(Press-News.org) Boston, MA – A new study of men with prostate cancer finds that physical activity is associated with a lower risk of overall mortality and of death due to prostate cancer. The Harvard School of Public Health and University of California, San Francisco researchers also found that men who did more vigorous activity had the lowest risk of dying from the disease. It is the first study in men with prostate cancer to evaluate physical activity after diagnosis in relation to prostate cancer-specific mortality and overall mortality.
The study appears in an advance online edition of the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
"Our results suggest that men can reduce their risk of prostate cancer progression after a diagnosis of prostate cancer by adding physical activity to their daily routine," said Stacey Kenfield, lead author of the study and a Harvard School of Public Health researcher. "This is good news for men living with prostate cancer who wonder what lifestyle practices to follow to improve cancer survival."
Prostate cancer is the most frequently diagnosed form of cancer among men in the United States and affects one in six U.S. men during their lifetime. More than 2 million men in the U.S. and 16 million men worldwide are prostate cancer survivors.
The study was conducted in 2,705 men diagnosed with prostate cancer in the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study over an 18-year period. The participants reported the average time per week they spent doing physical activity, including walking, running, bicycling, swimming and other sports and outdoor work.
The results showed that both non-vigorous and vigorous activity were beneficial for overall survival. Compared with men who walked less than 90 minutes per week at an easy pace, those who walked 90 or more minutes per week at a normal to very brisk pace had a 46% lower risk of dying from any cause.
Only vigorous activity—defined as more than three hours per week—was associated with reduced prostate cancer mortality. Men who did vigorous activity had a 61% lower risk of prostate cancer-specific death compared with men who did less than one hour per week of vigorous activity.
"We observed benefits at very attainable levels of activity and our results suggest that men with prostate cancer should do some physical activity for their overall health, even if it is a small amount, such as 15 minutes of activity per day of walking, jogging, biking or gardening," said Kenfield. "However, doing vigorous activity for three or more hours per week may be especially beneficial for prostate cancer, as well as overall health," she said.
###
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, Charles A. King Trust and the Prostate Cancer Foundation.
"Physical Activity and Survival After Prostate Cancer Diagnosis in the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study," Stacey A. Kenfield, Meir J. Stampfer, Edward Giovannucci, June M. Chan, Journal of Clinical Oncology, online January 4, 2011.
Visit the HSPH website for the latest news, press releases and multimedia offerings.
Harvard School of Public Health (http://www.hsph.harvard.edu ) is dedicated to advancing the public's health through learning, discovery, and communication. More than 400 faculty members are engaged in teaching and training the 1,000-plus student body in a broad spectrum of disciplines crucial to the health and well being of individuals and populations around the world. Programs and projects range from the molecular biology of AIDS vaccines to the epidemiology of cancer; from risk analysis to violence prevention; from maternal and children's health to quality of care measurement; from health care management to international health and human rights. For more information on the school visit: http://www.hsph.harvard.edu
HSPH on Twitter: http://twitter.com/HarvardHSPH
HSPH on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/harvardpublichealth
HSPH on You Tube: http://www.youtube.com/user/HarvardPublicHealth
HSPH home page: http://www.hsph.harvard.edu
END
PROVIDENCE, RI – When methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) is carried in the nose (nares), it is a risk factor for an invasive infection, including a surgical site infection. Some studies have found that the heavier the carriage of MRSA in the nose, the greater the risk of transmission to others and the greater risk of infection to the patient. Few studies to date have assessed the differences in quantity of MRSA at different body sites. A new study from Rhode Island Hospital now sheds light on both the quantity of MRSA at different body sites and the relationship between ...
Using a thermostatic mixer valve to control the maximum temperature of children's bath water can significantly reduce the temperature of hot bath water and should reduce the risk of scalding, according to researchers at The University of Nottingham.
The study, carried out in partnership with Glasgow Housing Association, found that families with a thermostatic mixing valve (TMV) fitted to the hot and cold water pipes in their bathroom had bath water temperatures that were up to 11˚C cooler than those without and their baths were within the recommended temperature ...
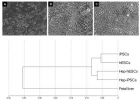
Numerous patients suffering from chronic liver diseases are currently receiving inadequate treatment due to the lack of organs donated for transplantation. However, hepatocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) could offer an alternative for the future. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics in Berlin compared hepatocytes from embryonic stem cells with hepatocytes from iPS cells and found that their gene expression is very similar. Nevertheless, in comparison to "real" hepatocytes, just under half of the genes exhibited a different ...
Regularly drinking green tea could protect the brain against developing Alzheimer's and other forms of dementia, according to latest research by scientists at Newcastle University.
The study, published in the academic journal Phytomedicine, also suggests this ancient Chinese remedy could play a vital role in protecting the body against cancer.
Led by Dr Ed Okello, the Newcastle team wanted to know if the protective properties of green tea – which have previously been shown to be present in the undigested, freshly brewed form of the drink – were still active once the tea ...
While a much hailed communication intervention works for families making decisions for chronically-ill loved ones in medical intensive care units, Case Western Reserve University researchers found the intervention was less effective for surgical and neurological ICU patients.
Barbara Daly and Sara Douglas, the study's lead researchers from the Frances Payne Bolton School of Nursing at Case Western Reserve, attribute the varied results to different types of patients served by the three types of ICUs and differences among ICU cultures.
"We found the same approach is ...
The use of environmental DNA (eDNA) by scientists from the University of Notre Dame and The Nature Conservancy to detect invasive Asian carp in the Chicago-area waterway has been validated in Conservation Letters, a new flagship peer-reviewed journal published by the Society for Conservation Biology.
"When you are dealing with cutting-edge research like eDNA, a very important part of the process is getting your science peer-reviewed and published in a well-respected journal," said Professor David Lodge, director of the University of Notre Dame's Environmental Change Initiative. ...
Sometimes it's almost impossible to talk without using your hands. These gestures seem to be important to how we think. They provide a visual clue to our thoughts and, a new theory suggests, may even change our thoughts by grounding them in action.
University of Chicago psychological scientists Sian Beilock and Susan Goldin-Meadow are bringing together two lines of research: Beilock's work on how action affects thought and Goldin-Meadow's work on gesture. After a chat at a conference instigated by Ed Diener, the founding editor of Perspectives on Psychological Science, ...
Artificial joint replacements can drastically change a patient's quality of life. Painful, arthritic knees, shoulders and hips can be replaced with state-of-the-art metal or ceramic implants, eliminating pain and giving a person a new lease on life. But, what if, instead of metal and plastic, doctors were able to take a patient's cells and grow an entirely new joint, replacing the old one with a fully functional biological joint? A team of University of Missouri and Columbia University researchers have found a way to create these biological joints in animals, and they believe ...
New Rochelle, NY, January 5, 2011—A new, simplified method for producing large amounts of viral vector cassettes capable of shuttling genes into host cells will help advance the promising field of gene therapy as applications move into large animal studies and human clinical trials. The novel adeno-associated virus (AAV) production method is described in an article published Instant Online ahead of publication in Human Gene Therapy, a peer-reviewed journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. (www.liebertpub.com). The article is available free online at www.liebertpub.com/hum
This ...
In a finding that gives new meaning to the adage, "waste not, want not," scientists are reporting that household sewage has far more potential as an alternative energy source than previously thought. They say the discovery, which increases the estimated potential energy in wastewater by almost 20 percent, could spur efforts to extract methane, hydrogen and other fuels from this vast and, as yet, untapped resource. Their report appears in ACS' journal Environmental Science & Technology.
Elizabeth S. Heidrich and colleagues note that sewage treatment plants in the United ...