(Press-News.org) During a time when hospitals were overrun with COVID-19 patients and ventilators were in high demand, the nation’s
focus was not on firearm-related injuries. With our attention elsewhere, it may have seemed that these injuries
appeared to decrease and mass shootings seemed to disappear. But that doesn’t mean firearm injuries went away. In
fact, for one group of children in particular, firearm trauma rates grew. In a new study, investigators at Children’s
Hospital Los Angeles reveal that children from lower opportunity neighborhoods had a significantly higher rate of
firearm-related injury during the pandemic.
In March of 2020, people could be seen hoarding toilet paper in grocery checkout lines. Less conspicuously, firearm sales
increased too. From March to mid-July, more than 6 million Americans bought their first firearm. This translated to
almost 5 million more children now living in homes with firearms.
Also happening at this very moment in time: a stay-at-home order to minimize the spread of COVID-19. This was
logistically difficult for many families, as childcare options dwindled due to mass closures. Paired with the increase in
homes with firearms, sheltering in place set the stage for an increase in firearm-related trauma in the pediatric
population.
Only, this didn’t happen. At least not for everyone.
The CHLA study, published in the journal Pediatrics, indicates that the rate of injury due to firearms was only
increased in children from lower opportunity neighborhoods. Investigators used the well-established Child Opportunity
Index, or COI, which takes into account more than just household income. The COI factors in resources that are vital to
children—like quality of schools, safe housing, access to nutrition, clean air and more.
Previous research has shown that children in low COI neighborhoods are more likely to be treated for firearm-related
trauma. The current study reveals that this, combined with the stress of an unprecedented international emergency,
translated to an even larger disadvantage to low-COI areas.
The authors suggest that this increase may have been a result of unsafe storage of guns and single-parent households
where the parent needed to return to work resulting in less child supervision since schools and daycare centers
remained closed. In addition to finding that the pandemic exacerbated an already growing disparity it also highlights just
how important community environments are to children.
Lead investigator on the study was MaKayla L O’Guinn, DO and Ryan Spurrier, MD, was senior author on the publication.
Other investigators were Sami Siddiqui, Shadassa Ourshalimian, MPH, and Pradip P Chaudhari, MD, all at Children’s
Hospital Los Angeles.
END
Firearm injuries and the pandemic: Lower opportunity neighborhoods are disproportionately affected
Kids from lower opportunity areas were more affected by firearm injuries during the pandemic.
2023-08-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dramatic reductions in malaria cases and deaths continue over five years with seasonal malaria vaccine-drug combination
2023-08-23
Final results of landmark study confirm two-thirds reduction in cases of malaria, including cases of severe malaria, and deaths from malaria, for RTS,S-drug combination over either intervention given alone in settings of highly seasonal malaria transmission.
RTS,S vaccine has similar high efficacy to drugs in preventing malaria in highly seasonal transmission settings.
Overall reduction in malaria incidence likely “tops” 90% among children protected by bednets, vaccines, and drugs.
Seattle and London, August 22, 2023—The final results of a landmark study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases ...
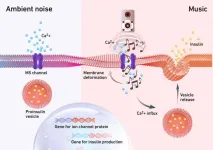
Cells with an ear for music release insulin
2023-08-23
Diabetes is a condition in which the body produces too little or no insulin. Diabetics thus depend on an external supply of this hormone via injection or pump. Researchers led by Martin Fussenegger from the Department of Biosystems Science and Engineering at ETH Zurich in Basel want to make the lives of these people easier and are looking for solutions to produce and administer insulin directly in the body.
One such solution the scientists are pursuing is enclosing insulin-producing designer cells in capsules that can be implanted in the body. To be able to control from the outside when and how much insulin the cells release into the blood, researchers have studied and applied ...
Birds living at UCLA were less afraid of humans after the pandemic closure
2023-08-23
When UCLA shifted to remote instruction during the early days of COVID-19, the campus was much less populated — but it wasn’t totally empty. Several species of animals continued to go about their daily lives, just with far fewer disturbances from humans.
