(Press-News.org) In a new study, the attitudes of non-Muslim American participants towards Muslim Americans who identified strongly with both parts of their dual identity—Muslim and American—were just as positive as their attitudes towards Muslim Americans who identified only as American. In addition, exposure to dual-identified Muslim Americans was linked to more positive attitudes towards non-American Muslims. The same was also found in the American-Mexican context. Aharon Levy of Columbia University and Yale University, US, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 16, 2023.
Many prior studies have shown that people tend to have positive attitudes towards others who are part of their own social ingroup and negative attitudes towards outgroup members. However, people increasingly encounter individuals with dual or multiple social identities, and relatively few studies have examined people’s attitudes towards others with dual identities that simultaneously include both an ingroup and an outgroup.
To help deepen understanding of such attitudes, Levy and colleagues conducted a series of survey-based analyses involving a total of several hundred American participants. The researchers first evaluated non-Muslim American participants’ attitudes towards Muslim Americans who identified more strongly as Americans (the ingroup), as Muslims (the outgroup), or as both, equally. They also conducted a similar analysis focused on Mexican Americans.
In the context of both Muslim Americans and Mexican Americans, the analyses showed that participants’ attitudes towards people who equally strongly identified with both the ingroup and outgroup parts of their identity (dual-identified) were just as positive as towards those who primarily identified with the ingroup.
There were also signs of a “gateway group effect:” exposure to strongly dual-identified people was associated with more positive attitudes towards the relevant outgroup—that is, non-American Muslims or non-American Mexicans. However, when people with dual identities identified more strongly with the outgroup part of their identity (Muslim or Mexican), the gateway effect disappeared, and attitudes towards the outgroup sometimes became more negative.
The researchers acknowledge limitations to their study and outline how future research could further deepen understanding. Nonetheless, they note, their findings could help inform efforts to improve intergroup relations.
The authors add: “Many people believe that to be fully accepted by a host culture, minority groups must assimilate with the majority culture (e.g., Latinx immigrants becoming more American). However, our findings suggest that, in terms of intergroup attitudes, explicitly embracing both identities (e.g., Latinx & American) can be as beneficial as fully assimilating only to the majority identity. This means that minorities may not need to relinquish any part of their identity as long as they also identify with the majority group identity. Moreover, we have found that the positive influence of the dual identification is also extended to the corresponding outgroup (e.g., the relationship between non-Latinx Americans and Latin America), with the dual-identity group serving as a gateway to more positive intergroup attitudes.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287631
Citation: Levy A, Galinsky A, Nguyen CQ, Saguy T, Ikizer EG, Dovidio JF (2023) Ingroup love, outgroup hate, and the gateway group effect: Comparing the direct and indirect impact of dual versus single identification. PLoS ONE 18(8): e0287631. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0287631
Author Countries: USA, Israel
Funding: This research was supported by National Science Foundation Grant #1823763 given to authors AL, TS, and JF. https://www.nsf.gov/. The funders did not play any role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Attitudes toward minorities with dual social identities appear to be driven more by the positive influence of the shared identity than the potential negative influence of the unshared foreign identity
Exposure to groups explicitly identifying with dual social identities is linked with improved intergroup attitudes amongst both Muslim-Americans and Mexican-Americans
2023-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mosquito nets treated with multiple insecticides can control malaria when pyrethroid resistance leads normal nets to fail
2023-08-16
Mosquito nets treated with multiple insecticides can control malaria when pyrethroid resistance leads normal nets to fail
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0289469
Article Title: Effectiveness of dual active ingredient insecticide-treated nets in preventing malaria: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Author Countries: Australia, USA, Malawi
Funding: This work was funded by the World Health Organisation, APW202903809 The funder of the study had a role in the development of the protocol, the wording and development of the review questions, the interpretation ...
Good dogs: owners of recently-adopted shelter dogs tend to report high satisfaction with their new pet despite also reporting increases in problem behavior over time
2023-08-16
Shelter dogs followed at their new homes for six months post-adoption were reported as showing more behaviors like stranger aggression or training problems by the end of the study—but owner satisfaction remained high, with 94 percent of owners reporting their dog’s behavior as excellent or good, according to a study published August 16, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Kyle Bohland from the Ohio State University, US, and colleagues.
Although two million dogs are adopted from US shelters every year, very little research has been done on shelter dog behavior after placement into a home. Bohland and colleagues surveyed ...
Study uncovers impact of 1918 “Spanish flu” pandemic on infant health
2023-08-16
In the wake of the 1918/1919 “Spanish flu” influenza pandemic, the probability of low birth weight and stillbirth increased among women in Switzerland, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE Kaspar Staub of the University of Zurich, Switzerland, and colleagues.
