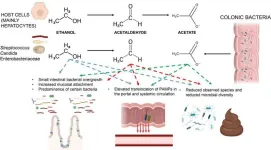
(Press-News.org) Alcohol consumption is a significant risk factor for gastrointestinal diseases, including cancer. Alcohol can damage the gastrointestinal tract in several ways. It can promote an impairment of several intestinal barrier functions, leading to leaky gut and dysbiosis. Ethanol metabolism can also produce toxic substances such as acetaldehyde and acetate, further damaging the gut and potentially promoting cancer. Ethanol and its metabolites enhance DNA damage response and dysregulate the epithelial proliferation/differentiation program, thereby increasing the risk of cancer development.
In a new paper published in eGastroenterology, a team of scientists led by Professor Bin Gao from the National Institute of Health reviewed alcohol-associated bowel disease and the existing literature in the field.
Gastrointestinal diseases (GI diseases) are disorders of the digestive tract, which include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. They can also affect the accessory digestive glands, such as the liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and biliary tract.
Alcohol-associated bowel disease (ABD) is a poorly understood condition characterized by small and large intestine damage. ABD is thought to be caused by alcohol-induced damage to the gut and underlying genetic and environmental factors. The clinical diagnosis of ABD has not been defined. It may be based on alcohol drinking history, increased gut permeability, elevated systemic translocation of microbial products, and gut tissue histology.
The structural and functional changes in ABD need to be better understood. They may include pathologic changes in the intestine, such as leaky gut, changes in the intestinal epithelium, gut immune dysfunctions, and alterations in the intestinal microbiome. The pathophysiology of ABD has yet to be fully understood, but it is thought to involve the metabolism of ethanol and its principal metabolites, acetaldehyde and acetate. These metabolites can impair different functions in the digestive tract, leading to various GI diseases, including ABD.
One challenge in studying ABD is that studies are primarily descriptive. In addition, investigations of the intestinal barrier in humans often consider only advanced stages of alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD), in which additional factors such as portal hypertension or decompensation of liver function are influencing, per se, the digestive tract.
Ethanol, as well as acetaldehyde and acetate produced by ethanol metabolism in chronically alcohol abusers, may promote and/or contribute to bowel pathogenesis. Epithelial and non-epithelial cells and microbes along the different intestinal tract sites could be impacted by ethanol itself and by differential doses of acetaldehyde and acetate due to ethanol metabolism. However, the exact contribution of the digestive tract in ethanol metabolism remains to be elucidated.
More research is needed to understand ABD's mechanisms and develop effective treatments. There is some evidence to suggest that ABD may precede or contribute to ALD. For example, approximately 90 per cent of alcohol user disorder (AUD) patients present with mild liver disease. However, most will likely have certain degrees of bowel dysfunctions (e.g., malabsorption, intestinal permeability, immune dysfunctions), suggesting that ABD may precede in certain patients and promote or contribute to ALD.
Future studies are needed to better understand the role of the intestine in ethanol metabolism and the impact of ethanol on the intestine. These studies could help identify new targets for preventing and treating ABD.
About the eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery).
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
END
#FRANKFURT. Immediately after the infection of a cell in the throat or lungs, the SARS-CoV-2 virus works very hard to replicate, using the human cell’s metabolic pathways to produce its proteins and make sure that its genetic material (the RNA genome) is copied. The RNA genome is then packaged very compactly into new virus particles that are released from the cell to infect more cells.
One viral protein, called the nucleocapsid protein (N), is particularly important for rapid and efficient replication. ...
Applying ground-up silicate rock to Midwestern farm fields can capture significant amounts of carbon dioxide and prevent it from accumulating in the atmosphere, according to a new study that successfully quantified those climate benefits for the first time.
Working with Eion Corp., researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the Leverhulme Centre for Climate Change Mitigation (LC3M) developed a new method to calculate the CO2-reduction potential of basalt rock amendments applied to cropland soil, a process known as enhanced weathering.
Traditional row-crop agriculture releases sizable amounts of soil-derived carbon to the atmosphere as CO2, a greenhouse gas ...
About The Study: The findings of this study indicate that COVID-19 was not associated with any clinically significant excess mortality among those who survived at least 180 days compared with closely risk-matched comparators, despite having worse 2-year total mortality. This finding has individual level and health system planning implications and should be reassuring to persons who have survived COVID-19 for at least 180 days.
Authors: Theodore J. Iwashyna, M.D., Ph.D., of the Ann Arbor VA in Ann Arbor, Michigan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
About The Study: In this study including 7,097 mother-child pairs, greater screen time for children at age 1 was associated with developmental delays in communication and problem-solving at ages 2 and 4. These findings suggest that domains of developmental delay should be considered separately in future discussions on screen time and child development.
Authors: Taku Obara, Ph.D., of Tohoku University in Sendai, Japan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
About The Study: This study including 31,000 hospitalized children with SARS-CoV-2 infection suggested that while intensive care unit admission decreased over the course of the pandemic in all age groups, ventilatory and oxygen support did not decrease over time in children younger than age 5. These findings highlight the importance of considering different pediatric age groups when assessing disease severity in COVID-19.
Authors: Kirsty Short, Ph.D., of the University of Queensland in Brisbane, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3117)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: In this study including content analysis of 27 websites across multiple countries, most websites selling direct-to-consumer Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH) tests included false and misleading claims which might lead consumers to purchase an AMH test in the belief that it can reliably predict fertility potential and age of menopause. Depending on the test result, this may in turn lead to misplaced anxiety or reassurance about one’s fertility and modifications to subsequent conception or contraceptive plans and behavior.
Authors: Tessa Copp, Ph.D., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, Australia, is the ...
With the advent of ChatGPT4, the use of artificial intelligence in medicine has absorbed the public’s attention, dominated news headlines, and sparked vigorous debates about the promise and peril of medical AI.
But the potential of AI reaches far beyond the frontlines of medicine.
AI is already changing the way scientists discover and design drugs. It is predicting how molecules interact and proteins fold with never-before-seen speed and accuracy. One day, AI may even be used routinely to safeguard the function of nuclear reactors.
These are but a few of the exciting applications of AI in the natural sciences, ...
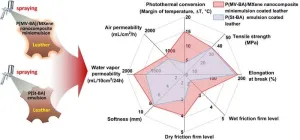
A study published in the journal of Engineering reveals a remarkable development in the field of green coating materials for leather. Researchers have successfully synthesized a solvent-free, bio-based antibacterial agent and aromatic monomer called methacrylated vanillin (MV). This innovative compound not only imparts antibacterial properties to leather coatings but also serves as an eco-friendly alternative to the petroleum-based carcinogen styrene (St).
In this research article, titled "Bio-based ...
Clopidogrel is a commonly prescribed medication used to prevent further heart attacks after an initial event. It needs to be activated in the body to be effective. Studies of European populations show that 30% of individuals have genetic variants that reduce or prevent activation through the production of an enzyme called CYP2C19. People of South Asian ancestry have high rates of cardiovascular disease, but previous studies have not looked for these variants in UK South Asian populations or linked these variants with risk of recurrent heart attacks if prescribed clopidogrel in South Asian ancestry ...
As our planet undergoes significant transformations due to climate change, habitats are being altered, appearing, disappearing, or changing in quality. Understanding the impact of these changes on the geographic distributions of species is of great significance. The shrinking ranges of protected organisms and the expanding ranges of noxious species, such as pests and pathogens, highlight the urgent need to monitor range movements precisely. However, this task poses challenges as the available observation time is often short compared to the pace of underlying population processes, making it difficult to distinguish between directional shifts and random fluctuations.
Addressing ...