Among them were around 300 dark-eyed juncos, a bird species that has thrived at UCLA for probably around 20 years.
A group of UCLA scientists who have been studying fear and aggression in urban juncos for years recognized that the dramatic shift in human activity presented a unique opportunity for an experiment: ...
Guiding the design of silicon devices with improved efficiency
2023-08-23
Silicon is one of the most pervasive functional materials of the modern age, underpinning semiconductor technologies ranging from microelectronics to solar cells. Indeed, silicon transistors enable computing applications from cell phones to supercomputers, while silicon photovoltaics are the most widely deployed solar-cell technology to date. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) reports that nearly 50% of new electric generation capacity in 2022 came from solar cells, and according to the International Energy Agency (IEA), silicon has a 95% market share. Yet despite silicon’s ...
NREL analysis quantifies impacts of setback ordinances on land available for renewable energy deployment
2023-08-23
The number of local zoning ordinances governing renewable energy deployment is growing in the United States, according to new research by the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). The amount of land available to deploy renewables depends on the characteristics of the ordinances.
“It’s important to understand the types of ordinances in effect, specifically setback ordinances, or the required distance from a specific feature like a house,” said Anthony ...
BU research probes the contradictory roles of SAA in fighting inflammation and infection while triggering life-threatening disease
2023-08-22
(Boston) – Serum amyloid A (SAA) is a family of ancient proteins that can be traced from present-day humans back half a billion years to sea cucumbers and oysters. A new study by researchers from the Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine explores the link between the dual nature of this small plasma protein: how it works to clear toxic debris from wounds and inflammation sites, but also its role in forming fibrous deposits of the pathologic amyloid in vital organs such as the ...
AI can predict certain forms of esophageal and stomach cancer
2023-08-22
In the United States and other western countries, a form of esophageal and stomach cancer has risen dramatically over the last five decades. Rates of esophageal adenocarcinoma, or EAC, and gastric cardia adenocarcinoma, or GCA, are both highly fatal.
However, Joel Rubenstein, M.D., M.S., a research scientist at the Lieutenant Colonel Charles S. Kettles Veterans Affairs Center for Clinical Management Research and professor of internal medicine at Michigan Medicine, says that preventative measures can be a saving grace.
“Screening can identify pre-cancerous changes in ...
Cuproptosis-related MTF1 inhibits kidney renal clear cell carcinoma progression by suppressing proliferation and regulating immune cell infiltration
2023-08-22
https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/AMM-2023-0016
Announcing a new publication for Acta Materia Medica journal. Cuproptosis is a newly identified specific form of programmed cell death. This study aims to identify cuproptosis-related genes (CRGs) in patients with kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC) from the The Cancer Genome Atlas database and to evaluate CRG biological functions. Using lasso regression, four KIRC prognosis-associated CRGs were identified and an associated prognostic risk signature was constructed. Kaplan-Meier curves showed that patients with ...
Study finds high levels of exposure to the COVID-19 virus may reduce protection provided by vaccination and prior infection
2023-08-22
New Haven, Conn. — High levels of exposure to the virus that causes COVID-19 may reduce or overcome the protection that vaccination and prior infection provides, according to a new study by researchers from Yale University, the University of Florida, and the Connecticut Department of Correction.
The findings, published Aug. 19 in Nature Communications, suggest that in densely crowded settings, control measures that reduce levels of exposure to the virus — such as masking, improved ventilation, and distancing — may afford additional benefit in preventing new infections among people who have been ...
AIAA recognizes Pitt’s Peyman Givi with prestigious Dryden Lecture in Research award
2023-08-22
For his contributions to the aerospace community, Peyman Givi, Distinguished Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science at the University of Pittsburgh, was selected to present the 2024 Dryden Lecture in Research, by the Honors and Awards Committee and the Board of Trustees of the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA).
According to AIAA, the Dryden Lectureship in Research, established in 1961, is one of the Institute’s most prestigious lectureships and emphasizes the importance ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Firearm injuries and the pandemic: Lower opportunity neighborhoods are disproportionately affectedKids from lower opportunity areas were more affected by firearm injuries during the pandemic.