Inaugural theme issue: Precision public health from online Journal of Public Health Informatics
2023-08-16
(Press-News.org) Online Journal of Public Health Informatics (OJPHI) Editor-in-Chief: Edward K Mensah PhD, MPhil and theme editor Nsikak Akpakpan MD, PhD welcome submissions to a special theme issue examining "Precision Public Health."
The inaugural issue of the Online Journal of Public Health Informatics under the JMIR Publications platform will feature articles on precision public health, a technology-enhanced, data-driven targeted approach to public health practice and research.
The current special issue invites articles in the following as well as other interesting areas of precision public health:
Use of big data to predict public health risks such as smoking progression, gun violence, air or water pollution, emerging infectious diseases (including zoonotic diseases), antibiotic resistance, asthma, diabetes, implementation of precision public health programs
Integration of the social determinants of health and electronic health records in precision public health programs
Application of DHIS2 (District Health Information System 2), the world’s largest health information systems platform, in precision public health programs in middle- and low-income countries
Measurement of the multidimensional attributes of data quality used in precision public health programs, given the fact that data constitute the most important asset of precision public health
Application of effective interventions to homogeneous subpopulations within a larger heterogeneous population in order to contain the spread of diseases in higher-income countries and the Global South
Socioeconomic benefits of implementing precision public health programs for risk identification, disease surveillance, and preventive interventions
Innovations in the application of AI and big data to precision public health use cases such as the tracking of infectious disease pathways
Research in the areas of risk, legal and ethical issues, and governance problems arising from the implementation of AI and predictive analytics in precision public health programs
Risks and challenges of using big data in precision public health programs
OJPHI invites authors to submit original research, literature reviews, and scholarly or well-argued viewpoints to this call for papers on precision public health. We welcome original, unpublished submissions from researchers and practitioners in public health, medicine, health care, computer science, and related fields.
The deadline for submissions is November 30, 2023. All accepted manuscripts will be published as part of the OJPHI special theme issue on Precision Public Health Informatics.
To learn more please visit: https://ojphi.jmir.org/announcements/397
###
About JMIR Publications
JMIR Publications is a leading, born-digital, open access publisher of 30+ academic journals and other innovative scientific communication products that focus on the intersection of health and technology. Its flagship journal, the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is the leading digital health journal globally in content breadth and visibility, and it is the largest journal in the medical informatics field.
To learn more about JMIR Publications, please visit https://www.JMIRPublications.com or connect with us via Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram.
Head office: 130 Queens Quay East, Unit 1100, Toronto, ON, M5A 0P6 Canada
Media contact: communications@JMIR.org
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-16
Irvine, Calif., Aug. 16, 2023 — Human-caused climate change is shortening the snow cover period in the Arctic. But according to new research led by Earth system scientists at the University of California, Irvine, some parts of the Arctic are getting deeper snowpack than normal, and that deep snow is driving the thawing of long-frozen permafrost carbon reserves and leading to increased emissions of greenhouse gasses like carbon dioxide and methane.
“It is the first long-term experiment where we directly measure the mobilization of ancient carbon year-round to show that deeper snow has the possibility to rather ...
2023-08-16
The Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation has named 13 new Damon Runyon Fellows, exceptional postdoctoral scientists conducting basic and translational cancer research in the laboratories of leading senior investigators. This prestigious Fellowship encourages the nation’s most promising young scientists to pursue careers in cancer research by providing them with independent funding to investigate cancer causes, mechanisms, therapies, and prevention. In July 2023, the Board of Directors announced a 15% ...
2023-08-16
Phytoplankton determine how much life the ocean is able to support and play a role in controlling atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations, thereby regulating our climate. These tiny marine plants depend on sunlight as well as nutrients to thrive – including elements such as iron or nitrogen that can be brought to the ocean surface by currents and upwelling.
To understand phytoplankton nutrient limitations in the ocean, scientists typically conduct experiments during research expeditions at sea. However, this approach documents only a tiny fraction of the ocean at a certain point in time. Therefore, an international team of researchers tested if a signal detected by satellites in ...
2023-08-16
Medications to treat various chronic diseases may hinder the body’s ability to lose heat and regulate its core temperature to optimal levels. The loss of effective thermoregulation has implications for elderly people receiving treatment for illnesses like cancer, cardiovascular, Parkinson’s disease/dementia and diabetes, particularly during hot weather, according to a review by a team of scientists from various institutions in Singapore.
The group, led by Associate Professor Jason Lee from the Human Potential Translational Research Programme at the Yong Loo Lin School of ...
2023-08-16
Leaf-tailed geckos are masters of camouflage. Some species have skin flaps around the whole body and head, as well as flattened tails. During the day, they rest head-down on tree trunks with these skin flaps spread out, and blend seamlessly into their surroundings, making them nearly impossible to spot. At night, they awaken to prowl the fine branches of the understory looking for invertebrate prey.
“When we first discovered this species in 2000, we already suspected it might be new to science,” says Dr Frank Glaw, curator of herpetology at the Bavarian State Collection of Zoology, lead author on the study. “But ...
2023-08-16
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include a novel single-cell sequencing technology that allows for rapid analyses of archived and frozen cells, greater understanding of the ...
2023-08-16
Researchers have found a way to control the interaction of light and quantum ‘spin’ in organic semiconductors, that works even at room temperature.
Spin is the term for the intrinsic angular momentum of electrons, which is referred to as up or down. Using the up/down spin states of electrons instead of the 0 and 1 in conventional computer logic could transform the way in which computers process information. And sensors based on quantum principles could vastly improve our abilities to measure and study the world around us.
An international team of researchers, led by the University of ...
2023-08-16
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs BST 16 August 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
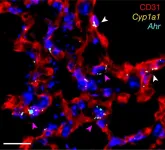
Research finds that molecules in vegetables can help to ease lung infection
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have found that molecules in vegetables like broccoli or cauliflower help to maintain a healthy barrier in the lung and ease infection.
The AHR – aryl hydrocarbon receptor – is a protein found at barrier sites like the gut and the lung. Natural molecules in cruciferous vegetables – for example, kale, cauliflower, broccoli, or cabbage – are dietary ...
2023-08-16
In countries such as Peru, Bolivia and Chile, it’s not uncommon for people who live in foggy areas to hang up nets to catch droplets of water. The same is true of Morocco and Oman. These droplets then trickle down the mesh and are collected to provide water for drinking, cooking and washing. As much as several hundred litres of water can be harvested daily using a fog net only a few square metres in area. For regions with little rain or spring water, but where fog is a common occurrence, this can be a blessing.
One crucial drawback with this method, however, ...
2023-08-16
About The Study: Children who experienced assault had, on average, a 2 times higher risk of receiving a mental illness diagnosis and were more likely than children who had not experienced assault to present to acute care for mental illness. Early intervention to support mental health of assaulted children is warranted, particularly in the first year following assault.
Authors: Natasha Ruth Saunders, M.D., M.Sc., of the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Inaugural theme issue: Precision public health from online Journal of Public Health Informatics