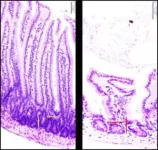
(Press-News.org)
A new powerful antibiotic, isolated from bacteria that could not be studied before, seems capable to combat harmful bacteria and even multi-resistant ‘superbugs’. Named Clovibactin, the antibiotic appears to kill bacteria in an unusual way, making it more difficult for bacteria to develop any resistance against it. Researchers from Utrecht University, Bonn University (Germany), the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), Northeastern University of Boston (USA), and the company NovoBiotic Pharmaceuticals (Cambridge, USA) now share the discovery of Clovibactin and its killing mechanism in the scientific journal Cell.
Urgent need for new antibiotics
Antimicrobial resistance is a major problem for human health and researchers worldwide are looking for new solutions. “We urgently need new antibiotics to combat bacteria that become increasingly resistant to most clinically used antibiotics,” says Dr. Markus Weingarth, a researcher from the Chemistry Department of Utrecht University.
However, the discovery of new antibiotics is a challenge: few new antibiotics have been introduced into the clinics over the last decades, and then they often resemble older, already known antibiotics.
“Clovibactin is different,” says Weingarth. “Since Clovibactin was isolated from bacteria that could not be grown before, pathogenic bacteria have not seen such an antibiotic before and had no time to develop resistance.”
Antibiotic from bacterial dark matter
Clovibactin was discovered by NovoBiotic Pharmaceuticals, a small US-based early-stage company, and microbiologist Prof. Kim Lewis from Northeastern University, Boston. Earlier, they developed a device that allows to grow ‘bacterial dark matter’, which are so-called unculturable bacteria. Intriguingly, 99% of all bacteria are ‘unculturable’ and could not be grown in laboratories previously, hence they could not be mined for novel antibiotics. Using the device, called iCHip, the US researchers discovered Clovibactin in a bacterium isolated from a sandy soil from North Carolina: E. terrae ssp. Carolina.
In the joint Cell publication, NovoBiotic Pharmaceuticals shows that Clovibactin successfully attacks a broad spectrum of bacterial pathogens. It was also successfully used to treated mice infected with the superbug Staphylococcus aureus.
A broad target spectrum
Clovibactin appears to have an unusual killing mechanism. It targets not just one, but three different precursor molecules that are all essential for the construction of the cell wall, an envelope-like structure that surrounds bacteria. This was discovered by the group of Prof. Tanja Schneider from the University of Bonn in Germany, one of the Cell paper’s co-authors.
Schneider: “The multi-target attack mechanism of Clovibactin blocks bacterial cell wall synthesis simultaneously at different positions. This improves the drug’s activity and substantially increases its robustness to resistance development.”
A cage-like structure
How exactly Clovibactin blocks the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall was unraveled by the team of Dr. Markus Weingarth from Utrecht University. They used a special technique called solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) that allows to study Clovibactin’s mechanism under similar conditions as in bacteria.
“Clovibactin wraps around the pyrophosphate like a tightly sitting glove. Like a cage that encloses its target” says Weingarth. This is was gives Clovibactin its name, which is derived from Greek word “Klouvi”, which means cage. The remarkable aspect of Clovibactin’s mechanism is that it only binds to the immutable pyrophosphate that is common to cell wall precursors, but it ignores that variable sugar-peptide part of the targets. “As Clovibactin only binds to the immutable, conserved part of its targets, bacteria will have a much harder time developing any resistance against it. In fact, we did not observe any resistance to Clovibactin in our studies.”
Fibrils capture the targets
Clovibactin can do even more. Upon binding the target molecules, it self-assembles into large fibrils on the surface of bacterial membranes. These fibrils are stable for a long time and thereby ensure that the target molecules remain sequestered for as long as necessary to kill bacteria.
“Since these fibrils only form on bacterial membranes and not on human membranes, they are presumably also the reason why Clovibactin selectively damages bacterial cells but is not toxic to human cells,” says Weingarth. “Clovibactin hence has potential for the design of improved therapeutics that kill bacterial pathogens without resistance development.”.
Publication details
A new antibiotic from an uncultured bacterium binds to an immutable target, Cell, DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.07.038
Rhythm Shukla, Aaron J. Peoples, Kevin C. Ludwig, Sourav Maity, Maik G.N. Derks, Stefania De Benedetti, Annika M Krueger, Bram J.A. Vermeulen, Theresa Harbig, Francesca Lavore, Raj Kumar, Rodrigo V. Honorato, Fabian Grein, Kay Nieselt, Yangping Liu, Alexandre Bonvin, Marc Baldus, Ulrich Kubitscheck, Eefjan Breukink, Catherine Achorn, Anthony Nitti, Christopher J. Schwalen, Amy L. Spoering, Losee Lucy Ling, Dallas Hughes, Moreno Lelli, Wouter H. Roos, Kim Lewis, Tanja Schneider, Markus Weingarth
Contact information for media:
Dr. Markus Weingarth
Department of Chemistry
Utrecht University
Tel. +31 (0)640828581
E-Mail: m.h.weingarth@uu.nl
Prof. Dr. Tanja Schneider
Institut für Phamazeutische Mikrobiologie
Universität Bonn
Tel. +49 (0)228 735688
E-Mail: tschneider@uni-bonn.de
END
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial that included 626 children, maternal structured lifestyle interventions during pregnancy based on a Mediterranean diet or mindfulness-based stress reduction significantly improved child neurodevelopmental outcomes at age 2.
