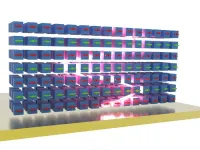
(Press-News.org) A new study led by Vinod M. Menon and his group at the City College of New York shows that trapping light inside magnetic materials may dramatically enhance their intrinsic properties. Strong optical responses of magnets are important for the development of magnetic lasers and magneto-optical memory devices, as well as for emerging quantum transduction applications.
In their new article in Nature, Menon and his team report the properties of a layered magnet that hosts strongly bound excitons -- quasiparticles with particularly strong optical interactions. Because of that, the material is capable of trapping light -- all by itself. As their experiments show, the optical responses of this material to magnetic phenomena are orders of magnitude stronger than those in typical magnets. "Since the light bounces back and forth inside the magnet, interactions are genuinely enhanced," said Dr. Florian Dirnberger, the lead-author of the study. "To give an example, when we apply an external magnetic field the near-infrared reflection of light is altered so much, the material basically changes its color. That's a pretty strong magneto-optic response."
"Ordinarily, light does not respond so strongly to magnetism," said Menon. "This is why technological applications based on magneto-optic effects often require the implementation of sensitive optical detection schemes.”
On how the advances can benefit ordinary people, study co-author Jiamin Quan said: “Technological applications of magnetic materials today are mostly related to magneto-electric phenomena. Given such strong interactions between magnetism and light, we can now hope to one day create magnetic lasers and may reconsider old concepts of optically controlled magnetic memory." Rezlind Bushati, a graduate student in the Menon group, also contributed to the experimental work.
The study conducted in close collaboration with Andrea Alù and his group at CUNY Advanced Science Research Center is the result of a major international collaboration. Experiments conducted at CCNY and ASRC were complemented by measurements taken at the University of Washington in the group of Prof. Xiaodong Xu by Dr. Geoffrey Diederich. Theoretical support was provided by Dr. Akashdeep Kamra and Prof. Francisco J. Garcia-Vidal from the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid and Dr. Matthias Florian from the University of Michigan. The materials were grown by Prof. Zdenek Sofer and Kseniia Mosina at the UCT Prague and the project was further supported by Dr. Julian Klein at MIT. The work at CCNY was supported through the US Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the National Science Foundation (NSF) – Division of Materials Research, the NSF CREST IDEALS center, DARPA and the German Research Foundation.
END
CCNY scientists trap light inside a magnet
2023-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Canadian researchers find radiation not necessary for patients with low-risk breast cancer
2023-08-16
HAMILTON, ON (August 16, 2023) – Some women with early-stage, low-risk breast cancer may not need radiotherapy after breast conserving surgery according to new research led by McMaster University, BC Cancer, Hamilton Heath Sciences, and the University of British Columbia.
The research, published in The New England Journal of Medicine on Aug. 17, shows women 55 or older with a specific subtype of Stage 1 breast cancer can be effectively treated with just surgery and endocrine therapy.
The ...
Small percentage of people with early dementia eligible for new Alzheimer’s drugs
2023-08-16
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, AUGUST 16, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Only a small percentage of older adults who are in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease meet the eligibility criteria to receive new monoclonal antibody treatments, drugs that target amyloid-ß plaques in the brain, an early sign of Alzheimer’s disease. The new research is published in the August 16, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Clinical trial results for these drugs are only available in people in the early symptomatic stages of the disease, mild cognitive impairment ...
Adherence to a Mediterranean lifestyle associated with lower risk of all-cause and cancer mortality
2023-08-16
Key points:
In a study of adults in the United Kingdom, those who adhered closely to a Mediterranean lifestyle—including eating a healthy, plant-based diet with limited added salts and sugars and getting adequate rest, exercise, and socialization—were found to have a 29% lower risk of all-cause mortality and a 28% lower risk of cancer mortality compared to those who were nonadherent to the lifestyle.
Adherence to Mediterranean lifestyle habits around adequate rest, exercise, and socialization was most strongly associated with lower risk of all-cause and cancer mortality, and was independently associated with a lower ...