Impaired neonatal health is an ongoing public health concern worldwide. Understanding determinants that impede normal fetal and infant development and growth is crucial for ameliorating neonatal ...
Schizophrenia genetic risk factor impairs mitochondrial function
2023-08-16
Researchers at Rutgers and Emory University are gaining insights into how schizophrenia develops by studying the strongest-known genetic risk factor.
When a small portion of Chromosome 3 is missing – known as 3q29 deletion syndrome – it increases the risk for schizophrenia by about 40 fold. Researchers have now analyzed overlapping patterns of altered gene activity in two models of 3q29 deletion syndrome, including mice where the deletion has been engineered in using CRIPSR, and human brain organoids, or three-dimensional tissue cultures used to study disease. These two systems both exhibit impaired mitochondrial ...
Greater excess mortality after hurricanes more recently and for most socially vulnerable in the U.S.
2023-08-16
Over recent decades, there was a large variation in cyclone-related excess deaths by hurricane, state, county, year, and social vulnerability for counties in the United States, with 83 percent of hurricane-related deaths occurring more recently and 94 percent in more socially vulnerable counties. Results of a study by researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, Colorado State University, Imperial College London, University of California Irvine, and Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health are published in the journal Science ...
Research informs WHO malaria net guideline update
2023-08-16
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has updated its recommendation for malaria-preventing mosquito nets based on new research from the University of Adelaide.
Dr Timothy Barker, of the JBI Adelaide GRADE Centre, located at the University of Adelaide, led a team which proved the effectiveness of a combination of insecticides when used to treat malaria-preventing mosquito nets.
Mosquito nets treated with pyrethroid insecticides have been distributed into malaria-prone regions globally since 2005, but some mosquito populations have developed a resistance to the substance.
“The number of malaria cases actually ...
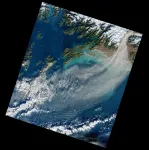
What role do dust storms play in the world’s climate?
2023-08-16
Giant dust storms in the Gulf of Alaska can last for many days and send tonnes of fine sediment or silt into the atmosphere, and it is having an impact on the global climate system, say scientists.
The storms are so extensive they can be seen by satellites orbiting the Earth. An image captured by the Landsat satellite in 2020 shows dust blowing out of the valley and over Alaska’s south coast.
Exactly how the dust may be influencing the global climate system is not yet clear, although new research from the University of Leeds and the National Centre for Atmospheric ...
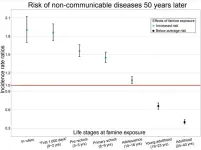
Children and adolescents of the 1959-61 Chinese famine: Survivors face increased risk of non-communicable diseases 50 years later, with those exposed in utero or under age 2 at double the risk
2023-08-16
Children and adolescents of the 1959-61 Chinese famine: Survivors face increased risk of non-communicable diseases 50 years later, with those exposed in utero or under age 2 at double the risk.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0002161
Article Title: Exposure to the 1959–1961 Chinese famine and risk of non-communicable diseases in later life: A life course perspective
Author Countries: Switzerland, UK
Funding: Mengling Cheng acknowledges funding from the Swiss National Centre of Competence in Research “LIVES - Overcoming vulnerability: ...
The evolution of complex grammars
2023-08-16
Languages around the world differ greatly in how many grammatical distinctions they make. This variation is observable even between closely related languages. The speakers of Swedish, Danish, and Norwegian, for example, use the same word hunden, meaning "the dog", to communicate that the dog is in the house or that someone found the dog or gave food to the dog. In Icelandic, on the other hand, three different word forms would be used in these situations, corresponding to the nominative, accusative, and dative case respectively: hundurinn, hundinn, and hundinum.
This grammatical distinction in the case system, along with many others, sets Icelandic apart ...
DOE’s Office of Science is now accepting applications for Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) Awards
2023-08-16
Washington, D.C. - The Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science is pleased to announce that the Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) program is now accepting applications for the 2023 Solicitation 2 cycle. Applications are due on November 8, 2023, at 5:00 pm ET.
SCGSR application assistance workshops will be held on Thursday, September 14, 2023, 2:00 PM – 3:30 PM ET and Tuesday, October 10, 2023, 2:00 PM – 4:30 PM ET. The first workshop will provide a general overview of the program and the application requirements and will include a time for discussing potential research topics ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
[Press-News.org] Attitudes toward minorities with dual social identities appear to be driven more by the positive influence of the shared identity than the potential negative influence of the unshared foreign identityExposure to groups explicitly identifying with dual social identities is linked with improved intergroup attitudes amongst both Muslim-Americans and Mexican-Americans