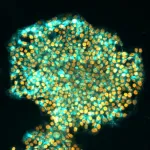
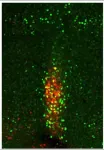
(Press-News.org) In a groundbreaking study published today in Nature, Australian scientists have resolved a long-standing problem in regenerative medicine. Led by Professor Ryan Lister from the Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research and The University of Western Australia and Professor Jose M Polo from Monash University and the University of Adelaide, the team developed a new method to reprogram human cells to better mimic embryonic stem cells, with significant implications for biomedical and therapeutic uses.
In a revolutionary advance in the mid-2000s, it was discovered that the non-reproductive adult cells of the body, called ‘somatic’ cells, could be artificially reprogrammed into a state that resembles embryonic stem (ES) cells which have the capacity to then generate any cell of the body.
The ability to artificially reprogram human somatic cells, such as skin cells, into these so-called induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells provided a way to make an essentially unlimited supply of ES-like cells, with widespread applications in disease modelling, drug screening and cell-based therapies.
“However, a persistent problem with the conventional reprograming process is that iPS cells can retain an epigenetic memory of their original somatic state, as well as other epigenetic abnormalities,” Professor Lister said. “This can create functional differences between the iPS cells and the ES cells they’re supposed to imitate, and specialised cells subsequently derived from them, which limits their use,”.
Professor Jose Polo, who is also with the Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute, explained that they have now developed a new method, called transient-naive-treatment (TNT) reprogramming, that mimics the reset of a cell’s epigenome that happens in very early embryonic development.
“This significantly reduces the differences between iPS cells and ES cells and maximises the effectiveness of how human iPS cells can be applied,” he said.
Dr Sam Buckberry, a computational scientist from the Harry Perkins Institute, UWA, and Telethon Kids Institute, and co-first author of the study, said by studying how the somatic cell epigenome changed throughout the reprogramming process, they pinpointed when epigenetic aberrations emerged, and introduced a new epigenome reset step to avoid them and erase the memory.
Dr Xiaodong Liu, a stem cell scientist who also spearheaded the research said the new human TNT-iPS cells much more closely resembled human ES cells – both molecularly and functionally – than those produced using conventional reprograming.
Dr Daniel Poppe, a cell biologist from UWA, the Harry Perkins Institute and co-first author, said the iPS cells generated using the TNT method differentiated into many other cells, such as neuron progenitors, better than the iPS cells generated with the standard method.
Monash University student and co-first author Jia Tan, said the team’s TNT method was dynamite.
“It solves problems associated with conventionally generated iPS cells that if not addressed could have severely detrimental consequences for cell therapies in the long run,” he said.
Professor Polo said the precise molecular mechanisms underlying the iPS epigenome aberrations and their correction were not fully known, and further research was needed to understand them.
“We predict that TNT reprogramming will establish a new benchmark for cell therapies and biomedical research, and substantially advance their progress,” Professor Lister said.
The collaborative research project also included researchers from the Australian National University, Westlake University, Queen Mary University of London, Mater Research Institute, University of Queensland, Queensland Brain Institute, South Australian Health & Medical Research Institute, Duke-NUS Medical School and CSIRO.
END
Scientists find way to wipe a cell’s memory to better reprogram it as a stem cell
A new method to reprogram human cells to better mimic embryonic stem cells
2023-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Paternal depression and risk of depression among offspring
2023-08-16
About The Study: Paternal depression was associated with subsequent offspring depression in this systematic review and meta-analysis including 7.1 million father-child dyads from 16 observational studies. This finding shows the intergenerational transmission of mental health problems and suggests that mental health interventions benefit not only the patient but also the family as a whole, including both parents.
Authors: Berihun Dachew, Ph.D., of Curtin University in Perth, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Normal graft function after pig-to-human kidney xenotransplant
2023-08-16
About The Study: The findings from this case series show that pig-to-human xenotransplant provided life-sustaining kidney function in a deceased human with chronic kidney disease. Future research in living human recipients is necessary to determine long-term xenograft kidney function and whether xenografts could serve as a bridge or destination therapy for end-stage kidney disease.
Authors: Jayme E. Locke, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Alabama at Birmingham Heersink School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.2774)
Editor’s ...
Blood factor can turn back time in the aging brain
2023-08-16
Blood Factor Can Turn Back Time in the Aging Brain
Platelets are behind the cognitive benefits of young blood, exercise and the longevity hormone klotho
In a remarkable convergence, scientists have discovered that the same blood factor is responsible for the cognitive enhancement that results from young blood transfusion, the longevity hormone klotho, and exercise.
