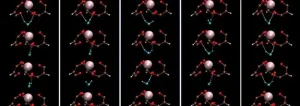
(Press-News.org) Researchers from The University of Warwick and the University of Manchester have finally solved the long-standing puzzle of why graphene is so much more permeable to protons than expected by theory.
A decade ago, scientists at The University of Manchester demonstrated that graphene is permeable to protons, nuclei of hydrogen atoms.
The unexpected result started a debate in the community because theory predicted that it would take billions of years for a proton to permeate through graphene’s dense crystalline structure. This had led to suggestions that protons permeate not through the crystal lattice itself, but through the pinholes in its structure.
Now, writing in Nature, a collaboration between the University of Warwick, led by Prof. Patrick Unwin, and The University of Manchester, led by Dr. Marcelo Lozada-Hidalgo and Prof. Andre Geim, report ultra-high spatial resolution measurements of proton transport through graphene and prove that perfect graphene crystals are permeable to protons. Unexpectedly, protons are strongly accelerated around nanoscale wrinkles and ripples in the crystal.
The discovery has the potential to accelerate the hydrogen economy. Expensive catalysts and membranes, sometimes with significant environmental footprint, currently used to generate and utilise hydrogen could be replaced with more sustainable 2D crystals, reducing carbon emissions, and contributing to Net Zero through the generation of green hydrogen.
The team used a technique known as scanning electrochemical cell microscopy (SECCM) to measure minute proton currents collected from nanometre-sized areas. This allowed the researchers to visualise the spatial distribution of proton currents through graphene membranes.
If proton transport took place through holes as some scientists speculated, the currents would be concentrated in a few isolated spots. No such isolated spots were found, which ruled out the presence of holes in the graphene membranes.
Drs. Segun Wahab and Enrico Daviddi, leading authors of the paper, commented: “We were surprised to see absolutely no defects in the graphene crystals. Our results provide microscopic proof that graphene is intrinsically permeable to protons.”
Unexpectedly, the proton currents were found to be accelerated around nanometre-sized wrinkles in the crystals. The scientists found that this arises because the wrinkles effectively ‘stretch’ the graphene lattice, thus providing a larger space for protons to permeate through the pristine crystal lattice. This observation now reconciles the experiment and theory.
Dr. Lozada-Hidalgo said: “We are effectively stretching an atomic scale mesh and observing a higher current through the stretched interatomic spaces in this mesh – this is truly mind-boggling.”
Prof. Unwin commented: “These results showcase SECCM, developed in our lab, as a powerful technique to obtain microscopic insights into electrochemical interfaces, which opens up exciting possibilities for the design of next-generation membranes and separators involving protons.”
The authors are excited about the potential of this discovery to enable new hydrogen-based technologies. Dr. Lozada-Hidalgo said, "Exploiting the catalytic activity of ripples and wrinkles in 2D crystals is a fundamentally new way to accelerate ion transport and chemical reactions. This could lead to the development of low-cost catalysts for hydrogen-related technologies."
Read the full paper here https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06247-6
END
Graphene discovery could help generate hydrogen cheaply and sustainably
Researchers from The University of Warwick and the University of Manchester have finally solved the long-standing puzzle of why graphene is so much more permeable to protons than expected by theory
2023-08-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adding immunity to human kidney-on-a-chip advances cancer drug testing
2023-08-23
By Benjamin Boettner
(Boston) — A growing repertoire of cell and molecule-based immunotherapies is offering patients with indomitable cancers new hope by mobilizing their immune systems against tumor cells. An emerging class of such immunotherapeutics, known as T cell bispecific antibodies (TCBs), are of growing importance with several TCBs that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for the treatment of leukemias, lymphomas, and myelomas. These antibody drugs label tumor cells with one of their ends, and attract immune cells with another end to coerce them into tumor cell killing.
One major challenge in the development of TCBs and other immunotherapy ...
Fungus gnats as pollinators not pests
2023-08-23
Many plants and crops rely on insects to pollinate them so they can reproduce. A new study has shown that several flowering plants from the group Euonymus are pollinated by fungus gnats, a dipteran insect. Specifically, they pollinate Euonymus plants which have red-petaled flowers with short stamens and yogurt-like scent. Although fungus gnats are known to pollinate hundreds of plant species, this study shows that the particular traits of red Euonymus flowers were likely to have been acquired via pollination syndrome, evolving over a process of natural selection to be pollinated specifically by fungus gnats. This research highlights the important role of Diptera, which are commonly regarded ...
Solar powered irrigation: a game-changer for small-scale farms in sub-Saharan Africa
2023-08-23
In sub-Saharan Africa 80% of agricultural production is from smallholder farmers, who face constraints on increasing farm productivity resulting in a large yield gap. Extensive rain-fed agriculture (90% of all cropland) under unpredictable and erratic rainfall pattern is a leading cause of the low productivity and food insecurity in Africa, together with a low degree of mechanization. This has been reinforcing a persistent poverty trap, triggered by cyclical famines that are jeopardizing local development opportunities.
