(Press-News.org) The National Institutes of Health recently awarded Cleveland Clinic’s Jacob Scott, M.D., D.Phil., and collaborators $2.8 million to translate research on how cancer cells evolve and compete into patient care. The project aims to move previous advances done in vitro closer to clinical reality by developing computer and preclinical models side-by-side, a significant step in the fight against multidrug-resistant cancers that are responsible for more than 90% of cancer deaths.
This is a milestone for research into “evolutionary games” or the interactions between cancer cells within tumors that lead to treatment resistance. Cancer cells evolve to grow and survive in harsh environments caused by medications and surrounding healthy cells, affecting one another in an ecosystem. These interactions are important but have traditionally been studied theoretically or in petri dishes, making translation to the clinic difficult.
Computational models are the “bridge” necessary to study these models in patients, said Dr. Scott, a radiation oncologist and head of Translational Hematology & Oncology Research’s Theory Division at Cleveland Clinic. Treating cancer is a months-long process, so time is a challenge in collecting the data necessary for clinical application.
“As we pursue targeted therapies using drugs that inhibit specific cancer processes, we need to explore how to predict cell evolution,” Dr. Scott said. “We have promising mathematical models and results in a dish, but we need to develop the processes necessary to study these systems in animal models to allow application to humans.”
This five-year project focuses on lung cancer, but the goal is to gradually build models for other cancers – even per patient, Dr. Scott added.
Dr. Scott is co-principal investigator with Andriy Marusyk, Ph.D., a long-time collaborator at Moffit Cancer Center. Another collaborator is Emily Dolson, Ph.D., former post-doctoral fellow in Dr. Scott’s lab and now an assistant professor at Michigan State University.
This grant builds on years of research in Dr. Scott’s lab, which developed an assay for measuring the interactions between healthy and cancerous cells that lead to treatment resistance. Last year, the team (including Dr. Marusyk) published results in Science Advances using the assay.
That study serves as an example of how studying these interactions can provide clues for cancer care. Cells evolved differently depending on the concentration and timing of the administration of the drug gefitinib. The findings demonstrate how this research holds promise for shaping treatment, as alternative schedules (including less medication) have shown promise in reducing tumor size and delaying the onset of drug resistance.
“Developing new models is critical for advancing this field to where we can use it to shape treatment type, length and amount,” Dr. Scott commented. “This project could lead to seeing these evolutionary principles that have been around since the times of Charles Darwin aid innovative cancer care.”
END
Cleveland Clinic-led team awarded $2.8 million to translate cancer cell evolution research to clinical care
Work with computer and preclinical models aims to bridge the gap between studying evolutionary biology in the lab and patient care
2023-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Digital real estate listings with more photos, descriptions earn higher sale prices
2023-08-22
AMES, IA — Buying a home is a time-consuming process, in part because it requires balancing financial realities with a long checklist of expectations and desires. People care about a solid foundation and certain number of bedrooms. But a property’s curb appeal, neighbors and proximity to work or good schools also matter.
For most house-hunters in the U.S., setting up filters and scrolling listings on Zillow has become a crucial first step.
“Digital real estate platforms like Zillow help people see what’s available, ...
Can sound waves help people quit cocaine? Cutting-edge clinical trial focuses in
2023-08-22
Pioneering researchers at UVA Health are testing whether focused sound waves can help people overcome cocaine addiction, a growing problem across the nation.
The scientists have launched a clinical trial, believed to be the first of its kind in the world, to test whether low-intensity focused ultrasound can help reprogram brain cells to reduce the desire for cocaine. The noninvasive approach focuses sound waves on a portion of the brain called the insula, thought to play a critical role in multiple forms of addiction. If the trial is successful, it could pave the way for an important new tool to treat addiction in general.
“This ...
Innovative breakthrough in sustainable chemical production
2023-08-22
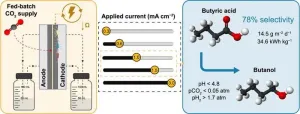
Carbon capture and utilization (CCU) technologies are crucial for addressing climate change while ensuring economic viability. MES has emerged as a promising approach for CO2 reduction to biofuels and platform chemicals. However, the industrial adoption of MES has been hindered by low-value products like acetate or methane and high electric power demand.
In a new study recently published on 26 July 2023, in the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers from University of Girona conducted a study that focused on electrically ...
