(Press-News.org) TAMPA, Fla. (Aug. 23, 2023) – A University of South Florida geoscientist led an international team of researchers to create a new method that can reconstruct the drift path and origin of debris from flight MH370, an aircraft that went missing over the Indian Ocean in 2014 with 239 passengers.
Associate Professor Gregory Herbert was inspired the moment he saw photographs of the plane debris that washed ashore Reunion Island off the coast of Africa a year after the crash.
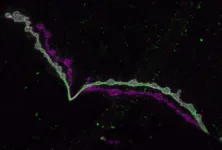
“The flaperon was covered in barnacles and as soon as I saw that, I immediately began sending emails to the search investigators because I knew the geochemistry of their shells could provide clues to the crash location,” Herbert said.
As an evolutionary and conservation biologist, Herbert studies marine systems with a particular focus on shelled marine invertebrates, such as oysters, conchs and barnacles. Over the last two decades, Herbert created and refined a method to extract ocean temperatures stored in the chemistry of invertebrate shells. Herbert has used the method previously to determine the ages and extinction risk of giant horse conchs and investigate the environmental circumstances surrounding the disappearance of the Jamestown colony.
Barnacles and other shelled marine invertebrates grow their shells daily, producing internal layers similar to tree rings. The chemistry of each layer is determined by temperature of the surrounding water at the time the layer was formed. In this study, published in AGU Advances, Herbert’s research team did a growth experiment with live barnacles to read their chemistry and for the first time, unlocked temperature records from the shells of barnacles.
After the experiment, they applied the successful method to small barnacles from MH370. With help from barnacle experts and oceanographers at the National University of Ireland Galway, they combined the barnacles’ water temperature records with oceanographic modeling and successfully generated a partial drift reconstruction.
“Sadly, the largest and oldest barnacles have not yet been made available for research, but with this study, we’ve proven this method can be applied to a barnacle that colonized on the debris shortly after the crash to reconstruct a complete drift path back to the crash origin,” Herbert said.
Up to this point, the search for MH370 spanned several thousands of miles along a north-south corridor deemed ‘The Seventh Arc,’ where investigators believe the plane could have glided after running out of fuel. Because ocean temperatures can change rapidly along the arc, Herbert says this method could reveal precisely where the plane is.
“French scientist Joseph Poupin, who was one of the first biologists to examine the flaperon, concluded that the largest barnacles attached were possibly old enough to have colonized on the wreckage very shortly after the crash and very close to the actual crash location where the plane is now,” Herbert said. “If so, the temperatures recorded in those shells could help investigators narrow their search.”
Even if the plane is not on the arc, Herbert says studying the oldest and largest barnacles can still narrow down the areas to search in the Indian Ocean.
“Knowing the tragic story behind the mystery motivated everyone involved in this project to get the data and have this work published,” said Nassar Al-Qattan, a recent USF geochemistry doctoral graduate who helped analyze the geochemistry of the barnacles. “The plane disappeared more than nine years ago, and we all worked aiming to introduce a new approach to help resume the search, suspended in January 2017, which might help bring some closure to the tens of families of those on the missing plane.”
This research was done in collaboration with Ran Tao, USF spatial geoscientist; Howard Spero, professor emeritus from University of California, Davis; and barnacle experts and oceanographers Sean McCarthy, Ryan McGeady and Anne-Marie Power at the National University of Ireland Galway.
###
About the University of South Florida
The University of South Florida, a high-impact research university dedicated to student success and committed to community engagement, generates an annual economic impact of more than $6 billion. With campuses in Tampa, St. Petersburg and Sarasota-Manatee, USF serves approximately 50,000 students who represent nearly 150 different countries. For four consecutive years, U.S. News & World Report has ranked USF as one of the nation’s top 50 public universities, including USF’s highest ranking ever in 2023 (No. 42). In 2023, USF became the first public university in Florida in nearly 40 years to be invited to join the Association of American Universities, a prestigious group of the leading universities in the United States and Canada. Through hundreds of millions of dollars in research activity each year and as one of top universities in the world for securing new patents, USF is a leader in solving global problems and improving lives. USF is a member of the American Athletic Conference. Learn more at www.usf.edu
END
DALLAS, August 23, 2023 — A 2023 survey from the American Heart Association conducted by The Harris Poll, found that a majority (70%) of heart attack and stroke survivors are unaware that LDL cholesterol is commonly referred to as 'bad cholesterol.' This matters because LDL cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) significantly contributes to the development of cardiovascular disease, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, ...
