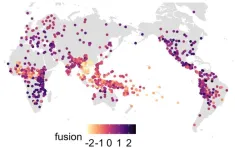
(Press-News.org) Languages around the world differ greatly in how many grammatical distinctions they make. This variation is observable even between closely related languages. The speakers of Swedish, Danish, and Norwegian, for example, use the same word hunden, meaning "the dog", to communicate that the dog is in the house or that someone found the dog or gave food to the dog. In Icelandic, on the other hand, three different word forms would be used in these situations, corresponding to the nominative, accusative, and dative case respectively: hundurinn, hundinn, and hundinum.
This grammatical distinction in the case system, along with many others, sets Icelandic apart from its closely related sister languages. “One prominent hypothesis about why some languages show more complex grammar than others links grammatical complexity to the social environments in which these languages are used”, says first author Olena Shcherbakova from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. For example, Icelandic is primarily learned and used by the local population of over 350,000 people. Such relatively small isolated communities are also called ‘societies of intimates’. In contrast, the other Scandinavian countries, located in close proximity to their neighbours, have larger populations with substantial proportions of non-native speakers. Such communities are known as ‘societies of strangers’. Many linguists have claimed that languages with more non-native speakers tend to simplify their grammars as, unlike children, adult learners struggle to acquire complex grammatical rules to master the intricacies of their new language.
But is this Icelandic example representative of the striking linguistic diversity worldwide? Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Evolutionary Anthropology wanted to find out if the grammars of languages tend to evolve simpler when spoken by larger societies of strangers with many non-native speakers. They measured the grammatical complexity of 1,314 languages using data from Grambank – a newly released global database of grammatical features. These complexity scores were compared to variables detailing the number of non-native speakers in these languages.
Defining complexity
Language complexity is a hotly debated topic in linguistics, with many different opposing views. "Many of the disagreements are down to differences in how 'complexity' is defined", says Hedvig Skirgård from the Max Planck Institute of Evolutionary Anthropology. "In this study, we improved the methodology by teasing out two distinct measures: fusion (how many affixes verbs and nouns have) and informativity (how many distinctions are made).“
The results show that societies of strangers do not speak less complex languages. “Instead, our study reveals that the variation in grammatical complexity generally accumulates too slowly to adapt to the immediate environment”, states Shcherbakova. The well-known counter-example to the claim about social environment shaping grammatical complexity is German. German is learned and spoken by a large number of non-native speakers and yet, it retained its case system and many other grammatical distinctions.
The study tests the influence of social environment on grammatical complexity, while accounting for the expected similarities arising from both genealogical inheritance and contact. “Our study highlights the significance of using large-scale data and accounting for the influence of inheritance and contact when addressing long-standing questions about the evolution of languages. It shows how received linguistic wisdom can be rigorously tested with the global datasets that are increasingly becoming available,” concludes Simon Greenhill from the University of Auckland.
END
The evolution of complex grammars
A new study shows that changes in grammatical complexity are not shaped by social environments
2023-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
DOE’s Office of Science is now accepting applications for Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) Awards
2023-08-16
Washington, D.C. - The Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science is pleased to announce that the Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) program is now accepting applications for the 2023 Solicitation 2 cycle. Applications are due on November 8, 2023, at 5:00 pm ET.
SCGSR application assistance workshops will be held on Thursday, September 14, 2023, 2:00 PM – 3:30 PM ET and Tuesday, October 10, 2023, 2:00 PM – 4:30 PM ET. The first workshop will provide a general overview of the program and the application requirements and will include a time for discussing potential research topics ...
Occupational safety and health training program grant renewed
2023-08-16
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, a division of the National Institutes of Health, awarded a $750,000 training program grant to researchers at the Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health to support master’s students in the Industrial Hygiene Program.
Industrial hygiene is the art and science devoted to the anticipation, recognition, evaluation and control of workplace hazards. It focuses on worker protection from hazards that could include chemical, physical, biological, radiological and ergonomic agents.
“Occupational injury and illness affect millions of workers and their families every year and are tremendous ...
Inaugural theme issue: Precision public health from online Journal of Public Health Informatics
2023-08-16
Online Journal of Public Health Informatics (OJPHI) Editor-in-Chief: Edward K Mensah PhD, MPhil and theme editor Nsikak Akpakpan MD, PhD welcome submissions to a special theme issue examining "Precision Public Health."
The inaugural issue of the Online Journal of Public Health Informatics under the JMIR Publications platform will feature articles on precision public health, a technology-enhanced, data-driven targeted approach to public health practice and research.
The current special issue invites articles in the following as well ...
UC Irvine scientists say deepening Arctic snowpack drives greenhouse gas emissions
2023-08-16
Irvine, Calif., Aug. 16, 2023 — Human-caused climate change is shortening the snow cover period in the Arctic. But according to new research led by Earth system scientists at the University of California, Irvine, some parts of the Arctic are getting deeper snowpack than normal, and that deep snow is driving the thawing of long-frozen permafrost carbon reserves and leading to increased emissions of greenhouse gasses like carbon dioxide and methane.
