(Press-News.org) The COVID-19 pandemic took disinfecting to new heights. Now, a new study examining a commonly used item might convince you not to let your guard down just yet.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University’s Charles E. Schmidt College of Science tested wristbands of various textures to determine their risk for harboring potentially harmful pathogenic bacteria. Despite being worn daily, routine cleaning of wristbands is generally overlooked or simply ignored.
For the study, researchers tested plastic, rubber, cloth, leather and metal (gold and silver) wristbands to see if there is a correlation between wristband material and the prevalence of bacteria. They investigated the hygienic state of these various types of wristbands worn by active individuals and identified the best protocols to properly disinfect them.
Using standard microbiological assays, researchers looked at bacterial counts, type of bacteria and their distribution on the wristband surfaces. They also conducted a bacteria susceptibility assay study screening the effectiveness of three different disinfectant solutions: Lysol™ Disinfectant Spray; 70 percent ethanol, commonly used in hospitals and alcohol wipes; and a more natural solution, apple cider vinegar.
Results of the study, published in the journal Advances in Infectious Diseases, suggest you may want to “go for the gold” or silver the next time you purchase a wristband. Nearly all wristbands (95 percent) were contaminated. However, rubber and plastic wristbands had higher bacterial counts, while metal ones, especially gold and silver, had little to no bacteria.
“Plastic and rubber wristbands may provide a more appropriate environment for bacterial growth as porous and static surfaces tend to attract and be colonized by bacteria,” said Nwadiuto Esiobu, Ph.D., senior author and a professor of biological sciences in the Charles E. Schmidt College of Science.
The most important predictor of wristband bacteria load was the texture of wristband material and activity (hygiene) of the subject at sampling time. There were no significant differences between males and females in the occurrence or distribution of the bacteria groups.
Bacteria found in the study were common skin residents of the genera Staphylococcus and Pseudomonas, and intestinal organisms of the genera Escherichia, specifically E. coli. Staphylococcus spp was prevalent on 85 percent of the wristbands; researchers found Pseudomonas spp on 30 percent of the wristbands; and they found E. coli bacteria on 60 percent of the wristbands, which most commonly begins infection through fecal-oral transmission.
The gym-goer showed the highest staphylococcal counts, which emphasizes the necessity of sanitizing wristbands after engaging in rigorous activity at the gym or at home.
Staphylococcus aureus is a type of bacteria found on human skin, in the nose, armpit, groin or other areas that cause a wide variety of clinical diseases. Pseudomonas spp., commonly in the environment, can cause infections in the blood, lungs (pneumonia) or other parts of the body after surgery. Enterobacteria are a large family of bacteria including many of the more familiar pathogens such as E. coli and Salmonella.
“The quantity and taxonomy of bacteria we found on the wristbands show that there is a need for regular sanitation of these surfaces,” said Esiobu. “Even at relatively low numbers these pathogens are of public health significance. Importantly, the ability of many of these bacteria to significantly affect the health of immunocompromised hosts indicates a special need for health care workers and others in hospital environments to regularly sanitize these surfaces.”
Findings from the study showed that Lysol™ Disinfectant Spray and 70 percent ethanol were highly effective regardless of the wristband material with 99.99 percent kill rate within 30 seconds. Apple cider vinegar was not as potent and required a full two-minute exposure to reduce bacterial counts. While these common household disinfectants all proved at least somewhat effective on all materials (rubber, plastic, cloth and metal), antibacterial efficacy was significantly increased at two minutes compared to thirty seconds.
Different disinfectants, depending on their active ingredients, kill bacteria in different ways, such as by disrupting cell membrane integrity, altering or removing proteins or interfering with metabolic activities.
“Other potential forms of bacterial transmission and facilitation of infection, such as earbuds or cell phones, should be similarly studied,” said Esiobu.
Study co-authors are Joseph Mendonca; Belen Wertheimer; Daynalee Dixon; Bodhi Stone; and Karim Dawkins, FAU undergraduate and graduate students within the Microbial Biotechnology Laboratory, Department of Biological Sciences, Charles E. Schmidt College of Science; and Miranda Christian, a former reporter in West Palm Beach.
- FAU -
About Florida Atlantic University:
Florida Atlantic University, established in 1961, officially opened its doors in 1964 as the fifth public university in Florida. Today, the University serves more than 30,000 undergraduate and graduate students across six campuses located along the southeast Florida coast. In recent years, the University has doubled its research expenditures and outpaced its peers in student achievement rates. Through the coexistence of access and excellence, FAU embodies an innovative model where traditional achievement gaps vanish. FAU is designated a Hispanic-serving institution, ranked as a top public university by U.S. News & World Report and a High Research Activity institution by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. For more information, visit www.fau.edu.