Worldwide, the practice of preparing agricultural fields by burning crop residue contributes large quantities of gaseous pollutants and aerosol particles to the atmosphere and is a known cardiorespiratory health hazard. It has been shown that combustion byproducts in smoke cross the blood-brain barrier causing brain inflammation, and repeated inhalation of smoke can contribute to cognitive decline and dementia among older adults.
Federal efforts to monitor air quality have been focused on population-dense urban communities. As such, impacts of smoke exposure from agricultural fires ...
Figuring out how hundreds of different kinds of brain cells develop from their unique expression of thousands of genes promises to not only advance understanding of how the brain works in health, but also what goes wrong in disease. A new MIT study that precisely probes this “molecular logic” in two neuron types of the Drosophila fruit fly, shows that even similar cells push and pull many levers to develop distinct functions.
In the study in Neuron, a team of neurobiologists at The Picower Institute for Learning and ...
INDIANAPOLIS – A new study from researchers at Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Dentistry reports on linking electronic health records and electronic dental records to provide better care and outcomes for individuals with Sjögren's disease, an autoimmune disorder that can affect the entire body, including teeth. Their work may have implications for other systemic autoimmune diseases, including lupus and possibly rheumatoid arthritis.
Sjögren’s is a chronic autoimmune connective tissue disorder affecting four million Americans ...
Researchers from Lehigh University, University of Hong Kong, and Wuhan University published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines in-feed advertising’s performance across subscription versus AI recommended news feeds.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Tales of Two Channels: Digital Advertising Performance Between AI Recommendation and User Subscription Channels” and is authored by Beibei Dong, Mengzhou Zhuang, Eric (Er) Fang, and Minxue Huang.
How ...
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [August 23, 2023] — Today the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—a not-for-profit alliance of leading academic cancer centers—announced Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, FACP, as incoming Chief Executive Officer (CEO). Dr. Denlinger—who is currently NCCN’s Senior Vice President, Chief Scientific Officer—is being promoted to lead the global guidelines organization following a national search to replace the retiring longtime CEO, Robert W. Carlson, MD.
Dr. Denlinger has a long history of global cancer care leadership with NCCN and beyond. She was named an ...
NEW YORK, August 23, 2023 — Physicist Matthew Sfeir is among 21 innovative mid-career scientists who will each receive $1.25 million from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation to pursue experimental physics research with the promise of significantly transforming understanding of physics and facilitating next-generation technological breakthroughs.
The five-year Experimental Physics Investigator Award will allow Sfeir—a Photonics Initiative professor with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) ...
New Yorkers can apparently breathe a sigh of relief, at least for now. Their exposure to the smoke in June 2023 from Canadian wildfires led to only a slightly higher bump in visits to New York City hospital emergency departments for breathing problems or asthma attacks than what is seen on days when pollen counts are high. However, authors of a new study say other possible health effects, such as possible heart attacks and stroke, still need to be investigated.
For the study, researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine analyzed daily levels of air pollution, as measured ...
When Dr. Bodo Beck first saw the three children of a family who had fled Syria sitting in his consultation room at University Hospital Cologne, the human geneticist was surprised. His genetic analysis diagnosed Bartter syndrome type 3, but never before had he seen such severe joint changes in patients with this rare disease.
The kidney disease is hereditary – affected individuals lack the CLCNKB gene, which is responsible for a specific chloride channel. The electrolyte balance becomes disrupted because the kidneys cannot reabsorb important nutrients and salts back into ...
A recent study in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research found that cast immobilization is as effective as surgery for treating older patients with bone fractures near the wrist.
The study included 276 patients aged 70–89 years who suffered a distal radius fracture that didn’t penetrate the skin and that was treated conservatively or surgically between August 2018 and January 2022. Cast immobilization was used on 213 patients, whereas the other 63 had plates or pins placed during different types of surgery.
Nineteen patients experienced complications within the first year, with the most common being complex regional pain syndrome (5 patients who ...