(Press-News.org) Leaf-tailed geckos are masters of camouflage. Some species have skin flaps around the whole body and head, as well as flattened tails. During the day, they rest head-down on tree trunks with these skin flaps spread out, and blend seamlessly into their surroundings, making them nearly impossible to spot. At night, they awaken to prowl the fine branches of the understory looking for invertebrate prey.
“When we first discovered this species in 2000, we already suspected it might be new to science,” says Dr Frank Glaw, curator of herpetology at the Bavarian State Collection of Zoology, lead author on the study. “But it has taken us many years to amass enough information to confidently describe it as a new species.” The team collected data on the genetics, morphology, and the distribution of the species. Several expeditions to northern Madagascar were undertaken that expanded knowledge of this new species. The discovery was announced on the 15th of August in the open-access scientific journal Salamandra.
One challenge was that Uroplatus garamaso is remarkably similar to another species, Uroplatus henkeli, and has been confused with it in the past. “This is quite common for reptiles from Madagascar” explains Dr Jörn Köhler of the Hessisches Landesmuseum Darmstadt. “There are a lot of these so-called ‘cryptic species’, which are waiting for taxonomic treatment.” By careful analysis, the authors were able to find some features that differentiate the two species. “The real key was the discovery that the tip of the tongue is blackish in U. henkeli, whereas it is pink in U. garamaso” says Dr Philip-Sebastian Gehring of the University of Bielefeld, Germany. At 20 cm long, the new species is also a little smaller than U. henkeli, and has a narrower tail.
“The new species is the latest in a series of new Uroplatus geckos described from Madagascar over the last few years,” says Dr Fanomezana Ratsoavina of the University of Antananarivo, Madagascar, who did her PhD on leaf-tailed geckos.
“We are close to completing the taxonomic inventory of the genus, but this is just the start of our understanding of their evolution and ecology,” says Dr Mark Scherz, curator of herpetology at the Natural History Museum of Denmark. “The mouth colour, which has been so useful to identify different species, has a totally unknown function. There is a lot we still do not know about these geckos, from their broader evolutionary relationships to their behaviour.”
Leaf-tailed geckos are masters of camouflage. Some species have skin flaps around the whole body and head, as well as flattened tails. During the day, they rest head-down on tree trunks with these skin flaps spread out, and blend seamlessly into their surroundings, making them nearly impossible to spot. At night, they awaken to prowl the fine branches of the understory looking for invertebrate prey.
“When we first discovered this species in 2000, we already suspected it might be new to science,” says Dr Frank Glaw, curator of herpetology at the Bavarian State Collection of Zoology, lead author on the study. “But it has taken us many years to amass enough information to confidently describe it as a new species.” The team collected data on the genetics, morphology, and the distribution of the species. Several expeditions to northern Madagascar were undertaken that expanded knowledge of this new species. The discovery was announced on the 15th of August in the open-access scientific journal Salamandra.
One challenge was that Uroplatus garamaso is remarkably similar to another species, Uroplatus henkeli, and has been confused with it in the past. “This is quite common for reptiles from Madagascar” explains Dr Jörn Köhler of the Hessisches Landesmuseum Darmstadt. “There are a lot of these so-called ‘cryptic species’, which are waiting for taxonomic treatment.” By careful analysis, the authors were able to find some features that differentiate the two species. “The real key was the discovery that the tip of the tongue is blackish in U. henkeli, whereas it is pink in U. garamaso” says Dr Philip-Sebastian Gehring of the University of Bielefeld, Germany. At 20 cm long, the new species is also a little smaller than U. henkeli, and has a narrower tail.
“The new species is the latest in a series of new Uroplatus geckos described from Madagascar over the last few years,” says Dr Fanomezana Ratsoavina of the University of Antananarivo, Madagascar, who did her PhD on leaf-tailed geckos.
“We are close to completing the taxonomic inventory of the genus, but this is just the start of our understanding of their evolution and ecology,” says Dr Mark Scherz, curator of herpetology at the Natural History Museum of Denmark. “The mouth colour, which has been so useful to identify different species, has a totally unknown function. There is a lot we still do not know about these geckos, from their broader evolutionary relationships to their behaviour.”
END
New leaf-tailed gecko from Madagascar is a master of disguise
An international team of researchers led by Dr. Frank Glaw of the Bavarian State Collection of Zoology has discovered and named a new leaf-tailed gecko from the north of Madagascar: Uroplatus garamaso.
2023-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MD Anderson research highlights for August 16, 2023
2023-08-16
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include a novel single-cell sequencing technology that allows for rapid analyses of archived and frozen cells, greater understanding of the ...