Bee populations at risk of one-two punch from heat waves, pathogen infection
2023-08-16
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The historically high heat waves that gripped the southwest United States and southern Europe this summer are causing problems for more than just humans. Extreme heat waves affect pollinators and the pathogens that live on them, creating a mutual imbalance that could have major economic and public health consequences.
A global research team led by Penn State was the first to study how extreme heat waves affect the host-pathogen relationship between two species of solitary bees (Osmia cornifrons and Osmia lignaria) and a protozoan pathogen (Crithidia mellificae). The researchers recently published their findings in the journal Frontiers ...
Brinter joins RegenMed Hub
2023-08-16
WINSTON-SALEM, NC, August 2023 – Brinter Bio-Implant company joined the RegeneratOR’s Innovation Accelerator in 2023, located in the Regenerative Medicine Hub (RegenMed Hub), a rapidly growing regenerative medicine ecosystem based in the Innovation Quarter, in Winston-Salem.
Brinter is developing the world’s first personalized 3D bioprinted implants for meniscus repair using the company’s patented 3D bioprinting technology. The company’s bioprinters use a modular multi-material 3D bioprinting platform scalable from manual ...
Researchers achieve high-speed super-resolution imaging with a large field of view
2023-08-16
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a fluorescence microscope that uses structured illumination for fast super-resolution imaging over a wide field of view. The new microscope was designed to image multiple living cells simultaneously with a very high resolution to study the effects of various drugs and mixtures of drugs on the body.
“Polypharmacy — the effect of the many combinations of drugs typically prescribed to the chronically sick or elderly — can lead to dangerous interactions and is becoming a major issue,” said Henning Ortkrass ...
Attitudes toward minorities with dual social identities appear to be driven more by the positive influence of the shared identity than the potential negative influence of the unshared foreign identity
2023-08-16
In a new study, the attitudes of non-Muslim American participants towards Muslim Americans who identified strongly with both parts of their dual identity—Muslim and American—were just as positive as their attitudes towards Muslim Americans who identified only as American. In addition, exposure to dual-identified Muslim Americans was linked to more positive attitudes towards non-American Muslims. The same was also found in the American-Mexican context. Aharon Levy of Columbia University and Yale University, US, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 16, 2023.
Many prior studies have shown that people tend to have positive attitudes ...
Mosquito nets treated with multiple insecticides can control malaria when pyrethroid resistance leads normal nets to fail
2023-08-16
Mosquito nets treated with multiple insecticides can control malaria when pyrethroid resistance leads normal nets to fail
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0289469
Article Title: Effectiveness of dual active ingredient insecticide-treated nets in preventing malaria: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Author Countries: Australia, USA, Malawi
Funding: This work was funded by the World Health Organisation, APW202903809 The funder of the study had a role in the development of the protocol, the wording and development of the review questions, the interpretation ...
Good dogs: owners of recently-adopted shelter dogs tend to report high satisfaction with their new pet despite also reporting increases in problem behavior over time
2023-08-16
Shelter dogs followed at their new homes for six months post-adoption were reported as showing more behaviors like stranger aggression or training problems by the end of the study—but owner satisfaction remained high, with 94 percent of owners reporting their dog’s behavior as excellent or good, according to a study published August 16, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Kyle Bohland from the Ohio State University, US, and colleagues.
Although two million dogs are adopted from US shelters every year, very little research has been done on shelter dog behavior after placement into a home. Bohland and colleagues surveyed ...
Study uncovers impact of 1918 “Spanish flu” pandemic on infant health
2023-08-16
In the wake of the 1918/1919 “Spanish flu” influenza pandemic, the probability of low birth weight and stillbirth increased among women in Switzerland, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE Kaspar Staub of the University of Zurich, Switzerland, and colleagues.
Impaired neonatal health is an ongoing public health concern worldwide. Understanding determinants that impede normal fetal and infant development and growth is crucial for ameliorating neonatal ...