Urban great tits have paler plumage than their forest-living relatives
2023-08-17
(Press-News.org)
As urban areas expand, animals increasingly find themselves living in towns and cities. While some animals may benefit from milder temperatures and fewer natural predators in urban settings, they also have to cope with pollutants and changes in their diet. Previous research has shown that animals in cities are “duller” in terms of yellow-orange-red colour tones compared to their non-urban counterparts. However, previous studies have only focused on single geographic locations.
“We used feather samples collected from great tits in cities and forests across Europe. Different methods all confirmed that urban great tits are paler,” says Hannah Watson, biology researcher at Lund University, and one of the authors behind the study.
The yellow colour in the great tit’s feathers comes from carotenoids, which the birds get from the insects they eat. These insects, in turn, obtain the nutrient from the plants they feed on. Carotenoids are important antioxidants that help the body combat the toxic effects of pollution. If great tits in cities cannot obtain enough carotenoids from their food, their plumage becomes paler, resulting in weaker defences against the adverse health effects of pollution.
“Our findings suggest that birds in the city are not getting the right diet. This can help us understand how to create urban environments that are more beneficial for biodiversity. By planting more native trees and plants in our gardens and parks we can help small birds, such as great tits, by providing them with a healthy diet of insects and spiders for themselves and their chicks,” says Hannah Watson.
Surprisingly, the researchers found that the effects of cities on birds vary across Europe. For example, in Lisbon, forest great tits displayed much brighter feathers than city great tits. In Malmö, on the other hand, the difference in plumage between city and forest great tits was considerably less noticeable.
“We need further research to understand why some cities have more favourable environments for birds and wildlife than others. This can help urban planners develop biodiversity-friendly policies and improve the quality of life for people living in cities,” says Hannah Watson.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-17
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — We’ve managed to accumulate so much plastic trash that it’s daunting to think about what could be done with the tons upon tons of nonbiodegradable waste. And as much as we are trying to scale back our dependence on single-use plastics, we continue to add to the global plastic trash hoard. Events like the COVID-19 pandemic only served to expand their use for personal protective equipment and disposable and take-away packaging.
But, for researchers at UC Santa Barbara, one person’s single-use packaging ...
2023-08-17
Group A streptococci are fairly common bacteria that can cause, among other things, strep throat or impetigo. However, if the bacteria become invasive, the situation can become very dangerous. In this case, the name sometimes changes to murder bacteria or flesh-eating bacteria and can give rise to life-threatening conditions such as blood poisoning and septic shock, or soft tissue infections that may make an amputation necessary.
Invasive streptococcal infections have increased in recent decades. The reason for this is not fully understood.
The outcome of infections can ...
2023-08-17
Prolonged exposure to low-dose ionising radiation is associated with a higher risk of death from cancer than previously thought, suggests research tracking the deaths of workers in the nuclear industry, published in The BMJ today.
The findings should inform current rules on workplace protection from low-dose radiation, say the researchers.
To date, estimates of the effects of radiation on the risk of dying from cancer have been based primarily on studies of survivors of atomic bombs dropped on Japan at the ...
2023-08-17
Access to a smartphone alcohol intervention app helped university students to cut down their overall alcohol consumption and the number of days they drank heavily, suggests a study published in The BMJ today.
Unhealthy drinking is the biggest risk factor to health for 15 to 49-year olds, and unhealthy use of alcohol is especially prevalent among adult students, prompting the authors to design a smartphone app to encourage healthier drinking among this group.
The authors tested the app in 1770 university students who had screened positive for ...
2023-08-17
*Please see end of press release for a link to the embargoed content*
Peer-reviewed / Randomised Controlled Trial / People
A randomised controlled trial of 860 women requesting emergency contraception found 95% of pregnancies were prevented following combined treatment with levonorgestrel and the anti-inflammatory medication piroxicam, compared to 63% of pregnancies being prevented when levonorgestrel was taken alone.
This is the first randomised trial where piroxicam has been studied for its contraceptive action in humans.
The authors say, if these results can be reproduced in future studies, co-treatment with piroxicam and levonorgestrel ...
2023-08-17
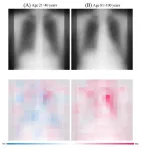
Osaka, Japan - What if “looking your age” refers not to your face, but to your chest? Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have developed an advanced artificial intelligence (AI) model that utilizes chest radiographs to accurately estimate a patient’s chronological age. More importantly, when there is a disparity, it can signal a correlation with chronic disease. These findings mark a leap in medical imaging, paving the way for improved early disease detection and intervention. The results are set to be published in The Lancet Healthy Longevity.
The research team, led by graduate student ...
2023-08-17
Epilepsy in infants ranges in severity and can leave caregivers with questions about their child’s health. While genetic testing to help determine the cause of epilepsy is possible, comprehensive testing does not always happen routinely and it can take a long time, leaving families waiting for answers.
Published in The Lancet Neurology, this international study sequenced the genomes of 100 infants with unexplained seizures, along with their parents, from four countries (England, USA, Canada and Australia) to better understand the potential strengths of early, broad genome sequencing (a process ...
2023-08-17
The BMJ’s editor in chief is urging the Academy of Medical Royal Colleges and its members to establish a standard for declaring payments they receive from industry and patient groups in the wake of a recent investigation by The BMJ into such payments.
The investigation, published by The BMJ in July,* found that royal colleges, responsible for doctors’ and some other healthcare professionals’ education and training, had received more than £9m in payments from drug and medical device companies since 2015 but that they didn’t always disclose these payments publicly in their annual reports.
In an open letter to the institutions ...
2023-08-17
Fresh evidence of ChatGPT’s political bias revealed by comprehensive new study
The artificial intelligence platform ChatGPT shows a significant and systemic left-wing bias, according to a new study by the University of East Anglia (UEA).
The team of researchers in the UK and Brazil developed a rigorous new method to check for political bias.
Published today in the journal Public Choice, the findings show that ChatGPT’s responses favour the Democrats in the US, the Labour Party in the UK, and in Brazil President Lula da Silva of the Workers’ Party.
Concerns ...
2023-08-17
An extremely rare collection of 160-million-year-old sea spider fossils from Southern France are closely related to living species, unlike older fossils of their kind.
These fossils are very important to understand the evolution of sea spiders. They show that the diversity of sea spiders that still exist today had already started to form by the Jurassic.
Lead author Dr Romain Sabroux from the University of Bristol’s School of Earth Sciences, said: “Sea spiders (Pycnogonida), are a group of marine animals that is overall very poorly studied.
“However, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Urban great tits have paler plumage than their forest-living relatives