Authors: Francesca Crovetto, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Barcelona in Barcelona, Spain, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.30255)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
About The Study: In this study of human-written and artificial intelligence (AI)-generated responses to 200 eye care questions from an online advice forum, a chatbot appeared capable of responding to long user-written eye health posts and largely generated appropriate responses that did not differ significantly from ophthalmologist-written responses in terms of incorrect information, likelihood of harm, extent of harm, or deviation from ophthalmologist community standards.
Authors: Sophia Y. Wang, M.D., M.S., of Stanford University in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
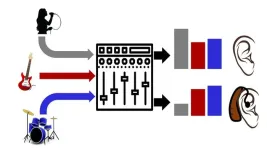
WASHINGTON, August 22, 2023 – Millions of people around the world experience some form of hearing loss, resulting in negative impacts to their health and quality of life. Treatments exist in the form of hearing aids and cochlear implants, but these assistive devices cannot replace the full functionality of human hearing and remain inaccessible for most people. Auditory experiences, such as speech and music, are affected the most.
In JASA, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society of America by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Oldenburg studied the impact of hearing loss on subjects’ enjoyment of different ...
LA JOLLA (August 22, 2023)—The prevalence of colorectal cancer in people under the age of 50 has risen in recent decades. One suspected reason: the increasing rate of obesity and high-fat diets. Now, researchers at the Salk Institute and UC San Diego have discovered how high-fat diets can change gut bacteria and alter digestive molecules called bile acids that are modified by those bacteria, predisposing mice to colorectal cancer.
In the study, published in Cell Reports on August 22, 2023, the team found increased levels of specific gut bacteria in mice fed high-fat diets. Those gut bacteria, they ...
(Boston)—For more than 100 years, it has been believed that sunlight and vitamin D deficiency were associated with the risk for many deadly cancers including colorectal, prostate and breast. But some scientists remained skeptical that this nutrient provides any benefit for reducing cancer risk and morbidity and mortality and several randomized controlled trials that have supported this doubt.
However, in a new commentary in JAMA Network Open, Michael F. Holick, PhD, MD, professor of medicine, pharmacology, physiology & biophysics and molecular medicine at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, explores the controversy as to ...
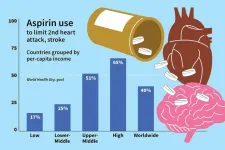
For people who have experienced a heart attack or stroke, taking a daily aspirin has been shown to help prevent a second one. Yet, despite aspirin’s low cost and its clear benefits in such scenarios, fewer than half of people worldwide who have had a heart attack or stroke take the medication, according to a new study led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the University of Michigan.
The study appears Aug. 22 in JAMA.
Cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and ...
While COVID-19 lockdowns are no longer mandated, the stress and anxiety of the pandemic still lingers, especially among young South Australians, say health experts at the University of South Australia.
In a new study released today, researchers show that children’s mental health and wellbeing have gradually worsened over the past six years, particular during and post the pandemic.
Examining measures of wellbeing – life satisfaction, optimism, happiness, cognitive engagement, emotional regulation, perseverance, worry, and sadness – ...
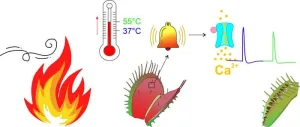
The Venus flytrap can survive in the nutrient-poor swamps of North and South Carolina because it compensates for the lack of nitrogen, phosphate and minerals by catching and eating small animals. It hunts with snap traps that have sensory hairs on them. If an insect touches these hairs two times, the traps shut and digests the prey.
In its location in the swamp, the carnivorous plant is often not visible because it is overgrown by grass. In summer, the grass dries up. Then it can catch fire from the frequent lightning storms typical of North Carolina – ...
The National Institutes of Health recently awarded Cleveland Clinic’s Jacob Scott, M.D., D.Phil., and collaborators $2.8 million to translate research on how cancer cells evolve and compete into patient care. The project aims to move previous advances done in vitro closer to clinical reality by developing computer and preclinical models side-by-side, a significant step in the fight against multidrug-resistant cancers that are responsible for more than 90% of cancer deaths.
This is a milestone for ...
AMES, IA — Buying a home is a time-consuming process, in part because it requires balancing financial realities with a long checklist of expectations and desires. People care about a solid foundation and certain number of bedrooms. But a property’s curb appeal, neighbors and proximity to work or good schools also matter.
For most house-hunters in the U.S., setting up filters and scrolling listings on Zillow has become a crucial first step.
“Digital real estate platforms like Zillow help people see what’s available, ...