END
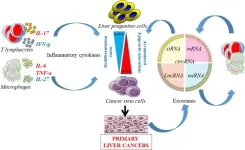
Primary liver cancers ranked as the sixth most commonly diagnosed cancers and the third leading cause of cancer-related death in 2020. Among all primary liver cancers, HCC is the most common cancer, accounting for more than 80% of cases with a 5-year survival rate of less than 10% in Western countries. Despite significant progress in diagnosis and treatments, HCC, often diagnosed at late stages, remains a life-threatening disease with an increasing incidence. Therefore, a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms triggering the early steps of tumorigenesis represents a great interest to predict and propose more effective therapeutic ...
Scientists in NEXT Lab, Tsinghua University have revealed the fabrication and engineering techniques of TMDs and provided a comparative view between TMDs and traditional semiconductors, demonstrating the benefit of combining TMDs with traditional semiconductors.
The research, published in IJEM, shows how to fabricate layered semiconductors modulated with various methods, including phase engineering, defect engineering, doping, and alloying. Then the authors discuss various possibilities to combine layered semiconductors with traditional semiconductors.
Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) with suitable ...
Traditional memory technologies face limitations in terms of speed, scalability, and power consumption, making them unsuitable for future data-intensive applications. Ferroelectric memory has garnered immense interest in recent years due to its potential for non-volatile storage, enabling data retention even when the power is turned off. The development of two-dimensional (2D) van der Waals material α-In2Se3 has also opened new opportunities for advancing memory technologies.
Interestingly, ferroelectric memory takes a giant step forward by incorporating the remarkable properties ...
SEATTLE, Wash. August 16, 2023–Distinguished global health leader Ibrahim Abubakar is the recipient of the 2023 Roux Prize for his dedication to improve health outcomes over the last three decades.
Now in its 10th year, the Roux Prize has been recognizing individuals all over the globe who have leveraged evidence-based health data to improve population health. The Roux Prize is awarded by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington’s School of Medicine.
“Prof. Abubakar has been steadfast in his contributions to global health. His expertise and advocacy have directly affected policy implementation and ...
A research team co-led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) and The University of Hong Kong (HKU) has recently made a significant advancement in spinal cord injury treatment by using genetically modified human neural stem cells (hNSCs). They found that specifically modulating a gene expression to a certain level in hNSCs can effectively promote the reconstruction of damaged neural circuits and restore locomotor functions, offering great potential for new therapeutic opportunities for patients with spinal cord injury.
Traumatic spinal cord injury ...
Commercially available mass spectrometers can reliably detect the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. In the journal "Clinical proteomics" researchers from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) present a new method which employs equipment that is already being used in hospitals and laboratories to detect bacterial and fungal infections. It takes just two hours from swab to result. According to the team, the approach can also be easily adapted to detect other pathogens and could thus help in future ...
A ban on using apps to collect data in order to personalize advertising would significantly reduce the spectrum of available apps and the number of updates, according to a study by the Technical University of Munich (TUM) based on the ban concerning Android apps for children. The findings can assist companies in defining their business models and policymakers when regulating targeted advertising.
Most smartphone apps are free. The providers finance them with advertising, often with what is referred to as targeted advertising: The apps evaluate data such as usage behavior and the user's location and even photos and messages ...
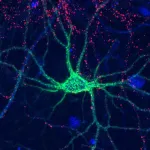
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 16, 2023 — Can you recognize someone you haven’t seen in years, but forget what you had for breakfast yesterday? Our brains constantly rearrange their circuitry to remember familiar faces or learn new skills, but the molecular basis of this process isn’t well understood. Today, scientists report that sulfate groups on complex sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) affect “plasticity” in the brains of mice. Determining how GAGs function could help us understand ...
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 16, 2023 — Indoor air pollution may have met its match. Today, scientists will report that they have designed catalyst-coated lampshades that transform indoor air pollutants into harmless compounds. The lampshades work with halogen and incandescent light bulbs, and the team is extending the technology so it will also be compatible with LEDs.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person ...
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 16, 2023 — A few years ago, amid lockdown boredom, it seemed like everyone was perfecting their sourdoughs. A simple, fermented mixture of flour and water, the bread is powered by microbes that provide its one-of-a-kind tangy flavor. For over a hundred years, sourdough bread has been synonymous with San Francisco, where today, scientists will report that they’ve identified and quantified 21 key chemical compounds that make this bread taste and smell so unique. They’ve also compared the levels of the compounds in different breads.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society ...