“It is the first long-term experiment where we directly measure the mobilization of ancient carbon year-round to show that deeper snow has the possibility to rather ...
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $3.9 million to exceptional early-career scientists
2023-08-16
The Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation has named 13 new Damon Runyon Fellows, exceptional postdoctoral scientists conducting basic and translational cancer research in the laboratories of leading senior investigators. This prestigious Fellowship encourages the nation’s most promising young scientists to pursue careers in cancer research by providing them with independent funding to investigate cancer causes, mechanisms, therapies, and prevention. In July 2023, the Board of Directors announced a 15% ...
Assessing controls on ocean productivity – from space
2023-08-16
Phytoplankton determine how much life the ocean is able to support and play a role in controlling atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations, thereby regulating our climate. These tiny marine plants depend on sunlight as well as nutrients to thrive – including elements such as iron or nitrogen that can be brought to the ocean surface by currents and upwelling.
To understand phytoplankton nutrient limitations in the ocean, scientists typically conduct experiments during research expeditions at sea. However, this approach documents only a tiny fraction of the ocean at a certain point in time. Therefore, an international team of researchers tested if a signal detected by satellites in ...
Medications for chronic diseases affect the body’s ability to regulate body temperature, keep cool
2023-08-16
Medications to treat various chronic diseases may hinder the body’s ability to lose heat and regulate its core temperature to optimal levels. The loss of effective thermoregulation has implications for elderly people receiving treatment for illnesses like cancer, cardiovascular, Parkinson’s disease/dementia and diabetes, particularly during hot weather, according to a review by a team of scientists from various institutions in Singapore.
The group, led by Associate Professor Jason Lee from the Human Potential Translational Research Programme at the Yong Loo Lin School of ...
New leaf-tailed gecko from Madagascar is a master of disguise
2023-08-16
Leaf-tailed geckos are masters of camouflage. Some species have skin flaps around the whole body and head, as well as flattened tails. During the day, they rest head-down on tree trunks with these skin flaps spread out, and blend seamlessly into their surroundings, making them nearly impossible to spot. At night, they awaken to prowl the fine branches of the understory looking for invertebrate prey.
“When we first discovered this species in 2000, we already suspected it might be new to science,” says Dr Frank Glaw, curator of herpetology at the Bavarian State Collection of Zoology, lead author on the study. “But ...
MD Anderson research highlights for August 16, 2023
2023-08-16
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include a novel single-cell sequencing technology that allows for rapid analyses of archived and frozen cells, greater understanding of the ...
Switching ‘spin’ on and off (and up and down) in quantum materials at room temperature
2023-08-16
Researchers have found a way to control the interaction of light and quantum ‘spin’ in organic semiconductors, that works even at room temperature.
Spin is the term for the intrinsic angular momentum of electrons, which is referred to as up or down. Using the up/down spin states of electrons instead of the 0 and 1 in conventional computer logic could transform the way in which computers process information. And sensors based on quantum principles could vastly improve our abilities to measure and study the world around us.
An international team of researchers, led by the University of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
People’s gut bacteria worse in areas with higher social deprivation
Unique analysis shows air-con heat relief significantly worsens climate change
Keto diet may restore exercise benefits in people with high blood sugar
Manchester researchers challenge misleading language around plastic waste solutions
Vessel traffic alters behavior, stress and population trends of marine megafauna
Your car’s tire sensors could be used to track you
Research confirms that ocean warming causes an annual decline in fish biomass of up to 19.8%
Local water supply crucial to success of hydrogen initiative in Europe
New blood test score detects hidden alcohol-related liver disease
High risk of readmission and death among heart failure patients
Code for Earth launches 2026 climate and weather data challenges
Three women named Britain’s Brightest Young Scientists, each winning ‘unrestricted’ £100,000 Blavatnik Awards prize
Have abortion-related laws affected broader access to maternal health care?
Do muscles remember being weak?
Do certain circulating small non-coding RNAs affect longevity?
How well are international guidelines followed for certain medications for high-risk pregnancies?
New blood test signals who is most likely to live longer, study finds
Global gaps in use of two life-saving antenatal treatments for premature babies, reveals worldwide analysis
Bug beats: caterpillars use complex rhythms to communicate with ants
High-risk patients account for 80% of post-surgery deaths
Celebrity dolphin of Venice doesn’t need special protection – except from humans
Tulane study reveals key differences in long-term brain effects of COVID-19 and flu
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
New method to remove toxic PFAS chemicals from water
The nanozymes hypothesis of the origin of life (on Earth) proposed
Microalgae-derived biochar enables fast, low-cost detection of hydrogen peroxide
Researchers highlight promise of biochar composites for sustainable 3D printing
Machine learning helps design low-cost biochar to fight phosphorus pollution in lakes
Urine tests confirm alcohol consumption in wild African chimpanzees
[Press-News.org] The evolution of complex grammarsA new study shows that changes in grammatical complexity are not shaped by social environments