In a new IIASA-led study as part of the research project Renewables for African Agriculture (RE4AFAGRI), an international ...
Looking out for kids: a case for better pediatric trauma interventions
2023-08-23
In the weeks following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, public health directives called for masking, social distancing, social isolation, and stay-at-home orders. Apart from the severe medical consequences as a direct result of the pandemic, the ensuing social isolation had far-reaching impacts on children. The pandemic control measures affected the pediatric population by increasing mental distress, limiting physical activity, changing sleep patterns, and reducing emergency room visits. Unfortunately, the scope of pediatric trauma during the pandemic remains ...
SwRI investigates the efficiency impact of smart-technology-enabled vehicles
2023-08-23
SAN ANTONIO — August 23, 2023 — A Southwest Research Institute project funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has demonstrated an average of 15% energy savings when vehicles outfitted with connected and automated vehicle systems, or CAVs, are introduced into traffic.
CAVs use wireless smart technology to communicate with other CAVs and traffic infrastructure. SwRI’s eco-driving framework uses custom software and predictive powertrain algorithms to enable human drivers to make more efficient driving ...
Nemours Children’s Health researchers to present at World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
2023-08-23
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. (August 23, 2023) – Researchers from Nemours Children’s Health will present a range of studies at the World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery, Aug. 27 – Sept. 1 in Washington D.C., the leading global conference in the field. Nemours Children’s presentations will highlight advances in complex congenital heart disease, prevention, cardiomyopathy in rare diseases, and the benefit of integration with other areas like psychology and telehealth.
"In pediatric cardiac surgery, the Nemours Children’s Cardiac Center has pioneered a number of procedures, and we are pleased to share our new findings with researchers and clinicians ...
Unravelling the water dynamics and structure of water-coordinated metal complexes
2023-08-23
Lanthanide-containing complexes are important compounds for sophisticated nuclear-fuel processing and medical imaging. Moreover, they often have interesting symmetric crystal structures and associated dynamics that render unique properties for practical applications.
The seven-coordinate lanthanide complex Ho(III) aqua-tris(dibenzoylmethane) or Ho-(DBM)3·H2O was first reported in the late 1960s. It has a three-fold symmetric structure with holmium (Ho) at the center of three propeller-shaped dibenzoylmethane (DBM) ligands and a water (H2O) ...
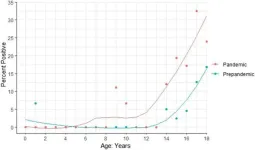
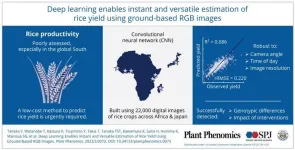
Artificial intelligence can now estimate rice yields, according to new study
2023-08-23
With the rise in global demand for staple crop products projected to substantially increase by 2050 due to population growth, rising per capita income, and the growing use of biofuels, it is necessary to adopt sustainable agricultural intensification practices in existing croplands to meet this demand. However, estimation processes currently employed in the global South remain inadequate. Traditional methods like self-reporting and crop cutting have their limitations, and remote sensing technologies are not fully utilized in this context.
However, recent advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, particularly deep learning with convolutional ...
NIH/National Institute on Aging’s $3 million R01 Grant supports study evaluating probiotic/prebiotic combination’s impact on maintaining bone health of older women
2023-08-23
The NIH/National Institute on Aging has awarded a R01 $3 million grant to study the impact of a probiotic/prebiotic (synbiotic) medical food developed by Solarea Bio on maintaining bone health of older women.
The study will support an 18-month clinical trial of a synbiotic medical food in 220 older women to test whether it maintains lumbar spine bone mineral density (BMD) with aging.
Grant recipients are Hebrew SeniorLife, USDA HNRCA at Tufts University, Maine Medical Center Research Institute, and Solarea Bio.
“There is an unmet need for safe and effective dietary interventions for the ...
University of South Florida scientist: Barnacles may help reveal location of lost Malaysia Airlines flight MH370
2023-08-23
TAMPA, Fla. (Aug. 23, 2023) – A University of South Florida geoscientist led an international team of researchers to create a new method that can reconstruct the drift path and origin of debris from flight MH370, an aircraft that went missing over the Indian Ocean in 2014 with 239 passengers.
Associate Professor Gregory Herbert was inspired the moment he saw photographs of the plane debris that washed ashore Reunion Island off the coast of Africa a year after the crash.
“The flaperon ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
[Press-News.org] Graphene discovery could help generate hydrogen cheaply and sustainablyResearchers from The University of Warwick and the University of Manchester have finally solved the long-standing puzzle of why graphene is so much more permeable to protons than expected by theory