In a trio of papers appearing in Nature, Nature Aging and Nature Communications on August 16, 2023, two UCSF teams and a team from the University of Queensland (Australia), identify platelet ...
How cold temperatures trigger the brain to boost appetite
2023-08-16
LA JOLLA, CA—Neuroscientists at Scripps Research have identified brain circuits that make mammals want to eat more when they are exposed to cold temperatures.
Mammals automatically burn more energy to maintain normal body temperature when exposed to cold. This cold-activated increase in energy expenditure triggers an increase in appetite and feeding, although the specific mechanism controlling this had been unknown. In the new study, reported on August 16, 2023, in Nature, the researchers identified a cluster of neurons that work as a “switch” for this cold-related, food-seeking behavior in mice. The discovery could lead to potential ...
Microplastic pollution: Plants could be the answer
2023-08-16
Could plants be the answer to the looming threat of microplastic pollution? Scientists at UBC’s BioProducts Institute found that if you add tannins—natural plant compounds that make your mouth pucker if you bite into an unripe fruit—to a layer of wood dust, you can create a filter that traps virtually all microplastic particles present in water.
While the experiment remains a lab set-up at this stage, the team is convinced that the solution can be scaled up easily and inexpensively once they find the right industry partner.
Microplastics ...
Directly involved war veterans exhibit nearly twice the PTSD symptoms years after 2014 Israel-Gaza conflict, affecting parents' well-being
2023-08-16
Hebrew University researchers, Shahaf Leshem, Eldad Keha, and Prof. Eyal Kalanthroff, have unveiled significant findings regarding the lasting psychological impacts stemming from the 2014 Israel-Gaza military conflict. The study sheds light on the deep repercussions of trauma for both war veterans and their parents. Notably, veterans directly involved in the conflict exhibited nearly twice the level of PTSD symptoms compared to indirectly active veterans, a difference persisting even five years after the conflict. Remarkably, ...
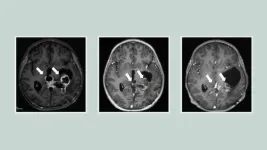
Study finds improved survival for incurable brain tumor, providing ‘a crack in the armor’
2023-08-16
Michigan — For the first time, researchers have found a potential drug candidate that improved outcomes for patients with a type of childhood brain tumor for which there are no effective treatments. The compound, called ONC201, nearly doubled survival for patients with diffuse midline glioma (DMG) or diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG), compared to previous patients.
The findings are reported by an international team of researcher led by the University of Michigan Health Rogel Cancer Center and the Chad Carr Pediatric Brain Tumor Center.
In addition to reporting on the results of two early stage clinical ...
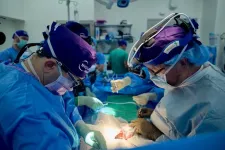
Pig kidney xenotransplantation performing optimally after 32 days in human body
2023-08-16
NEW YORK, NY, AUGUST 16, 2023 — Surgeons at NYU Langone Health have transplanted a genetically engineered pig kidney that continues to function well after 32 days in a man declared dead by neurologic criteria and maintained with a beating heart on ventilator support. This represents the longest period that a gene-edited pig kidney has functioned in a human, and the latest step toward the advent of an alternate, sustainable supply of organs for transplant.
Multimedia Materials Available
Multimedia materials, including photos and a B-roll package, are available for download.
About the Procedure
The procedure, performed on July 14, 2023, and led by Robert Montgomery, ...
ASBMB names 2024 award winners
2023-08-16
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology announced today the winners of its annual awards. Colleagues and other leaders in the field nominated the winners for making significant contributions to biochemistry and molecular biology and the training of emerging scientists.
The recipients will give talks about their work at the society’s 2024 annual meeting, Discover BMB, slated for March 23–26 in San Antonio.
In addition to cash prizes ranging from $2,000 to $35,000, each ASBMB award consists of a plaque and transportation ...
New and updated resources published to help guide oncology care in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA)
2023-08-16
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [August 16, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—today announced that a library of resources for improving cancer care in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) has been updated and expanded in collaboration with regional experts. The United States-based non-profit has worked with the King Abdulaziz Medical City in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, since 2015 to standardize cancer treatment based on the latest evidence and expert-consensus, as part of the MENA-NCCN Regional Coordinating Center. Their efforts have led to the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Scientists find way to wipe a cell’s memory to better reprogram it as a stem cellA new method to reprogram human cells to better mimic embryonic stem cells