(Press-News.org) Violent actions intended to provoke opposition to particular communities may paradoxically lead to lasting acceptance, according to a study. On March 15, 2019, a far-right extremist killed 51 Muslims in Christchurch, New Zealand. Immediately following the attacks there was a noticeable increase in public acceptance of the Muslim minority in the country. But was this acceptance sustained? To address this question, Joseph Bulbulia and colleagues used years of data from the New Zealand Attitudes and Values Study, a national longitudinal study. The author’s goal was to estimate the anticipated level of Muslim acceptance if the attacks had not occurred. These estimates were then compared with actual observations during the three years that followed the attacks.
The analysis showed that initial warmth towards Muslims among political liberals and moderates swiftly increased and then stabilized. Among political conservatives—a group the extremist aimed to agitate—warmth towards Muslims not only rose but maintained an upward trajectory, suggesting a particularly enduring impact within this demographic.
In stark contrast to the extremist's objective of inciting public sentiment against Muslims, the attack caused the reverse effect, particularly among conservatives. Instead, the attack nurtured a long-term acceptance of Muslims and eased social divisions. The intended result of the attacks completely backfired, according to the authors.
END
Unintended consequences: Terror attacks cause long-term acceptance of targeted communities
2023-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Uranium signatures in turtles and tortoises near nuclear testing and waste sites
2023-08-22
The shells of turtles, tortoises, and sea turtles keep growing as long as the animals live—and some of them live a remarkably long time. Cyler Conrad and colleagues analyzed the shells of five specimens from areas that potentially accumulated anthropogenic uranium through nuclear fallout and/or waste. Unusual uranium signatures were found in a green sea turtle from Enewetak Atoll in the Republic of the Marshall Islands, a desert tortoise from southwestern Utah near the Nevada National Security Site (formerly known as the Nevada Test Site), a river cooter from the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, and a box turtle from Oak Ridge, Tennessee, ...
Australia experiences intense surge in Strep A cases, similar to northern hemisphere wave
2023-08-22
Australia has experienced an intense surge in severe Strep A cases, similar to the northern hemisphere wave, despite differences in seasons and circulating respiratory viruses, according to a new study.
The national research project, involving researchers from Murdoch Children’s Research Institute and published in The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, highlighted how the unseasonal increase in case load across the southern hemisphere adds to the need for a safe and effective vaccine against Strep ...
Coffee offers performance boost for concrete
2023-08-22
Engineers in Australia have found a way of making stronger concrete with roasted used-coffee grounds, to give the drink-additive a “double shot” at life and reduce waste going to landfills.
Lead author Dr Rajeev Roychand from RMIT University said the team developed a technique to make concrete 30% stronger by turning waste coffee grounds into biochar, using a low-energy process without oxygen at 350 degrees Celsius.
“The disposal of organic waste poses an environmental challenge as it emits large amounts of greenhouse gases including methane and carbon dioxide, which contribute to climate change,” ...
As city heat rises, bird diversity declines
2023-08-22
Hangzhou, China & Ithaca, N.Y.—Humans aren't the only ones leaving town when city heat becomes unbearable. A study done on 336 cities in China concludes that heat-retaining buildings and paved surfaces are directly related to a loss in bird diversity. These findings from scientists at Zhejiang University and the Cornell Lab of Ornithology are published in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
“The heat-retention characteristic of cities is a well-known phenomenon called the urban heat island ...
NCCN releases new resource to help families understand pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma, part of award-winning patient information series
2023-08-22
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [August 22, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) today announced the publication of NCCN Guidelines for Patients®: Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children. The book offers a comprehensive analysis of the treatment options, benefits, and risks of care approaches for pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma, one of the most curable forms of childhood cancer, with long-term survival rates of 90% or higher.[1]
This free resource is available online at NCCN.org/patientguidelines and via the NCCN Patient Guides for Cancer App thanks to funding from the NCCN Foundation®.
“When a child is diagnosed ...
Cancel Cervical Cancer – In Conversation with Brazil, Colombia, and Uruguay Experts | BGI Insights
2023-08-22
Despite being highly preventable, the Pan American Health Organization estimates cervical cancer kills 35,700 women annually in the Americas, and 80 percent of these cases are in Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC). The recently released BGI Genomics 2023 Global State of Cervical Cancer Awareness Report reveals potential awareness gaps that may contribute to this disproportionate distribution of cervical cancer cases in these regions.
To offer greater insight into the steps needed to improve cervical ...
World’s largest aging research and drug discovery conference celebrates 10 years
2023-08-22
The Aging Research and Drug Discovery (ARDD) conference, being held at the University of Copenhagen Aug. 28-Sept. 1, is celebrating 10 years of convening top scientists, venture capitalists, business leaders, and journals engaged in aging research, medicine, and emerging technology.
The conference has grown significantly over its decade-long history. This year’s event kicks off with Longevity Medicine Day which will include speakers like Evelyne Bischof, MD, an expert in internal medicine, oncology, and longevity from Renji Hospital, Shanghai; Michael Basson, ...
A calculator to predict benefit from adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma
2023-08-22
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most commonly diagnosed cancer of the liver and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with China accounting for over half of the global annual cases and deaths. Hepatectomy is the standard curative-intent treatment option for appropriately selected patients with localized HCC. However, the high postoperative recurrence rate causes many patients to have a poor prognosis and a high incidence of cancer-specific death. This occurs in especially early recurrence within the first year after surgery, which is most likely due to occult micro-metastasis from the original tumor. Given that survival among patients with recurrence is markedly ...
Paired liver exchange developed by Boston College economists results in first four-way liver exchange
2023-08-22
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (8/22/2023) – In a breakthrough in liver transplantation that may lead to the ability to connect more living donors and patients, a new matching system designed by a team led by Boston College economists enabled the world’s first four-way liver exchange and a cascade of additional matches, researchers reported recently in the American Journal of Transplantation.
The results show that expanding the capacity of the donor-patient matching mechanism beyond the traditional 2-way change – matching two patients with two donors – can increase the number of ...
Understanding river alteration via shifting flow regime
2023-08-22
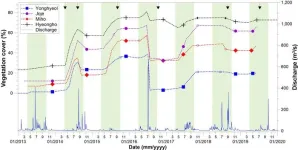
Researchers at the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-suk) published their findings on the drastic short-term alterations in rivers accompanied by shifts in vegetation and geomorphology drawn from actual on-site investigation and analyses and not from model simulations.
The alteration processes from a 'white river,' characterized by riverbeds with no vegetation including bare sandbars, to a densely vegetated 'green river' with grass and trees, have been ...