Detroit Public Schools Community District staff complete CPR training and education
2023-08-22
DETROIT, August 22, 2023 — Today, Detroit Public Schools Community District teachers and coaches completed either the American Heart Association’s Heartsaver® CPR AED (automated external defibrillator) course, which provides the highest quality evidence-based training in the lifesaving skills of CPR, as well as the appropriate use of an AED, or Hands-Only CPR education. Adding lifesavers to the chain of survival in the Detroit community through CPR training and education is a priority for the Detroit Lions Foundation.
“We are honored to use our platform to further bring awareness and education to our community ...
Groundbreaking Ultracompact Spoof Surface Plasmon Sensing System Revolutionizes Gas Detection with Smartphone Integration
2023-08-22
A team of researchers from Southeast University of China has developed a cutting-edge ultracompact sensing system that leverages the power of spoof surface plasmon resonance (SSPR) technology to enable adaptive and accurate gas detection using a smartphone. The research article detailing this breakthrough, titled "An Ultracompact Spoof Surface Plasmon Sensing System for Adaptive and Accurate Detection of Gas Using a Smartphone," has been published in the prestigious journal Engineering.
Traditional dielectric sensing methods often suffer from signal fluctuations, resulting in reduced sensitivity and accuracy. In response to the growing demand for precise gas detection in ...
Unintended consequences: Terror attacks cause long-term acceptance of targeted communities
2023-08-22
Violent actions intended to provoke opposition to particular communities may paradoxically lead to lasting acceptance, according to a study. On March 15, 2019, a far-right extremist killed 51 Muslims in Christchurch, New Zealand. Immediately following the attacks there was a noticeable increase in public acceptance of the Muslim minority in the country. But was this acceptance sustained? To address this question, Joseph Bulbulia and colleagues used years of data from the New Zealand Attitudes and Values Study, a national longitudinal study. The author’s goal was to estimate the anticipated level of Muslim acceptance if the attacks had not occurred. These ...
Uranium signatures in turtles and tortoises near nuclear testing and waste sites
2023-08-22
The shells of turtles, tortoises, and sea turtles keep growing as long as the animals live—and some of them live a remarkably long time. Cyler Conrad and colleagues analyzed the shells of five specimens from areas that potentially accumulated anthropogenic uranium through nuclear fallout and/or waste. Unusual uranium signatures were found in a green sea turtle from Enewetak Atoll in the Republic of the Marshall Islands, a desert tortoise from southwestern Utah near the Nevada National Security Site (formerly known as the Nevada Test Site), a river cooter from the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, and a box turtle from Oak Ridge, Tennessee, ...
Australia experiences intense surge in Strep A cases, similar to northern hemisphere wave
2023-08-22
Australia has experienced an intense surge in severe Strep A cases, similar to the northern hemisphere wave, despite differences in seasons and circulating respiratory viruses, according to a new study.
The national research project, involving researchers from Murdoch Children’s Research Institute and published in The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, highlighted how the unseasonal increase in case load across the southern hemisphere adds to the need for a safe and effective vaccine against Strep ...
Coffee offers performance boost for concrete
2023-08-22
Engineers in Australia have found a way of making stronger concrete with roasted used-coffee grounds, to give the drink-additive a “double shot” at life and reduce waste going to landfills.
Lead author Dr Rajeev Roychand from RMIT University said the team developed a technique to make concrete 30% stronger by turning waste coffee grounds into biochar, using a low-energy process without oxygen at 350 degrees Celsius.
“The disposal of organic waste poses an environmental challenge as it emits large amounts of greenhouse gases including methane and carbon dioxide, which contribute to climate change,” ...
As city heat rises, bird diversity declines
2023-08-22
Hangzhou, China & Ithaca, N.Y.—Humans aren't the only ones leaving town when city heat becomes unbearable. A study done on 336 cities in China concludes that heat-retaining buildings and paved surfaces are directly related to a loss in bird diversity. These findings from scientists at Zhejiang University and the Cornell Lab of Ornithology are published in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
“The heat-retention characteristic of cities is a well-known phenomenon called the urban heat island ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
[Press-News.org] Cleveland Clinic-led team awarded $2.8 million to translate cancer cell evolution research to clinical careWork with computer and preclinical models aims to bridge the gap between studying evolutionary biology in the lab and patient care