Switching ‘spin’ on and off (and up and down) in quantum materials at room temperature
2023-08-16
Researchers have found a way to control the interaction of light and quantum ‘spin’ in organic semiconductors, that works even at room temperature.
Spin is the term for the intrinsic angular momentum of electrons, which is referred to as up or down. Using the up/down spin states of electrons instead of the 0 and 1 in conventional computer logic could transform the way in which computers process information. And sensors based on quantum principles could vastly improve our abilities to measure and study the world around us.
An international team of researchers, led by the University of ...
Research finds that molecules in vegetables can help to ease lung infection
2023-08-16
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs BST 16 August 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
Research finds that molecules in vegetables can help to ease lung infection
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have found that molecules in vegetables like broccoli or cauliflower help to maintain a healthy barrier in the lung and ease infection.
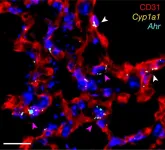
The AHR – aryl hydrocarbon receptor – is a protein found at barrier sites like the gut and the lung. Natural molecules in cruciferous vegetables – for example, kale, cauliflower, broccoli, or cabbage – are dietary ...
Collecting clean water from fog
2023-08-16
In countries such as Peru, Bolivia and Chile, it’s not uncommon for people who live in foggy areas to hang up nets to catch droplets of water. The same is true of Morocco and Oman. These droplets then trickle down the mesh and are collected to provide water for drinking, cooking and washing. As much as several hundred litres of water can be harvested daily using a fog net only a few square metres in area. For regions with little rain or spring water, but where fog is a common occurrence, this can be a blessing.
One crucial drawback with this method, however, ...
Mental illness following physical assault among children
2023-08-16
About The Study: Children who experienced assault had, on average, a 2 times higher risk of receiving a mental illness diagnosis and were more likely than children who had not experienced assault to present to acute care for mental illness. Early intervention to support mental health of assaulted children is warranted, particularly in the first year following assault.
Authors: Natasha Ruth Saunders, M.D., M.Sc., of the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Prevalence, factors associated with vaping CBD among adolescents
2023-08-16
About The Study: In this study of 28,000 middle and high school students, the prevalence of vaping cannabidiol (CBD) was high, particularly among e-cigarette users and Hispanic and sexual minority populations. The findings suggest that evidence-based educational campaigns, interventions, and public policy changes are needed to reduce the harmful health outcomes possible with vaping CBD among developing youths.
Authors: Hongying Daisy Dai, Ph.D., of the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.29167)
Editor’s ...
Patterns in cancer incidence among people younger than age 50
2023-08-16
About The Study: The incidence rates in the U.S. of early-onset cancer (younger than age 50) increased from 2010 to 2019 in this study of 562,000 patients. Although breast cancer had the highest number of incident cases, gastrointestinal cancers had the fastest-growing incidence rates among all early-onset cancers. These data may be useful for the development of surveillance strategies and funding priorities.
Authors: Daniel Q. Huang, M.B.B.S., M.M.E.D., and Cheng Han Ng, M.B.B.S., of the National University of Singapore, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Scientists find way to wipe a cell’s memory to better reprogram it as a stem cell
2023-08-16
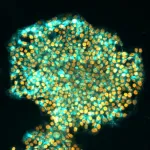
In a groundbreaking study published today in Nature, Australian scientists have resolved a long-standing problem in regenerative medicine. Led by Professor Ryan Lister from the Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research and The University of Western Australia and Professor Jose M Polo from Monash University and the University of Adelaide, the team developed a new method to reprogram human cells to better mimic embryonic stem cells, with significant implications for biomedical and therapeutic uses.
In a revolutionary advance in the mid-2000s, it was ...
Paternal depression and risk of depression among offspring
2023-08-16
About The Study: Paternal depression was associated with subsequent offspring depression in this systematic review and meta-analysis including 7.1 million father-child dyads from 16 observational studies. This finding shows the intergenerational transmission of mental health problems and suggests that mental health interventions benefit not only the patient but also the family as a whole, including both parents.
Authors: Berihun Dachew, Ph.D., of Curtin University in Perth, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Normal graft function after pig-to-human kidney xenotransplant
2023-08-16
About The Study: The findings from this case series show that pig-to-human xenotransplant provided life-sustaining kidney function in a deceased human with chronic kidney disease. Future research in living human recipients is necessary to determine long-term xenograft kidney function and whether xenografts could serve as a bridge or destination therapy for end-stage kidney disease.
Authors: Jayme E. Locke, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Alabama at Birmingham Heersink School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.2774)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
[Press-News.org] New leaf-tailed gecko from Madagascar is a master of disguiseAn international team of researchers led by Dr. Frank Glaw of the Bavarian State Collection of Zoology has discovered and named a new leaf-tailed gecko from the north of Madagascar: Uroplatus garamaso.