies…to the back-and-forth motion of a child’s swing… to slight variations in the otherwise steady lub-dub of the human heart.
But truly understanding those rhythms—called stochastic, or random, oscillations—has eluded scientists. While researchers and clinicians have some success in parsing brain waves and heartbeats, they’ve been unable to compare or catalogue an untold number of variations and sources.
Gaining such insight into the underlying ...
Robotic exoskeletons and neurorehabilitation for acquired brain injury: Determining the potential for recovery of overground walking
2023-08-15
East Hanover, NJ. August 15, 2023. A team of New Jersey researchers reviewed the evidence for the impact of robotic exoskeleton devices on recovery of ambulation among individua5ls with acquired brain injury, laying out a systematic framework for the evaluation of such devices that is needed for rigorous research studies. The open access article, "Lower extremity robotic exoskeleton devices for overground ambulation recovery in acquired brain injury – A review” (doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2023/1014616), was published ...
New genetic relations between irritable bowel syndrome and psychiatric diseases discovered
2023-08-15
We have all felt the workings of the so called “brain-gut-axis”, how our intestines get affected, for example, by stress. But still, researchers don’t know a lot about the relation between our gut and our brain.
Research has identified genetic correlations between patients suffering from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and psychiatric disorders, such as bipolar disorder.
By using new statistical methods, developed at NORMENT Centre, Post Doctor Markos Tesfaye at the University of Bergen and University of Oslo and his colleagues working under the leadership ...
First-of-its-kind study reveals predictive factors for outcomes of advanced stage AL amyloidosis
2023-08-15
(WASHINGTON, August 15, 2023) – Early improvements in cardiac and hematologic parameters may predict better survival outcomes for patients being treated for stage IIIb AL amyloidosis, a deadly disease with a median survival of 4-6 months caused by abnormal protein buildup, according to new research released today in Blood Advances.
Amyloidosis occurs when normal proteins in the body misfold and form amyloid deposits in vital organs and tissues, which can lead to organ dysfunction, failure, and death. The prognosis for patients with advanced cardiac amyloidosis is extremely poor, ...
Innovative research on schistosomiasis-associated colorectal cancer (SA-CRC) yields unique insights into genetic mutations and treatment implications
2023-08-15
In a study published in the journal Genes & Diseases, researchers from Naval Medical University and Soochow University conducted an in-depth investigation into the genomic landscape of schistosomiasis-associated colorectal cancer (SA-CRC). By utilizing whole exome sequencing on tumor tissues and their non-tumor counterparts obtained from thirty SA-CRC patients diagnosed at Changzheng Hospital from 2014 to 2020, the team successfully identified 2476 nonsynonymous mutations spanning across 1978 genes. This intricate analysis revealed a lower median tumor mutation burden (TMB) in SA-CRC compared to sporadic colorectal cancer (S-CRC), ...
15 students selected amongst hundreds to serve as national Youth Heart Ambassadors
2023-08-15
DALLAS, August 15, 2023 — Fifteen students from coast to coast are joining the American Heart Association, a global force for healthier lives for all, to champion their peers to live heart healthy. Representing a diversity of backgrounds and experiences, these youth selected as national volunteer Youth Heart Ambassadors for the association’s in-school programs, Kids Heart Challenge™ and American Heart Challenge™ will share how heart disease and stroke have impacted their lives while encouraging others to ...
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation awarded $2.2 million NIH grant to develop advanced treatment for diabetic foot ulcers
2023-08-15
(LOS ANGELES) – August 15, 2023 - A team of researchers from the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) and the University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC) has been awarded a multimillion-dollar grant from the National Institutes of Health to develop a superior, multi-pronged wound treatment for diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs).
DFUs remain a significant complication resulting from dysregulated internal pathophysiological conditions in diabetic patients. The unresolved diabetic wounds affect patients’ quality of life and can result in amputations ...
Novel study shows greater metabolic response to animal versus plant proteins in young and older adults
2023-08-15
Protein from two ounce-equivalents (oz-eq) of animal-based protein foods provides greater essential amino acids (EAA) bioavailability than an equal two oz-eq of plant-based protein foods, according to scientists at Purdue University.1
The protein quality of a food or meal (i.e., the EAA content of a meal) is a major factor in determining how the body can use amino acids for muscle and whole-body protein building.2-4
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGAs) puts an emphasis on consuming a variety of protein foods based on ounce-equivalent portions with similar nutritional ...
Gold buckyballs, oft-used nanoparticle ‘seeds’ are one and the same
2023-08-15
HOUSTON – (Aug. 15, 2023) – Rice University chemists have discovered that tiny gold “seed” particles, a key ingredient in one of the most common nanoparticle recipes, are one and the same as gold buckyballs, 32-atom spherical molecules that are cousins of the carbon buckyballs discovered at Rice in 1985.
Carbon buckyballs are hollow 60-atom molecules that were co-discovered and named by the late Rice chemist Richard Smalley. He dubbed them “buckminsterfullerenes” because their atomic structure reminded him of architect Buckminster Fuller’s geodesic domes, and the “fullerene” family has grown to include dozens of hollow ...
Weaker transcription factors are better when they work together
2023-08-15
HOUSTON – (Aug. 15, 2023) – Bioengineers can tailor the genomes of cells to create “cellular therapies” that fight disease, but they have found it difficult to design specialized activating proteins called transcription factors that can throw the switch on bioengineered genes without occasionally turning on some of the cell’s naturally occurring genes.
In a study published online in Cell, bioengineers from Rice University, Boston University, Harvard Medical School, Dartmouth College and Harvard University’s Wyss Institute showed they could all but eliminate such “off-target” gene ...