(Press-News.org) (Toronto, August 18, 2023) JMIR Publications is happy to announce that JMIR AI has been accepted and indexed with the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). The DOAJ applies strict criteria to review and index Open Access journals, which include licensing and copyright criteria, quality control processes, journal website technical and usability setups, and editorial evaluation.
JMIR AI (JMIR AI ISSN 2817-1705, Editors-in-Chief: Khaled El Emam, PhD and Bradley Malin, PhD) is a new journal (launched in 2022) focusing on the applications of AI in health settings. This includes contemporary developments as well as historical examples, with an emphasis on sound methodological evaluations of AI techniques and authoritative analyses.
JMIR AI aims to be the primary journal for applications of AI. The journal was created to enable the community to learn how techniques have been adapted, extended, and scaled to work in practice, as well as learn about the methods and methodological innovations to evaluate those techniques in real world settings. The journal has a strong emphasis on sharing the code and data that can enable others to replicate and build on that work. JMIR AI complements other journals in the JMIR Publications portfolio by concentrating the editorial expertise on AI and ensuring a consistent and high standard is maintained for these publications.
Additional JMIR Publications’ journals indexed/accepted in DOAJ include: Journal of Medical Internet Research, JMIR mHealth and uHealth, JMIR Research Protocols, JMIR Human Factors, JMIR Mental Health, JMIR Serious Games, JMIR Medical Informatics, JMIR Formative Research, JMIR Diabetes, JMIR Cancer, JMIR Pediatrics and Parenting, JMIR Medical Education, JMIR Aging, JMIR Rehabilitation and Assistive Technologies, JMIR Cardio, JMIR Public Health and Surveillance and the Interactive Journal of Medical Research.
Additional journals may currently be under evaluation. DOAJ is used by more than 5000 institutions worldwide, and JMIR Publications is delighted to be a part of this directory. To review all JMIR Publication journals included in the DOAJ, click here.
###
About DOAJ
The Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) was launched in 2003 with 300 open access journals. Today, this independent database contains over 16 500 peer-reviewed open access journals covering all areas of science, technology, medicine, social sciences, arts and humanities. DOAJ's mission is to increase the visibility, accessibility, reputation, usage and impact of quality, peer-reviewed, open access scholarly research journals globally, regardless of discipline, geography or language.
About JMIR Publications
JMIR Publications is a leading, born-digital, open access publisher of 30+ academic journals and other innovative scientific communication products that focus on the intersection of health, and technology. Its flagship journal, the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is the leading digital health journal globally in content breadth and visibility, and is the largest journal in the medical informatics field.
To learn more about JMIR Publications, please visit jmirpublications.com or connect with us via Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram.
Head office: 130 Queens Quay East, Unit 1100, Toronto, ON, M5A 0P6 Canada
Media contact: communications@jmir.org
END
At the outset of the COVID pandemic, men appeared to suffer higher rates of severe illness and death, leading researchers to suspect a link between androgen receptors—which bind to hormones like testosterone--and SARS-CoV-2 viral infection.
This observation spurred Michigan Medicine researchers to look into a drug in development to treat prostate cancer called proxalutamide, which works by blocking an enzyme called TMPRSS2 (transmembrane protease, serine 2) that is regulated by androgen receptors, as a potential therapeutic for COVID.
“We were already studying TMPRSS2 as part of the key gene driver ...
NYU Langone Health’s MCIT Department of Health Informatics, Institute for Innovation in Medical Education, and Institute for Excellence in Health Equity will hold the first Generative AI Prompt-A-Thon in Health Care on Aug 18. During the event, teams of clinicians, educators, and researchers will work together to find artificial intelligence (AI)-powered solutions to healthcare challenges using real-world, de-identified patient data.
The event addresses large language models (LLMs) that predict likely options for the next word in any sentence, paragraph, or essay, based on how real people used words in context billions of times in documents on the internet. Also called ...
Archaeologists have long been drawing conclusions about how ancient tools were used by the people who crafted them based on written records and context clues. But with dietary practices, they have had to make assumptions about what was eaten and how it was prepared. A new study published in the journal iScience on August 18 analyzed protein residues from ancient cooking cauldrons and found that the people of Caucasus ate deer, sheep, goats, and members of the cow family during the Maykop period (3700–2900 BCE).
“It’s really exciting to get an idea of what people were making ...
The US has committed to reaching net-zero emissions by 2050. To accomplish this goal, large cuts in emissions are necessary, especially in high-emission sectors like the building industry. In an article publishing on August 18 in the journal One Earth, a team of researchers use a computational model to analyze several scenarios of future building energy use in the US. They find that by tackling emissions on multiple fronts and placing focus on “demand-side measures” that affect how power is drawn from the ...
The summertime barbecue – an American tradition synonymous with celebrating freedom – may be tainted by a decidedly unfree market. A new Stanford study reveals how meat and dairy industry lobbying has influenced government regulations and funding to stifle competition from alternative meat products with smaller climate and environmental impacts. The analysis, published Aug. 18 in One Earth, compares innovations and policies related to plant-based meat alternatives and lab-grown meat in the U.S. and European Union. Its findings could help ensure ...
About The Study: The findings of this study that included 612 women suggest that adherence to preconception healthy dietary patterns before infertility treatment may be associated with a lower likelihood of pregnancy loss.
Authors: Jorge E. Chavarro, M.D., Sc.D., of the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.29982)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
About The Study: In a racially and ethnically diverse cohort of 34,000 adolescents, those from neighborhoods with extreme concentrations of racial and economic disadvantage were more likely to screen positive for depressive symptoms and suicidality at well-teen visits compared to their counterparts from the most racially and economically privileged neighborhoods.
Authors: Julia Acker, M.S., of the University of California, Berkeley, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.29825)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: Telemedicine was rapidly adopted in skilled nursing facilities (SNFs) in early 2020 but subsequently stabilized at a low use rate that was nonetheless higher than before 2020 in this study of more than 4.4 million residents at 15,000 SNFs. Higher telemedicine use in SNFs was associated with improved access to psychiatry visits in SNFs.
Authors: Michael L. Barnett, M.D., M.S., of the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.29895)
Editor’s ...
An estimated 1 in 4 older Americans with dementia or mild cognitive impairment lives alone and is at risk of practices like unsafe driving, wandering outside the home, mixing up medications and failing to attend medical appointments.
In a study publishing in JAMA Network Open on Aug. 18, 2023, researchers led by UC San Francisco concluded that the United States health system is poorly equipped to serve patients living solo with cognitive decline, a group whose numbers are predicted to swell as the population ages.
For these patients, living alone ...
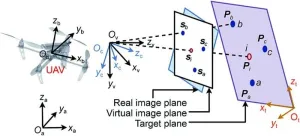
A study published in Engineering introduces a novel image-based visual servoing (IBVS) method for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to track dynamic targets in GPS-denied environments. Titled "Dynamic Target Tracking of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Under Unpredictable Disturbances," the research article presents a comprehensive approach that addresses the challenges of estimating target velocities, image depth estimation, and tracking stability in the presence of external disturbances.
The proposed method utilizes a constructed virtual camera to derive simplified and decoupled image dynamics for underactuated UAVs. By considering ...